1 master value rail/slave cascade, Master value rail/slave cascade 7, 18 function library – Lenze 8400 User Manual
Page 1267
Lenze · 8400 protec HighLine · Reference manual · DMS 3.0 EN · 03/2013 · TD05
1267
18
Function library
18.1
Function blocks | L_DFSET_1
_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
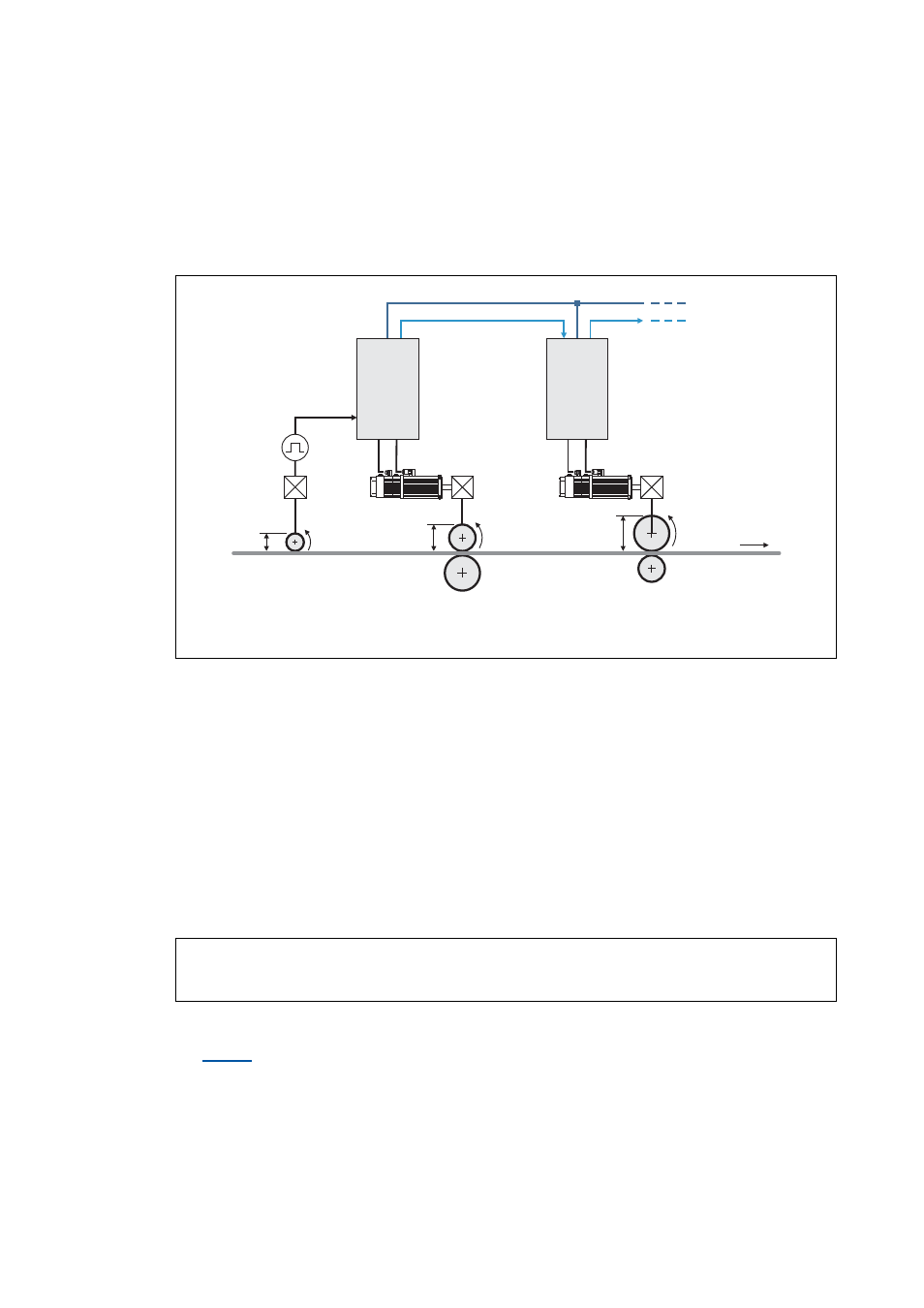
18.1.73.1 Master value rail/slave cascade
If there is only one master speed that is transmitted to all slave drives involved, e.g. via system bus
(CAN), it is called master value rail.
If a slave drive takes over the master value generation for the following slave, it is called slave
cascade.
[18-35] Example: Master value rail/slave cascade
18.1.73.2 Setpoint conditioning with stretch factor and gearbox factor
Stretch factor
The stretch factor is required for the "speed synchronism via master value cascade" mode. It defines
the ratio the slave drive is to be running with regard to its master value.
• The stretch factor evaluates the setpoint at the nSet_v input.
• The stretch factor must be selected via the wGainNum and wGainDenom inputs in the form of
numerators and denominators.
• The result is provided at the nSetGain_v output.
• Scaling: 16384 ≡ 15000 rpm
• If the stretch factor is 1 and the gearbox factors are selected correctly, the circumferential
speeds of the rolls for master and slave 1 are identical in the example shown in the illustration
[18-35]
.
Master value rail
Slave cascade
Master value encoder
v
i
Slave
Master/Slave
d
v
d
v
d
v
R1
R2
R3
1
2
3
i
1
i
2
3
System bus
8400
8400
nSetGain_v
nSet_v wGainNum
wGainDenom
------------------------------------
⋅
=
