Showing ipv6 addresses, Figure 345: configuring an ipv6 address – LevelOne GTL-2691 User Manual
Page 585
C
HAPTER
16
| IP Configuration
Setting the Switch’s IP Address (IP Version 6)
– 585 –
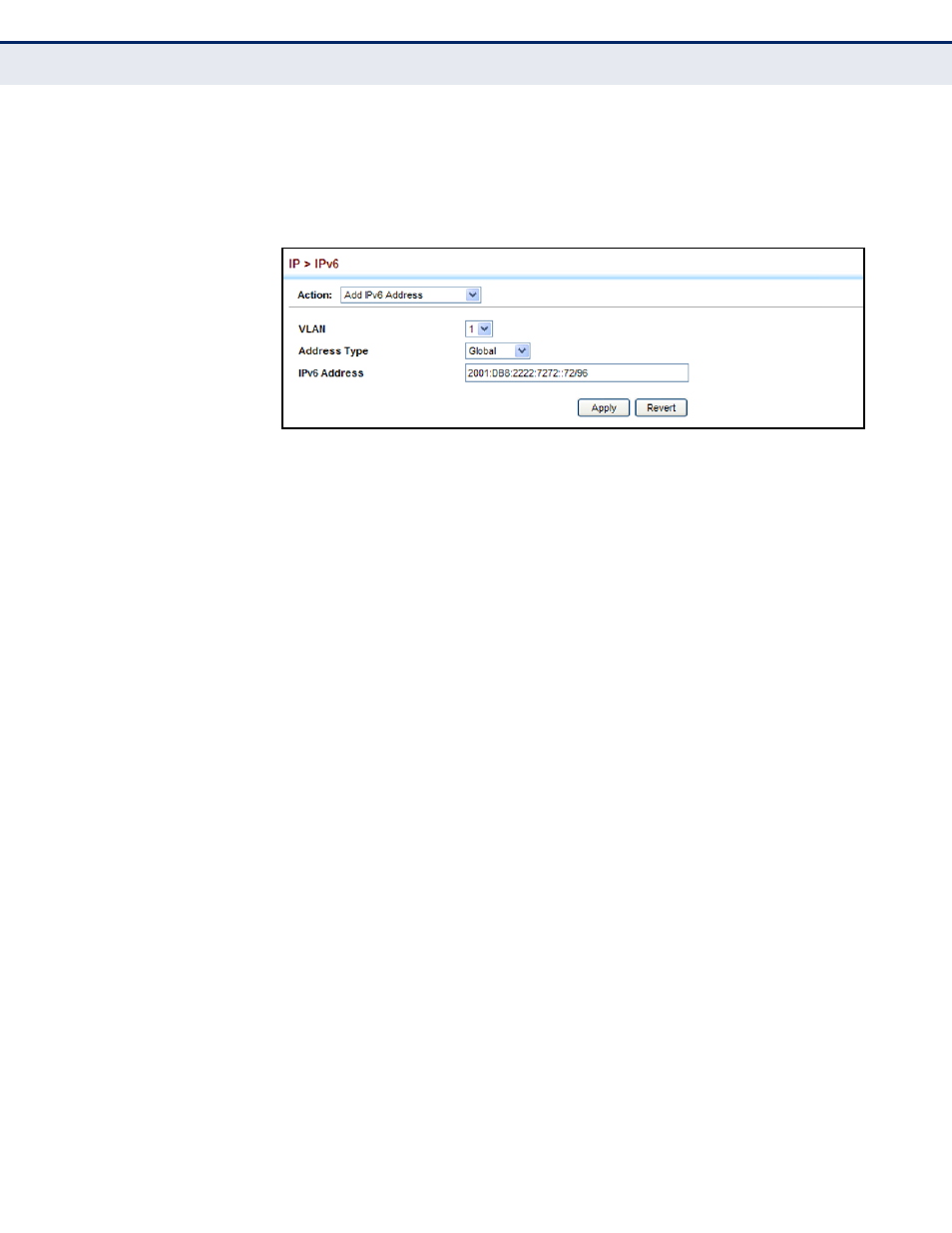
3.
Specify the VLAN to configure, select the address type, and then enter
an IPv6 address and prefix length.
4.
Click Apply.
Figure 345: Configuring an IPv6 Address
S
HOWING
IP
V
6
A
DDRESSES
Use the IP > IPv6 Configuration (Show IPv6 Address) page to display the
IPv6 addresses assigned to an interface.
CLI R
EFERENCES
◆
"show ipv6 interface" on page 1416
P
ARAMETERS
These parameters are displayed:
◆
VLAN – ID of a configured VLAN which is to be used for management
access, or for creating an interface to multiple subnets. By default, all
ports on the switch are members of VLAN 1. However, the management
station can be attached to a port belonging to any VLAN, as long as that
VLAN has been assigned an IP address. (Range: 1-4093)
◆
IP Address Type – The address type (Global, EUI-64, Link Local).
◆
IP Address – An IPv6 address assigned to this interface.
In addition to the unicast addresses assigned to an interface, a node is
also required to listen to the all-nodes multicast addresses FF01::1
(interface-local scope) and FF02::1 (link-local scope).
FF01::1/16 is the transient interface-local multicast address for all
attached IPv6 nodes, and FF02::1/16 is the link-local multicast address
for all attached IPv6 nodes. The interface-local multicast address is
only used for loopback transmission of multicast traffic. Link-local
multicast addresses cover the same types as used by link-local unicast
addresses, including all nodes (FF02::1), all routers (FF02::2), and
solicited nodes (FF02::1:FFXX:XXXX) as described below.
A node is also required to compute and join the associated solicited-
node multicast addresses for every unicast and anycast address it is
assigned. IPv6 addresses that differ only in the high-order bits, e.g.
due to multiple high-order prefixes associated with different
aggregations, will map to the same solicited-node address, thereby
reducing the number of multicast addresses a node must join. In this
