Brocade Multi-Service IronWare Multiprotocol Label Switch (MPLS) Configuration Guide (Supporting R05.6.00) User Manual
Page 476
452
Multi-Service IronWare Multiprotocol Label Switch (MPLS) Configuration Guide
53-1003031-02
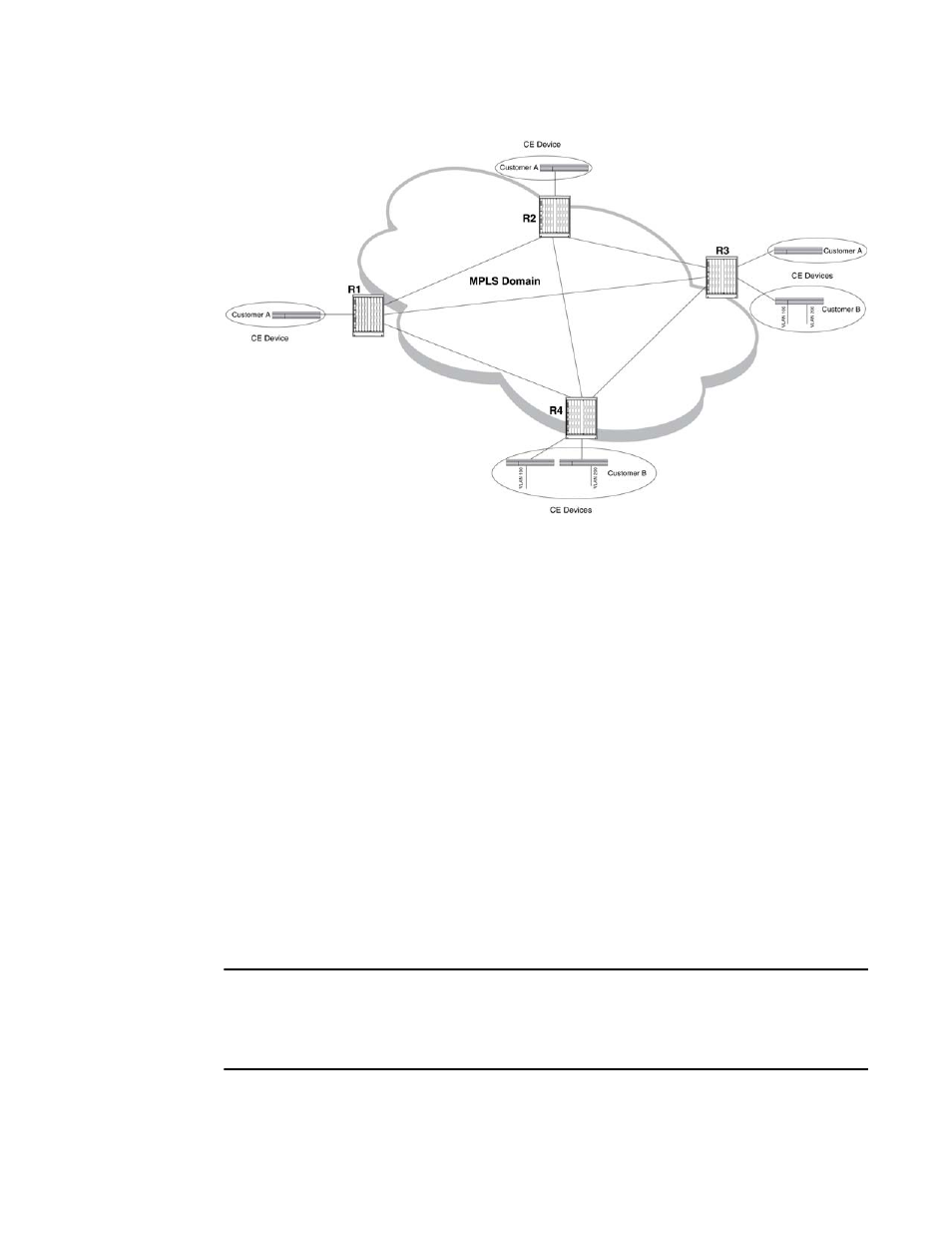
How VPLS works
3
A PE device in the VPLS configuration operates like a standard Layer 2 switch, in that it performs
MAC address learning, flooding, and forwarding for the CE devices in each VPLS instance. For
example, when PE device R1 receives a Layer 2 frame with a given MAC destination address from
Customer A’s CE device, it looks up the MAC address in a Layer 2 forwarding table that records
associations between MAC addresses and VC LSPs. This forwarding table is known as the VPLS
MAC database.
When the MAC address is found in the VPLS MAC database, the PE device finds the associated VC
LSP, encapsulates the frame as an MPLS packet, and pushes an inner VC label and outer tunnel
label onto the packet. The packet is then sent over a tunnel LSP to the VC peer. When the MAC
address is not found in the VPLS MAC database, the frame is flooded to all of the PE devices and
locally connected CE devices (except for the CE device that originated the frame) in the customer’s
VPLS instance. When a response is received, an entry for the MAC address and the VC from which
it arrived is added to the VPLS MAC database. Subsequent frames targeting the MAC address are
not flooded to the other devices in the VPLS instance. In this way, the PE device learns the MAC
addresses of the remotely connected customer devices. MAC addresses received at the local VPLS
endpoints are also learned in the VPLS MAC database for the VPLS instance.
The PE devices do not run Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) over the MPLS domain. The full mesh of PE
devices in a VPLS configuration allows one PE device to reach any other PE device in the VPN in
exactly one hop, with no transit PE devices in between. The PE devices apply a split horizon rule
when forwarding frames within the VPN. When a PE receives a customer frame from a VC LSP, it
can forward the frame only to a directly attached customer device, not to another VC LSP. This
allows the VPLS instance to have a loop-free topology without having to run STP.
NOTE
In releases prior to NetIron Release 03.7.00, packets that arrive on an interface with the same
destination MAC address as the interface are not subject to transparent VLAN flooding for Layer 2
switching, VPLS local switching, or VLL local switching. Beginning with NetIron Release 03.7.00,
these packets are forwarded in hardware just like packets with other destination addresses.
