Apple Motion 3 User Manual
Page 475
Chapter 5
Using Behaviors
475
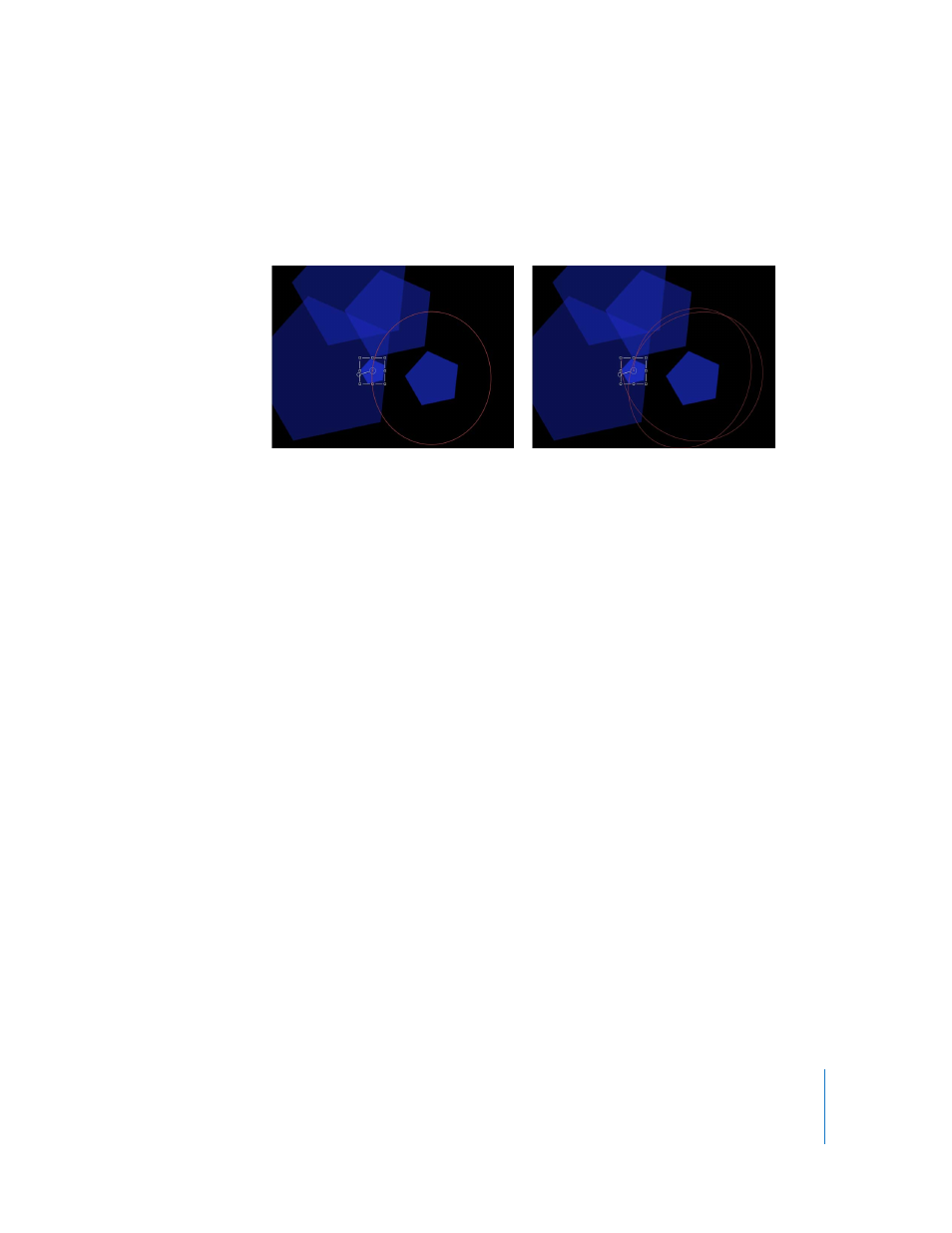
You can also use the Random Motion behavior to add variation to the animation paths
created by other behaviors that affect an object’s position. For example, adding
Random Motion to an object with the Orbit Around behavior results in a more erratic
animation path, although it still orbits as before.
HUD Control
The HUD has controls for the Amount, Frequency, Noisiness, Drag, axis assignment, and
Random Seed parameters. When applied to an object that contains multiple objects
(such as a group, particles, text, or a replicator), the Affect Subobjects checkbox also
appears in the HUD.
Parameters in the Inspector
Affect Subobjects: This parameter appears when this behavior is applied to an object
that contains multiple objects, such as a group, a particle emitter, a replicator, or a text
layer. When this checkbox is turned on, all objects within the parent object are affected
individually. When this checkbox is turned off, all objects within the parent object are
affected by the behavior together, as if they were a single object.
Amount: A slider that determines the speed the object moves by changing the length
of the animation path. Higher values result in faster motion and longer animation
paths.
Frequency: A slider that determines the number of twists and turns in the animation
path, which can be seen by the crookedness of the resulting animation path. Higher
values create more turns in the animation path. Lower values result in straighter
animation paths.
Noisiness: A slider that determines an additional level of jaggedness along the
animation path shape defined by the Amount parameter. Higher values result in a
more jagged-looking animation path.
Shape with Orbit Around behavior
Orbit Around behavior modified by Random
Motion
