5motor control (mctrl), Stop – Lenze 8400 TopLine User Manual
Page 285
Lenze · 8400 TopLine · Reference manual · DMS 6.0 EN · 06/2014 · TD05/TD14
285
5
Motor control (MCTRL)
5.12
Braking operation/brake energy management
_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
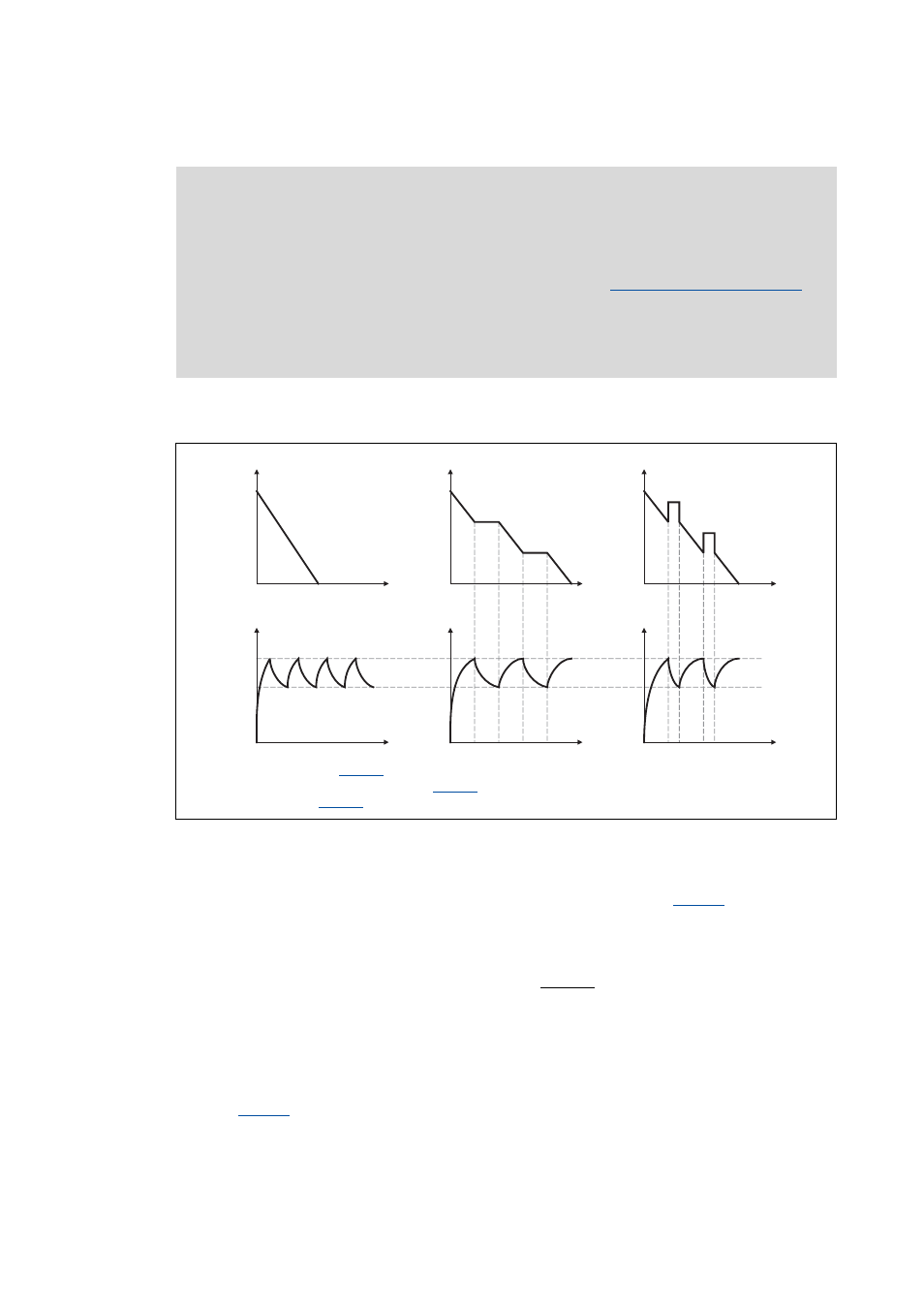
The way in which the different braking procedures work is demonstrated schematically in the
following illustration:
[5-29] Graph of the effective speed setpoint and the DC bus voltage during braking
Tip!
Independent of the selected motor control, all procedures given in
can be used. The
actual speed value always follows the speed setpoint in an optimal way when a brake
resistor is used.
If it is possible to dispense with exact adherence to the deceleration ramp in simple
applications, selection of a braking method without an external brake resistor enables
costs to be reduced due to the avoidance of having to use a brake resistor .
With the "inverter motor brake" function, an effective braking torque of 10 ... 20 % of the
rated motor torque can be achieved.
A combination of all three braking procedures is also possible, e.g. for emergency braking if
the brake resistor fails
(
= "4: Brake resistor + FI_MotBrk + RfgStop").
Stop!
• The two braking procedures "Stopping of the ramp function generator" and "Inverter
motor brake" can only be used for speed-controlled applications without the
influence of a position controller!
• When the "inverter motor brake" function is used, the
is
not adapted. If it is braked too frequently, there is a risk of the motor being thermally
overloaded or the motor overload monitoring does not work properly!
• The "inverter motor brake" function must not be used with vertical conveyors (hoists)
or with active loads!
Use of the brake resistor (
Stopping of the ramp function generator (
= "1: HlgStop")
Inverter motor brake (
= "3: FI_MotBrk + RfgStop)
n
Set
t
n
Set
t
1
2
n
Set
t
0
t
t
t
U
DC
U
DC
U
DC
