Routing an ipv6 packet through an mpls domain – Brocade Multi-Service IronWare Multiprotocol Label Switch (MPLS) Configuration Guide (Supporting R05.6.00) User Manual
Page 825
Multi-Service IronWare Multiprotocol Label Switch (MPLS) Configuration Guide
801
53-1003031-02
6PE over MPLS
9
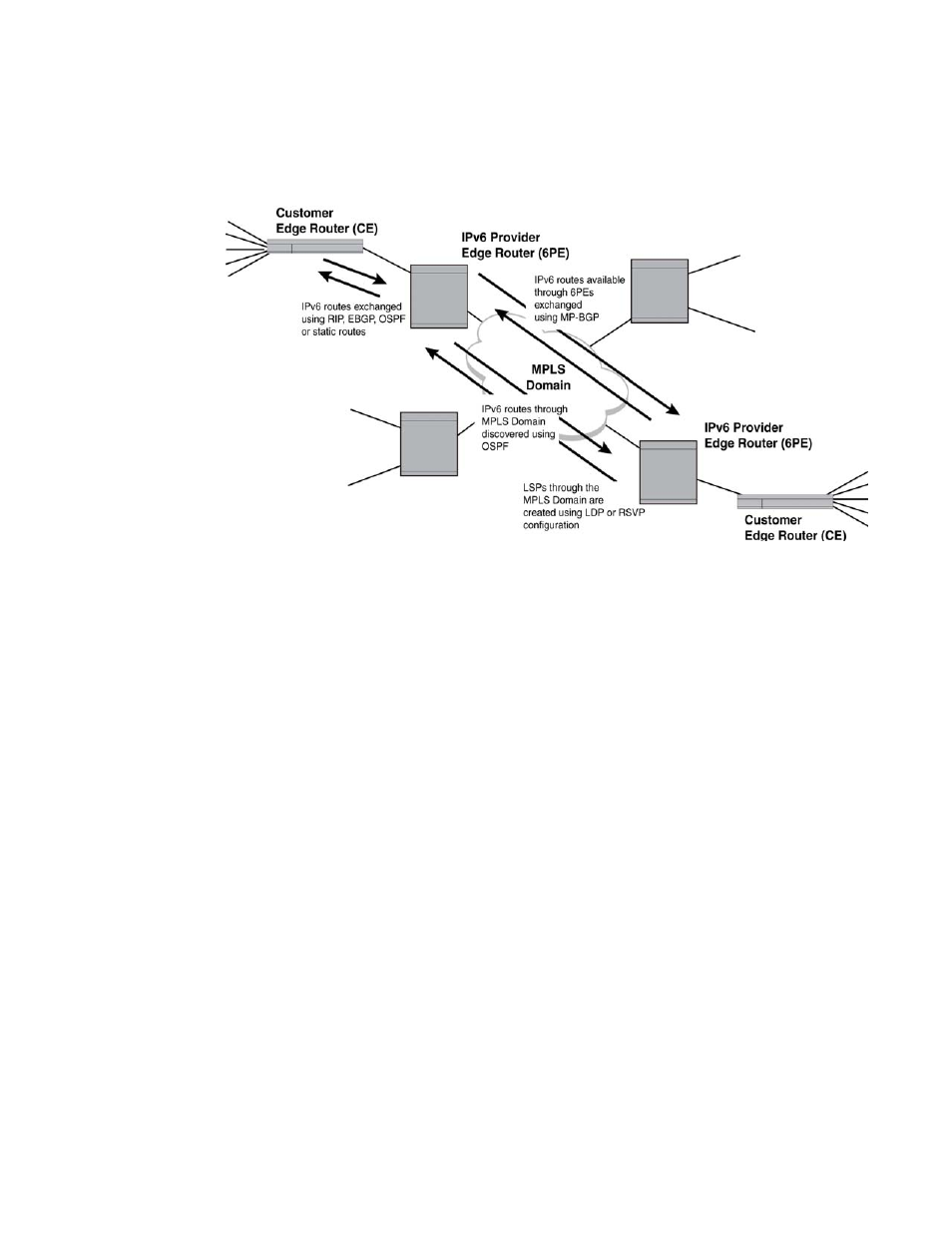
FIGURE 93
MPLS route discovery
Routing an IPv6 packet through an MPLS domain
The following steps describe how an IPv6 packet is routed through an existing MPLS domain.
1. The 6PE router receives the IPv6 packets from the CE router.
2. The 6PE router assigns labels to all the received IPv6 packets.
3. The 6PE router exchanges the IPv6 packets along with the labels with the other 6PE routers.
4. The 6PE router transports the IPv6 packets from the CE router using the existing IPv4 LSPs.
describes how an IPv6 packet is forwarded from CE1 to CE2 through the MPLS domain.
When an ingress 6PE router (6PE-I) receives the IPv6 packet from CE1, the 6PE-I assigns an inner
label containing IPv4-mapped IPv6 BGP next-hop information, and an outer label containing the
IPv4 address corresponding to the IPv4-mapped IPv6 address to the received IPv6 packet.
The egress 6PE router (6PE-E) advertises the IPv6 reachability information to the 6PE-I by
distributing the inner label using the MP-BGP. The 6PE-I obtains an LSP to switch the IPv6 packet to
the 6PE-E using LDP or RSVP. The packet is then forwarded through the MPLS domain and is
switched using the labels. At the penultimate device in the LSP, the outer label is removed and the
packet is forwarded to the 6PE-E. The 6PE-E uses the inner label to identify the destination router
(CE2) to which the packet must be forwarded. The 6PE-E removes the inner label and forwards the
packet to the CE2.
