Mpls sample configurations, Lsp with redundant paths – Brocade Multi-Service IronWare Multiprotocol Label Switch (MPLS) Configuration Guide (Supporting R05.6.00) User Manual
Page 296
272
Multi-Service IronWare Multiprotocol Label Switch (MPLS) Configuration Guide
53-1003031-02
Transit LSP statistics
1
end of MPLS configuration
To reset counter-mode to byte, enter the following command.
Brocade(config-mpls)# no counter-mode packet
To verify the configuration, enter the following command.
Brocade(config-mpls)# show mpls conf
router mpls
mpls-interface e1/11
end of MPLS configuration
MPLS sample configurations
This section presents examples of typical MPLS configurations.
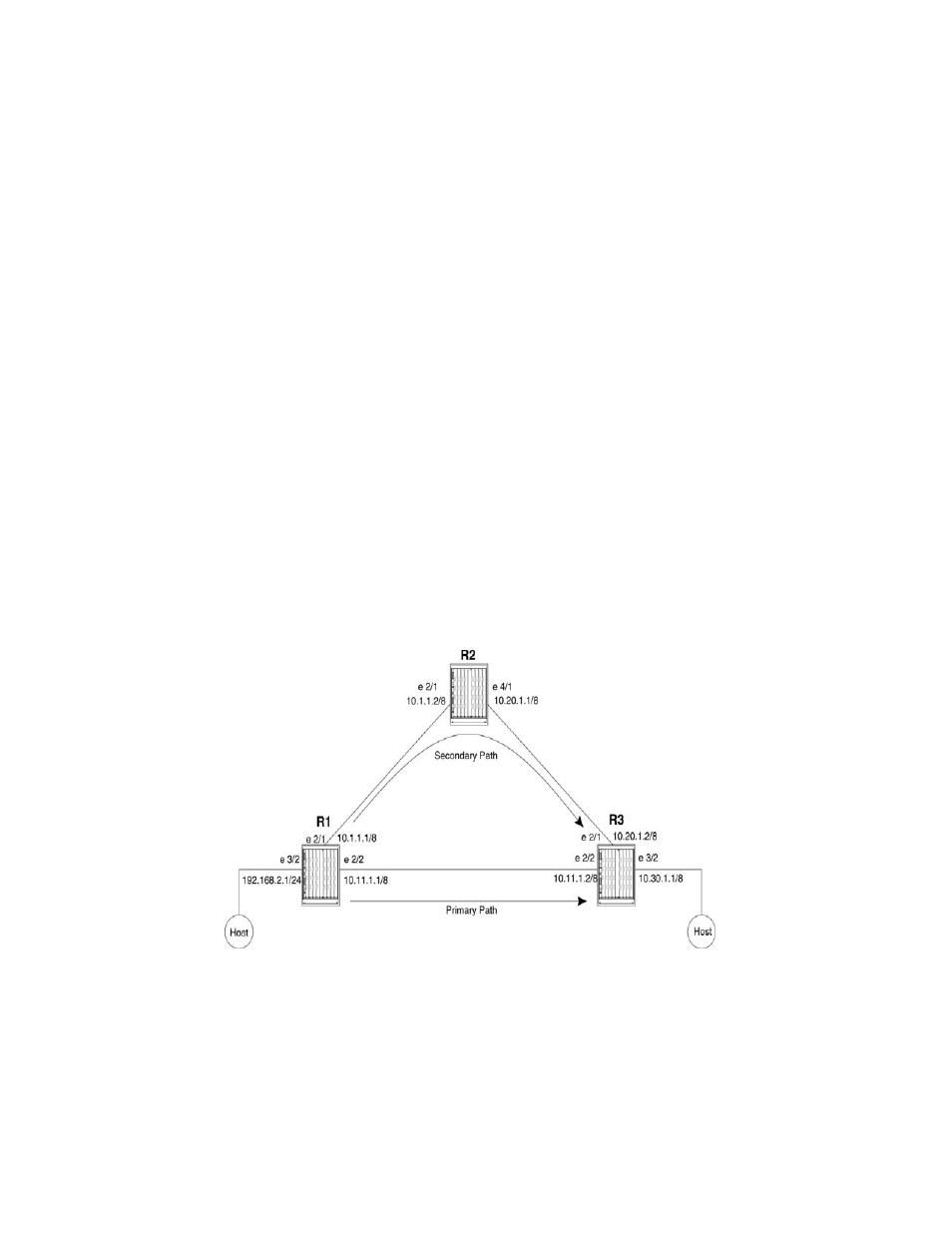
LSP with redundant paths
shows a signaled LSP configuration that has a primary and a secondary path. The
destination for this LSP is 10.1.1.1. The primary path to this destination is through interface e 2/2,
which has a direct link to interface e 2/2 on R3. When this link fails, the secondary path is
established. The secondary path goes through R2.
FIGURE 43
LSP configuration with primary and secondary paths
Router R1 is the ingress LER for signaled LSP t3. Packets whose destination is 10.1.1.1 are
assigned to this LSP. Two paths are configured, direct_conn and via_r2. Path direct_conn consists
of a single strict node, 10.1.1.2, which is a directly connected interface on the destination LSR, R3.
Path via_r2 also consists of a single strict node, 10.1.1.2, a directly connected interface on R2.
Since path via_r2 does not specify a node for R3, the hop between R2 and R3 is treated as a hop to
a loose node. This means standard hop-by-hop routing is used to determine the path between R2
and R3.
