Equal-cost multipath routing, Figure 391: displaying the routing table – LevelOne GTL-2691 User Manual
Page 637
C
HAPTER
18
| General IP Routing
Equal-cost Multipath Routing
– 637 –
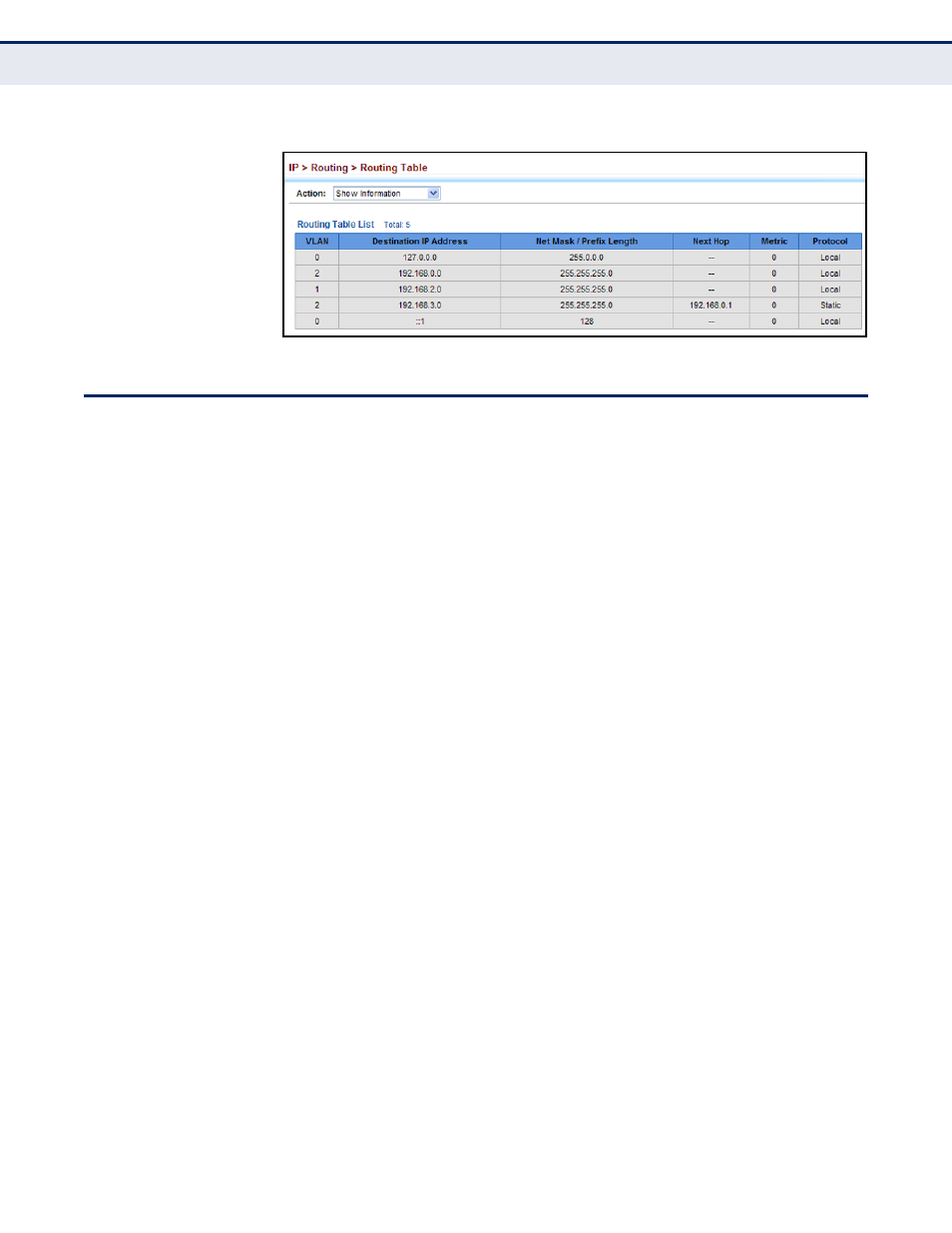
Figure 391: Displaying the Routing Table
E
QUAL
-
COST
M
ULTIPATH
R
OUTING
Use the IP > Routing > Routing Table (Configure ECMP Number) page to
configure the maximum number of equal-cost paths that can transmit
traffic to the same destination. The Equal-cost Multipath routing algorithm
is a technique that supports load sharing over multiple equal-cost paths for
data passing to the same destination. Whenever multiple paths with equal
path cost to the same destination are found in the routing table, the ECMP
algorithm first checks if the cost is lower than that of any other entries in
the routing table. If the cost is the lowest in the table, the switch will use
up to eight of the paths with equal lowest cost to balance the traffic
forwarded to the destination. ECMP uses either equal-cost multipaths
manually configured in the static routing table, or equal-cost multipaths
dynamically generated by the Open Shortest Path Algorithm (OSPF). In
other words, it uses either static or OSPF entries, not both. Normal unicast
routing simply selects the path to the destination that has the lowest cost.
Multipath routing still selects the path with the lowest cost, but can forward
traffic over multiple paths if they all have the same lowest cost. ECMP is
enabled by default on the switch. If there is only one lowest cost path
toward the destination, this path will be used to forward all traffic. If there
is more than one lowest-cost path configured in the static routing table
(see
"Configuring Static Routes" on page 633
), or dynamically generated
"Configuring the Open Shortest Path First Protocol (Version
), then up to 8 paths with the same lowest cost can be
used to forward traffic to the destination.
CLI R
EFERENCES
◆
C
OMMAND
U
SAGE
◆
ECMP only selects paths of the same protocol type. It cannot be applied
to both static paths and dynamic paths at the same time for the same
destination. If both static and dynamic paths have the same lowest
cost, the static paths have precedence over dynamic paths.
◆
Each path toward the same destination with equal-cost takes up one
entry in the routing table to record routing information. In other words,
a route with 8 paths will take up 8 entries.
