10 m2m dma functional description, 1 m2m dma control finite state machine, 10 m2m dma functional description -10 – Cirrus Logic EP93xx User Manual
Page 404: 1 m2m dma control finite state machine -10
10-10
DS785UM1
Copyright 2007 Cirrus Logic
DMA Controller
EP93xx User’s Guide
1
0
1
0
10
10.1.10 M2M DMA Functional Description
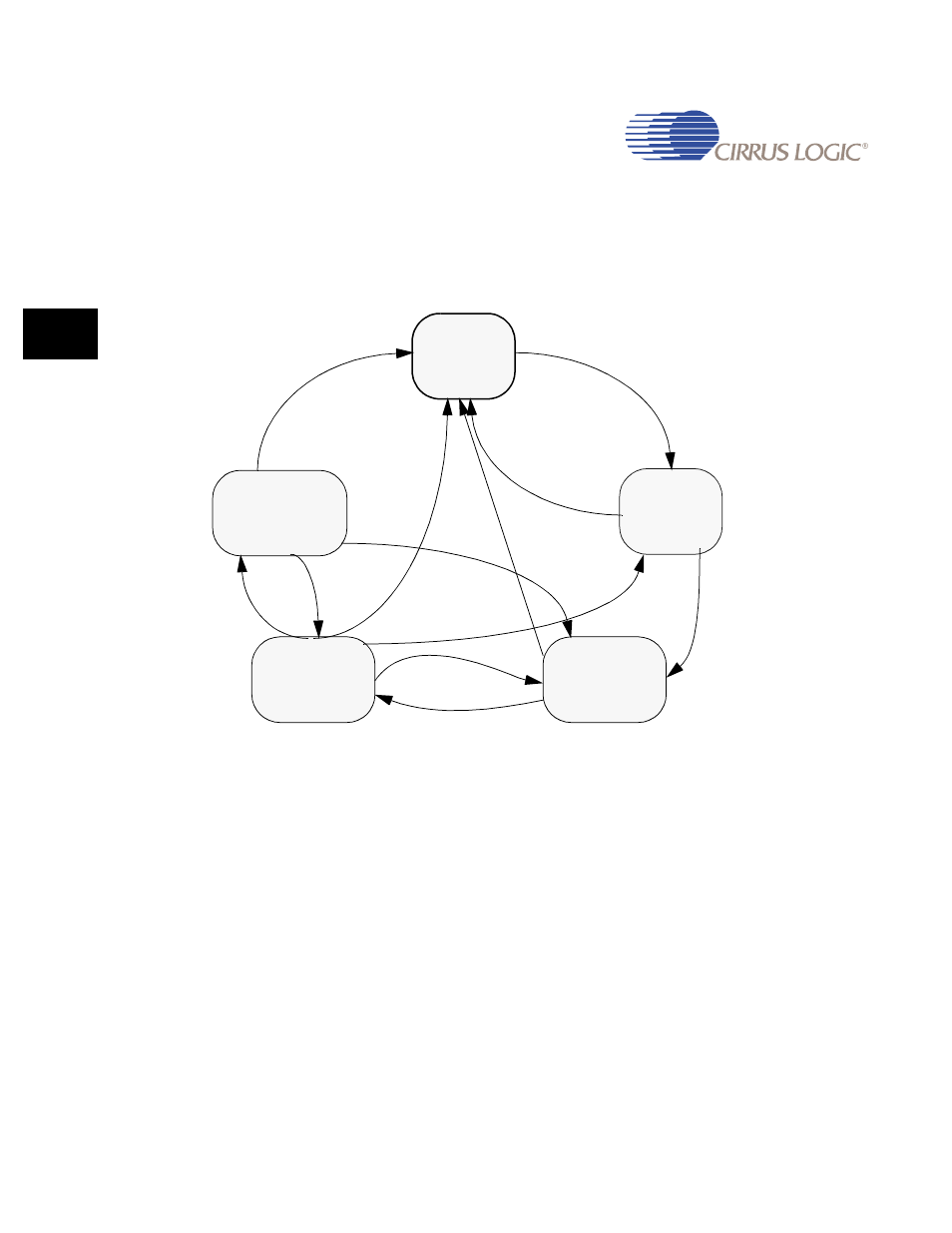
10.1.10.1 M2M DMA Control Finite State Machine
Each DMA M2M channel is controlled by 2 finite state machines (FSM) which determine
whether the channel is transferring data to or from memory, which buffer from the double-
buffer descriptor set it is using, and whether it is currently generating an interrupt.
Figure 10-2. M2M DMA Control Finite State Machine
10.1.10.1.1 DMA_IDLE
The DMA M2M Control FSM always resets to the DMA_IDLE state.
The DMA Control M2M FSM always enters the DMA_IDLE state when a channel is disabled
(CONTROL[3]).
The DMA Control M2M FSM exits the DMA_IDLE state and moves to the DMA_STALL state
when the ENABLE bit of the CONTROL register is set.
10.1.10.1.2 DMA_STALL
The DMA M2M Control FSM enters the DMA_STALL state when an M2M channel is enabled.
No STALL interrupt is generated for this condition.
The DMA M2M Control FSM enters the DMA_STALL state when a memory-to-memory
transfer has completed successfully. The DONE and STALL interrupts are generated for this
condition, if enabled.
DMA_IDLE
DMA_STALL
DMA_MEM_RD
DMA_MEM_WR
DMA_BWC_WAIT
ENABLE
DISABLE
DISABLE
DISABLE
DISABLE
(START, DREQ,
BCR_EQ_BWC
RX_TFR_END
TX_TFR_END
DONE/DEOT
RX_TFR_END
and BCR_VALID
IDEREQ, RXREQ,
or TXREQ)
