5 slave operations, Table 468. slave transactions, 468 slave transactions – Intel CONTROLLERS 413808 User Manual
Page 705: Table 468 describes the i
Intel
®
413808 and 413812 I/O Controllers in TPER Mode
October 2007
Developer’s Manual
Order Number: 317805-001US
705
I
2
C Bus Interface Units—Intel
®
413808 and 413812
14.3.5
Slave Operations
describes the I
2
C Bus Interface Unit’s responsibilities as a slave device.
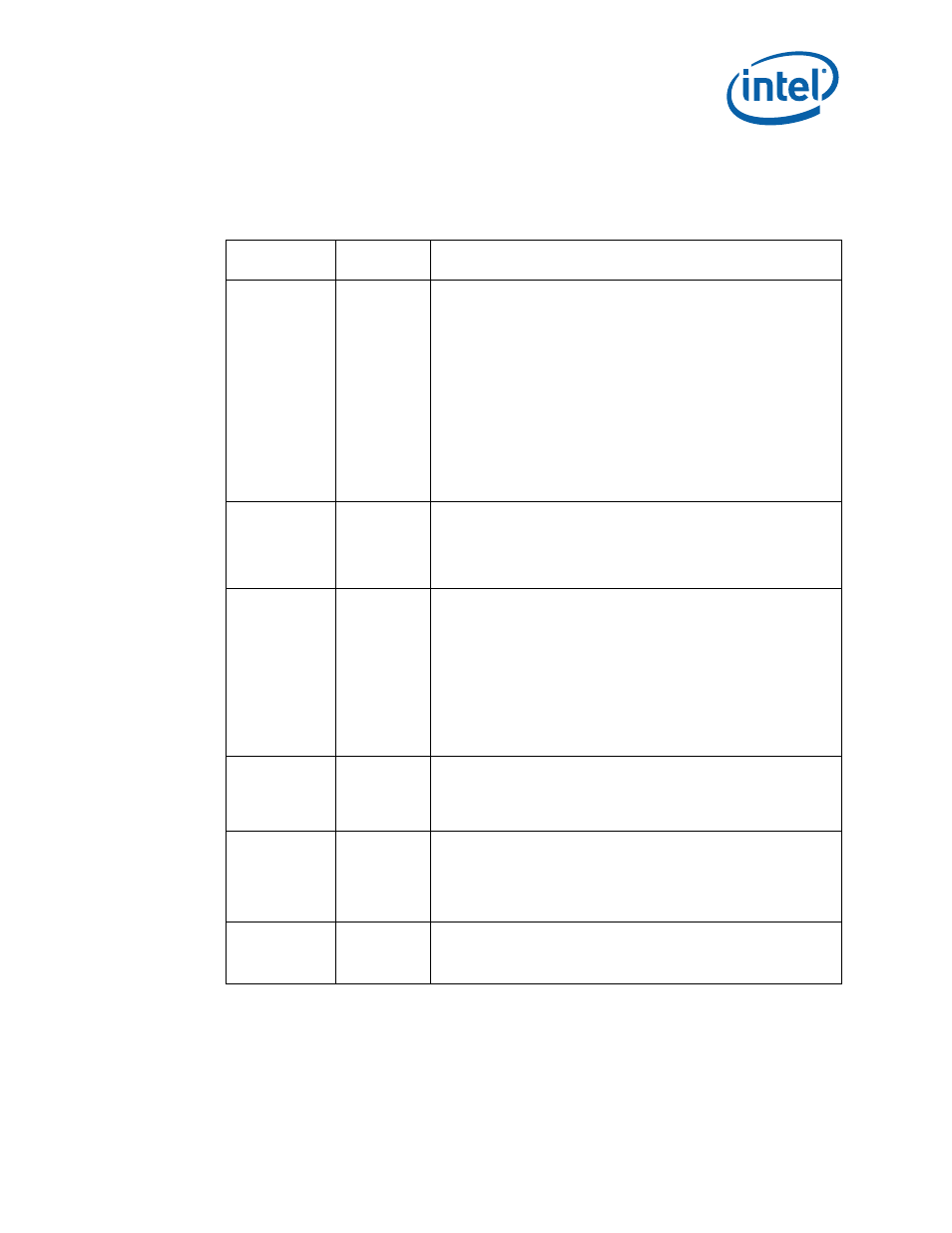
Table 468. Slave Transactions
I
2
C Slave Action
Mode of
Operation
Definition
Slave-receive
(default mode)
Slave-receive
only
• I
2
C Bus Interface Unit monitors all slave address transactions.
• The I
2
C Bus Interface Unit Enable bit must be set.
• I
2
C Bus Interface Unit monitors bus for START conditions. When a
START is detected, the interface reads the first 8 bits and compares
the most significant 7 bits with the 7 bit I
2
C Slave Address Register
and the General Call address (00H). When there is a match, the I
2
C
Bus Interface Unit sends an Ack.
• When the first 8 bits are all zeros, this is a general call address.
When the General Call Disable bit is clear, both the General Call
Address Detected bit and the Slave Mode Operation bit in the ISR are
set. See
.
• When the 8th bit of the first byte (R/W# bit) is low, the I
2
C Bus
Interface Unit stays in slave-receive mode and the Slave Mode
Operation bit is cleared. When the R/W# bit is high, the I
2
C Bus
Interface Unit transitions to slave-transmit mode and the Slave Mode
Operation bit is set.
Setting the Slave
Address Detected
bit
Slave-receive
Slave-transmit
• Indicates the interface has detected an I
2
C operation that addresses
the 4138xx
(this includes general call address). The Intel XScale
®
processor can distinguish an ISAR match from a General Call by
reading the General Call Address Detected bit.
• An interrupt is signalled (when enabled) after the matching slave
address is received and acknowledged.
Read one byte of
I
2
C Data from the
IDBR
Slave-receive
only
• Data receive mode of I
2
C slave operation.
• Eight bits are read from the serial bus into the shift register. When a
full byte has been received and the Ack/Nack bit has completed, the
byte is transferred from the shift register to the IDBR.
• Occurs when the IDBR Receive Full bit in the ISR is set and the
Transfer Byte bit is clear. When enabled, the IDBR Receive Full
Interrupt is signalled to the Intel XScale
®
processor.
• Intel XScale
®
processor reads 1 data byte from the IDBR. When the
IDBR is read, the Intel XScale
®
processor writes the desired
Ack/Nack Control bit and set the Transfer Byte bit. This causes the
I
2
C Bus Interface Unit to stop inserting wait states and let the master
transmitter write the next piece of information.
Transmit
Acknowledge to
master-transmitte
r
Slave-receive
only
• As a slave-receiver, the I
2
C Bus Interface Unit is responsible for
pulling the
SDA
line low to generate the Ack pulse during the high
SCL
period.
• The Ack/Nack Control bit controls the Ack data the I
2
C Bus Interface
Unit drives. See
Write one byte of
I
2
C data to the
IDBR
Slave-transmit
only
• Data transmit mode of I
2
C slave operation.
• Occurs when the IDBR Transmit Empty bit is set and the Transfer
Byte bit is clear. When enabled, the IDBR Transmit Empty Interrupt is
signalled to the Intel XScale
®
processor.
• Intel XScale
®
processor writes a data byte to the IDBR and set the
Transfer Byte bit to initiate the transfer.
Wait for
Acknowledge from
master-receiver
Slave-transmit
only
• As a slave-transmitter, the I
2
C Bus Interface Unit is responsible for
releasing the
SDA
line to allow the master-receiver to pull the line
low for the Ack.
.
