Configuring the secure shell – LevelOne GTL-2691 User Manual
Page 343
C
HAPTER
13
| Security Measures
Configuring the Secure Shell
– 343 –
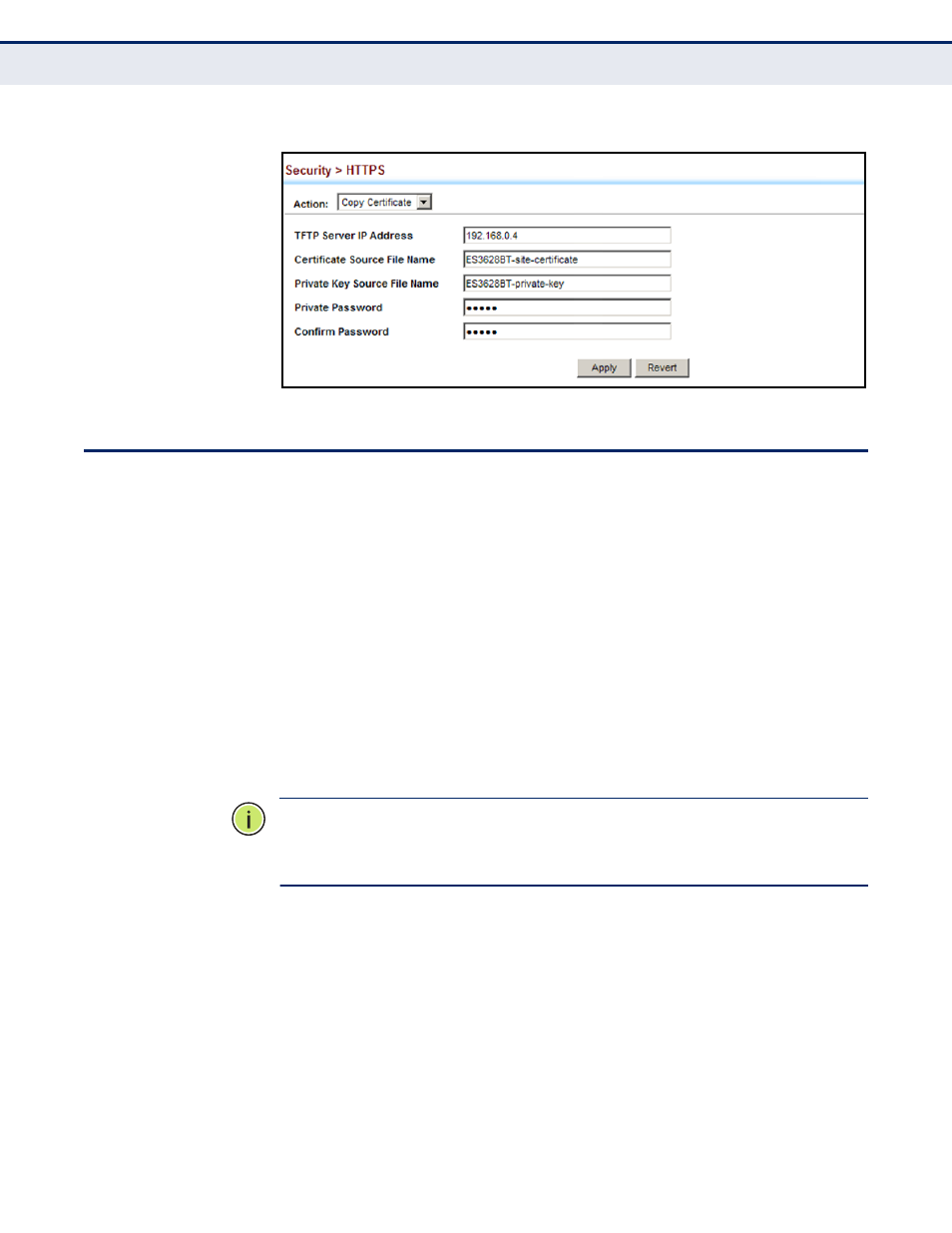
Figure 172: Downloading the Secure-Site Certificate
C
ONFIGURING
THE
S
ECURE
S
HELL
The Berkeley-standard includes remote access tools originally designed for
Unix systems. Some of these tools have also been implemented for
Microsoft Windows and other environments. These tools, including
commands such as rlogin (remote login), rsh (remote shell), and rcp
(remote copy), are not secure from hostile attacks.
The Secure Shell (SSH) includes server/client applications intended as a
secure replacement for the older Berkeley remote access tools. SSH can
also provide remote management access to this switch as a secure
replacement for Telnet. When the client contacts the switch via the SSH
protocol, the switch generates a public-key that the client uses along with a
local user name and password for access authentication. SSH also encrypts
all data transfers passing between the switch and SSH-enabled
management station clients, and ensures that data traveling over the
network arrives unaltered.
N
OTE
:
You need to install an SSH client on the management station to
access the switch for management via the SSH protocol.
N
OTE
:
The switch supports both SSH Version 1.5 and 2.0 clients.
C
OMMAND
U
SAGE
The SSH server on this switch supports both password and public key
authentication. If password authentication is specified by the SSH client,
then the password can be authenticated either locally or via a RADIUS or
TACACS+ remote authentication server, as specified on the System
Authentication page (
). If public key authentication is specified by
the client, then you must configure authentication keys on both the client
and the switch as described in the following section. Note that regardless of
whether you use public key or password authentication, you still have to
generate authentication keys on the switch (SSH Host Key Settings) and
enable the SSH server (Authentication Settings).
