5motor interface – Lenze 9400 User Manual
Page 130
5
Motor interface
5.3
Adjusting motor and controller to each other
130
Lenze · Servo-Inverter 9400 HighLine · Reference manual · DMS 10.0 EN · 11/2013 · TD05/06
_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
Procedure for "pole position identification 360°"
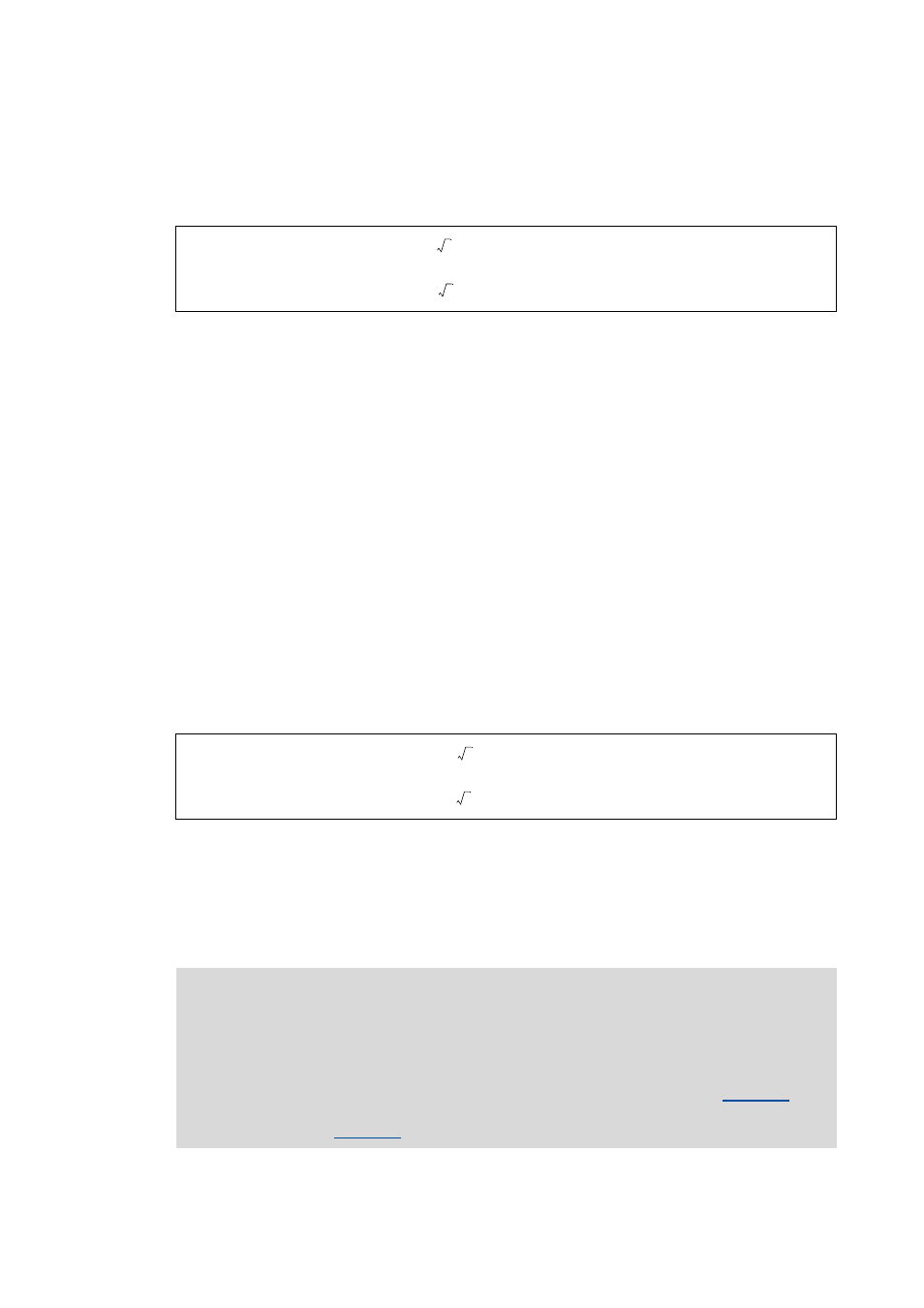
If all conditions are met, the motor is energised with a direct current corresponding to the lower of
the following two values:
• The rotor is aligned through the current flow. This is absolutely necessary for the procedure.
• To ensure that the torque-neutral axis is not accidentally energised and the rotor stops, a 45°
current vector is (electrically) generated for a short instant and then (electrically) switched back
to 0° (≡ phase U).
• Then a DC current of the above-mentioned value could be measured in this motor phase.
The next steps of the procedure depend on the feedback system used:
• If an absolute value encoder with Hiperface or EnDat protocol is used, the encoder position is set
to zero and the procedure is cancelled.
• If a resolver or an optical encoder without absolute track is used, the difference between the
preselected current angle and the mechanical rotor angle is determined. After this, the current
vector is (electrically) turned by another 22.5° and the difference between current angle and
rotor angle is determined once again.
• The procedure is repeated 16 times. This corresponds to one electrical revolution. The
machine rotates by 360° (mech.)/pole pair number.
• Take the average value of the 16 measurements to compensate for asymmetries.
Procedure for "pole position identification with minimal movement"
If all conditions are met, the motor current is increased step by step to the smaller of the following
two values:
• By the current flow the rotor aligns itself, which, however, is compensated by a position control.
• If the rotor moves electrically by more than 20°, a fault message is output and the value
measured is rejected. This may occur in the case of motors with a noticeable detent torque.
• In order to detect a non-permissible blocking of the machine, a positive and negative test angle
(± 20°) relative to the current position are defined after the identification. The machine must
align itself to these two test angles within a tolerance of 25 %.
or
or
Note!
In this procedure it is not written back into an optical absolute value encoder and all
feedback systems are treated the same way.
Unlike in the "pole position identification 360°" procedure where, when an optical
absolute value encoder is used, a "0" is entered into the encoder and into
this procedure nothing needs to be entered into the encoder and the identification result
is entered into
2 Rated device current
⋅
2 Rated motor current
⋅
25 %
2 Rated device current
⋅
⋅
25 %
2 Rated motor current
⋅
⋅
