Configuring nssa settings, Figure 430: showing nssas or stubs, Figure 431: ospf nssa – LevelOne GTL-2691 User Manual
Page 679: Nssa s
C
HAPTER
20
| Unicast Routing
Configuring the Open Shortest Path First Protocol (Version 2)
– 679 –
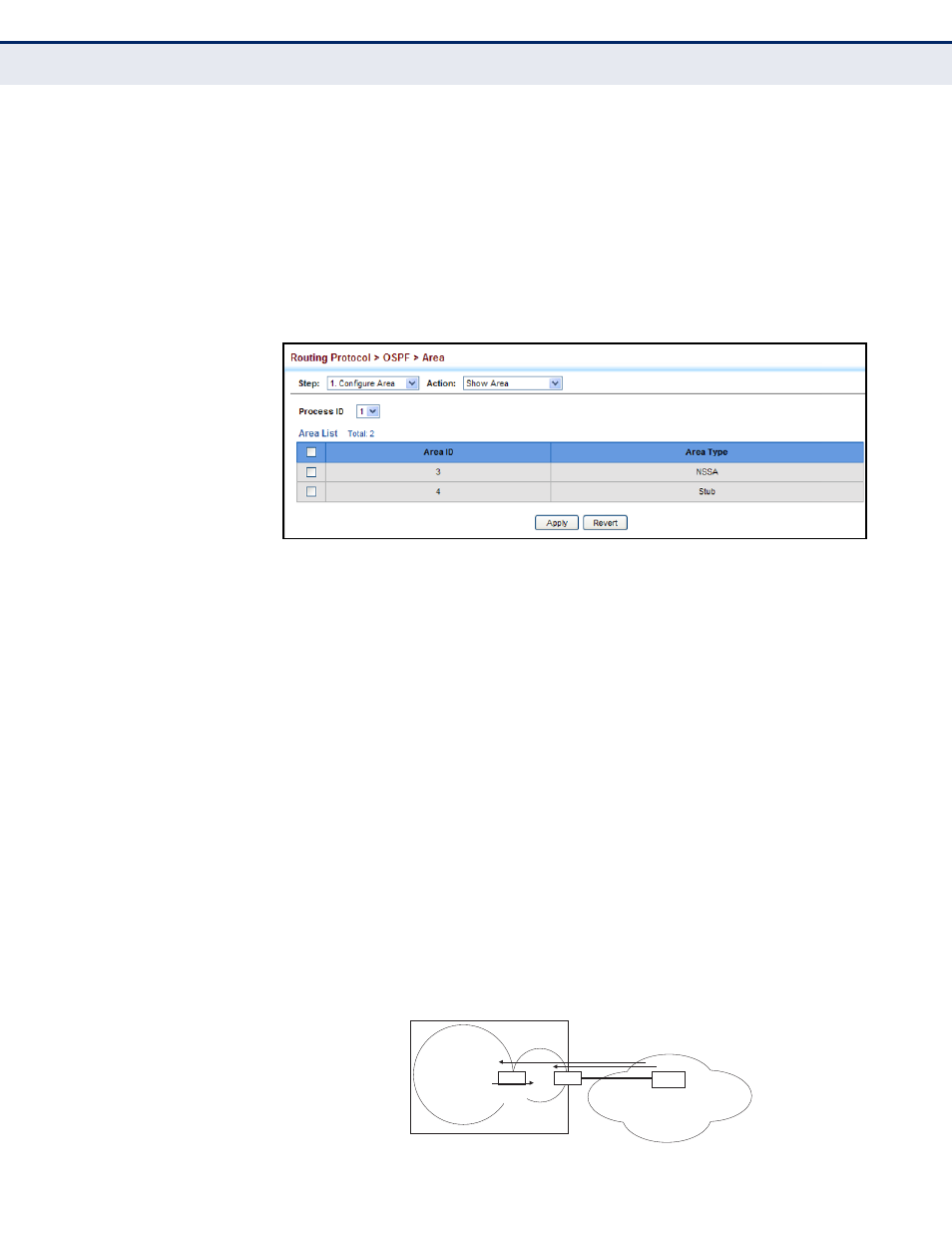
To show the NSSA or stubs added to the specified OSPF domain:
1.
Click Routing Protocol, OSPF, Area.
2.
Select Configure Area from the Step list.
3.
Select Show Area from the Action list.
4.
Select a Process ID.
Figure 430: Showing NSSAs or Stubs
C
ONFIGURING
NSSA
S
ETTINGS
Use the Routing Protocol > OSPF > Area (Configure Area – Configure NSSA
Area) page to configure protocol settings for a not-so-stubby area (NSSA).
An NSSA can be configured to control the use of default routes for Area
Border Routers (ABRs) and Autonomous System Boundary Routers
(ASBRs), or external routes learned from other routing domains and
imported through an ABR.
An NSSA is similar to a stub. It blocks most external routing information,
and can be configured to advertise a single default route for traffic passing
between the NSSA and other areas within the autonomous system (AS)
when the router is an ABR.
An NSSA can also import external routes from one or more small routing
domains that are not part of the AS, such as a RIP domain or locally
configured static routes. This external AS routing information is generated
by the NSSA’s ASBR and advertised only within the NSSA. By default, these
routes are not flooded onto the backbone or into any other area by ABRs.
However, the NSSA’s ABRs will convert NSSA external LSAs (Type 7) into
external LSAs (Type-5) which are propagated into other areas within the
AS.
Figure 431: OSPF NSSA
backbone
NSSA
ABR
default external
route for local AS
ASBR
external network
Router
default external
route for another
routing domain
7
5
AS
