Configuring access for snmp version 3 clients, Managing system files – LevelOne GTL-2691 User Manual
Page 99
C
HAPTER
2
| Initial Switch Configuration
Managing System Files
– 99 –
C
ONFIGURING
A
CCESS
FOR
SNMP V
ERSION
3 C
LIENTS
To configure management access for SNMPv3 clients, you need to first
create a view that defines the portions of MIB that the client can read or
write, assign the view to a group, and then assign the user to a group. The
following example creates one view called “mib-2” that includes the entire
MIB-2 tree branch, and then another view that includes the IEEE 802.1d
bridge MIB. It assigns these respective read and read/write views to a
group call “r&d” and specifies group authentication via MD5 or SHA. In the
last step, it assigns a v3 user to this group, indicating that MD5 will be
used for authentication, provides the password “greenpeace” for
authentication, and the password “einstien” for encryption.
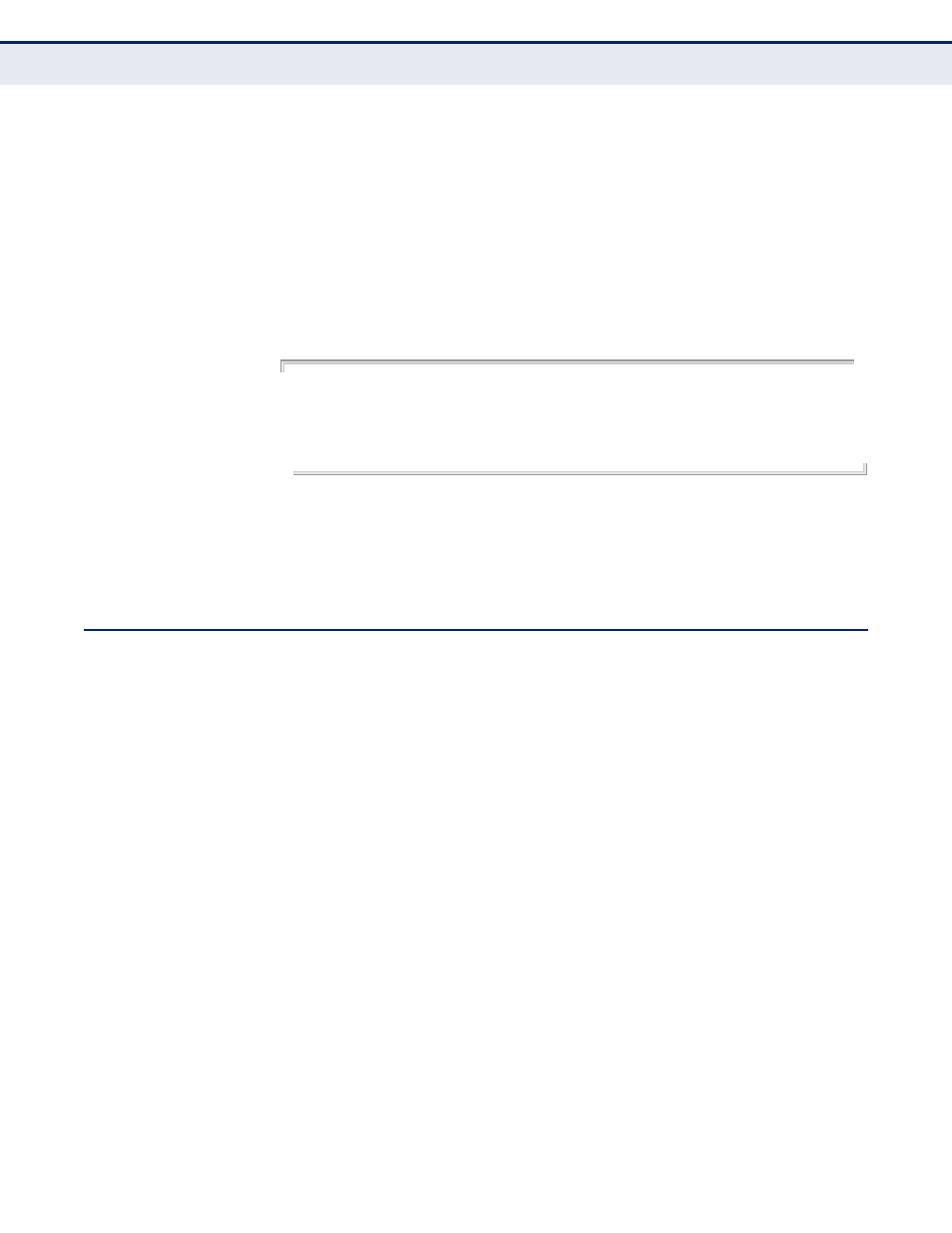
Console(config)#snmp-server view mib-2 1.3.6.1.2.1 included
Console(config)#snmp-server view 802.1d 1.3.6.1.2.1.17 included
Console(config)#snmp-server group r&d v3 auth mib-2 802.1d
Console(config)#snmp-server user steve group r&d v3 auth md5 greenpeace priv
des56 einstien
Console(config)#
For a more detailed explanation on how to configure the switch for access
from SNMP v3 clients, refer to
"Simple Network Management Protocol" on
, or refer to the specific CLI commands for SNMP starting on
M
ANAGING
S
YSTEM
F
ILES
The switch’s flash memory supports three types of system files that can be
managed by the CLI program, web interface, or SNMP. The switch’s file
system allows files to be uploaded and downloaded, copied, deleted, and
set as a start-up file.
The types of files are:
◆
Configuration — This file type stores system configuration information
and is created when configuration settings are saved. Saved
configuration files can be selected as a system start-up file or can be
uploaded via FTP/TFTP to a server for backup. The file named
“Factory_Default_Config.cfg” contains all the system default settings
and cannot be deleted from the system. If the system is booted with
the factory default settings, the master unit will also create a file
named “startup1.cfg” that contains system settings for stack
initialization, including information about the unit identifier, MAC
address for each unit. The configuration settings from the factory
defaults configuration file are copied to this file, which is then used to
boot the switch. See
"Saving or Restoring Configuration Settings" on
◆
Operation Code — System software that is executed after boot-up,
also known as run-time code. This code runs the switch operations and
provides the CLI and web management interfaces. See
for more information.
