Brocade Multi-Service IronWare Multiprotocol Label Switch (MPLS) Configuration Guide (Supporting R05.6.00) User Manual
Page 193
Multi-Service IronWare Multiprotocol Label Switch (MPLS) Configuration Guide
169
53-1003031-02
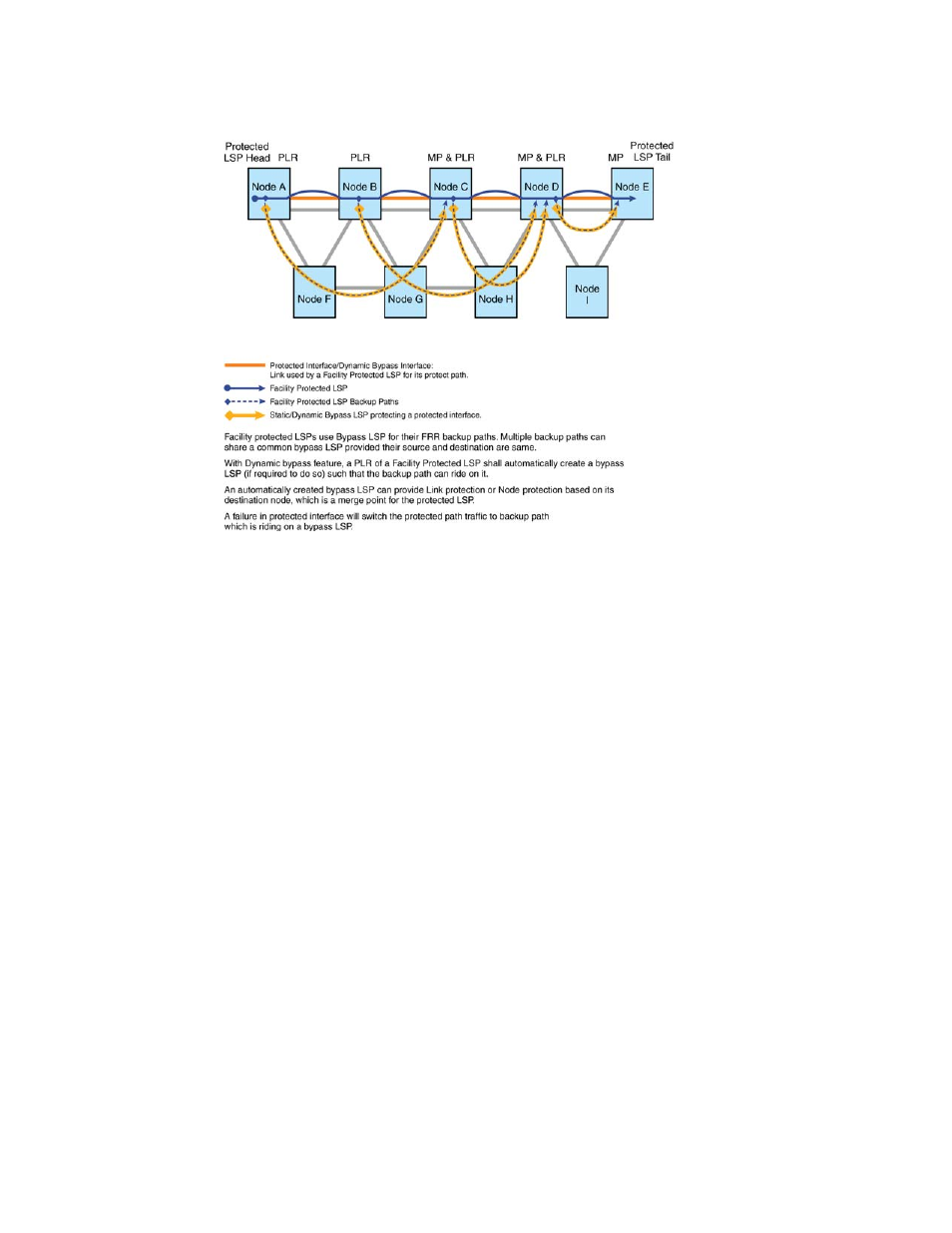
Dynamic Bypass LSPs
1
When establishing a facility protected LSP with link or node protection, each LSR on the primary
path verifies when there are any existing bypass LSPs that require protection constraints. When
finding a bypass, it updates its bandwidth, depending on the requesting backup path bandwidth.
The protected LSP backup path uses this bypass to reach its merge point. When there is no bypass
available, the LSR computes and establishes a new bypass LSP, addressing the backup path
constraints.
When an LSR is created for an interface, any number of facility protected LSPs may reuse or share
a bypass LSP. All of the protected LSPs must use the same protected interface and the bypass LSP
must satisfy the new LSPs backup path constraints. A periodic optimization of dynamic bypass
LSPs is performed using the make-before-break procedure.
Configuration parameters, such as bandwidth, hop-limit, and priority are set when creating the
dynamic bypass LSP. The system makes use of these parameters when creating a new dynamic
bypass LSP. Modifications on these parameters are taken into consideration during the next cycle
of re-optimization or can be manually initiated at the interface level re-optimization.
Bandwidth of the newly triggered bypass LSP is zero by default, unless it has an explicit
configuration. When a new facility protected LSP requests a bandwidth which cannot be
accommodated within an existing dynamic bypass LSP, there is no automatic make-before-break
for the existing dynamic bypass LSP. Instead, a new dynamic bypass is created, depending on the
configurations and system limits.
