IDEC High Performance Series User Manual
Page 1000
5 Script Coding Examples
20-36
WindO/I-NV2 User’s Manual
Script
Operation description
The bits in the value of LDR100 are flipped and stored in LDR200.
For example, if the value of LDR100 is 0, then LDR200 is 65535.
Script
Operation description
If the bitwise logical OR operation on the value of LM102 and the result of the bitwise logical AND operation on the
value of LM100 and the inverted result of the value of LM101 is 1, then LM200 changes to 1.
If the bitwise logical OR operation on the value of LM102 and the result of the bitwise logical AND operation on the
value of LM100 and the inverted result of the value of LM101 is 0, then LM200 changes to 0.
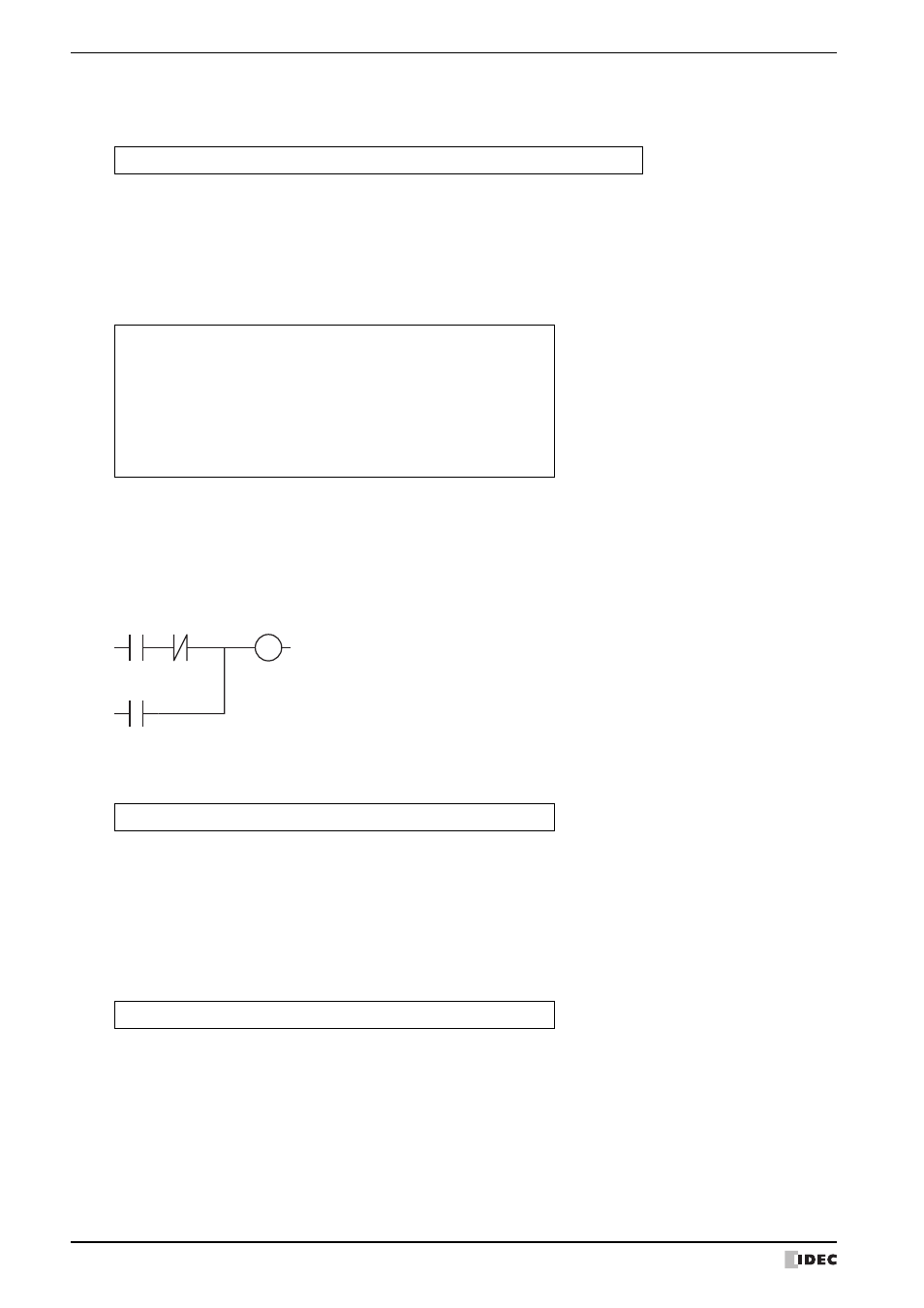
The operation is the same as the following ladder diagram.
Script
Operation description
The value of LDR100 is shifted left by only the amount of the value of LDR200 and the result is stored in LDR300.
For example, if the value of LDR100 is 1 and the value of LDR200 is 3, 1 is shifted 3 bits to the left and the result 8 is
stored in LDR300.
Script
Operation description
The value of LDR100 is shifted right by only the amount of the value of LDR200 and the result is stored in LDR300.
For example, if the value of LDR100 is 8 and the value of LDR200 is 3, 8 is shifted 3 bits to the right and the result 1
is stored in LDR300.
■
Example 5.5.4
Inversion
[LDR 200] = ~[LDR 100];
■
Example 5.5.5
Inversion
if (([LM 100] & ~ [LM 101]) | [LM 102])
{
SET([LM 200]);
}
else
{
RST([LM 200]);
}
LM100
LM102
LM200
LM101
■
Example 5.5.6
Left shift
[LDR 300] = [LDR 100] << [LDR 200];
■
Example 5.5.7
Right shift
[LDR 300] = [LDR 100] >> [LDR 200];
