Wireless sniffer, Ap provision, Band navigation – H3C Technologies H3C WX3000E Series Wireless Switches User Manual
Page 741
720
Wireless sniffer
Support for this feature depends on the device model. For more information, see "
Controllers Web-Based Configuration Guide
."
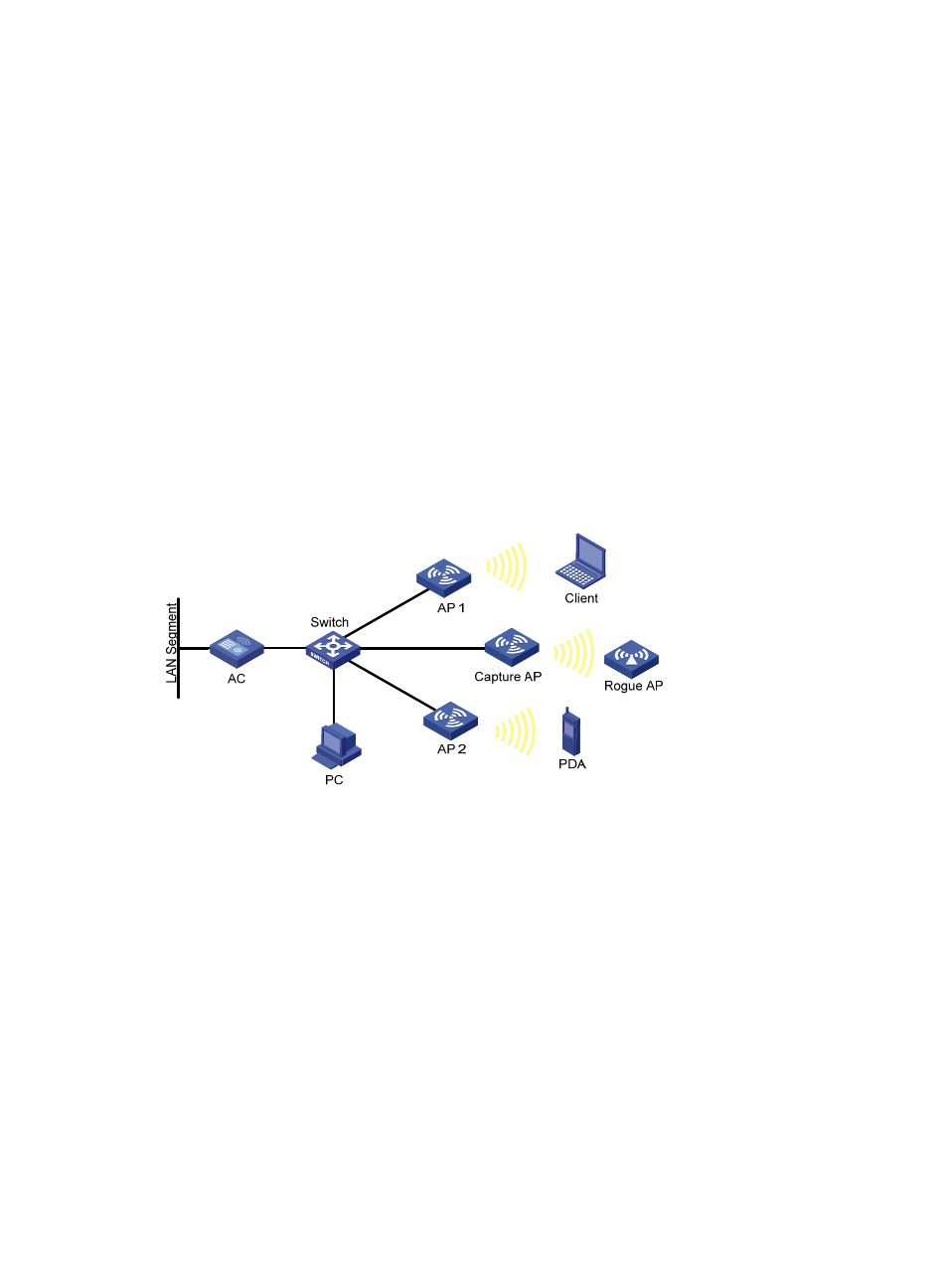
In a wireless network, it is difficult to locate signal interference or packet collision by debugging
information or terminal display information of WLAN devices. To facilitate the troubleshooting, configure
an AP as a packet sniffer to listen to, capture, and record wireless packets. The sniffed packets are
recorded in the .dmp file for troubleshooting.
As shown in
, enable wireless sniffer on the Capture AP. The Capture AP is able to listen to the
wireless packets in the network. Administrators can download the .dmp file to the PC and make further
analysis.
The device supports the following wireless sniffer methods:
•
Radio-based—If you enable WLAN sniffer on a radio of the AP, the radio can capture control,
management, and data packets that it can monitor on its working channel.
•
Client-based—You can use this method to capture management, control, and data packets sent or
received by specified clients. The packets contain client connection or status update information.
Figure 749 Network diagram
AP provision
AP provision enables you to configure network settings for fit APs on the AC. The AC automatically
assigns these settings to the fit APs in run state over tunnel connections. The settings are stored in the
proprietary configuration file on each AP and take effect after the AP restarts. This feature avoids
configuring network settings for APs one by one from a terminal, reducing the work load in large WLAN
networks.
Band navigation
The 2.4 GHz band is often congested. Band navigation enables APs to accept dual-band (2.4 GHz and
5 GHz) clients on their 5 GHz radio, increasing overall network performance.
When band navigation is enabled, the AP directs clients to its 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz radio by following
these principles:
•
For a 2.4 GHz client, the AP associates with the client after rejecting it several times.
- H3C WX5500E Series Access Controllers H3C WX3500E Series Access Controllers H3C WX2500E Series Access Controllers H3C WX6000 Series Access Controllers H3C WX5000 Series Access Controllers H3C LSUM3WCMD0 Access Controller Module H3C LSUM1WCME0 Access Controller Module H3C LSRM1WCM2A1 Access Controller Module
