Mpls. refer to, Mpls label header encoding, For specific information about the contents of a – Brocade Multi-Service IronWare Multiprotocol Label Switch (MPLS) Configuration Guide (Supporting R05.6.00) User Manual
Page 32
8
Multi-Service IronWare Multiprotocol Label Switch (MPLS) Configuration Guide
53-1003031-02
How MPLS works
1
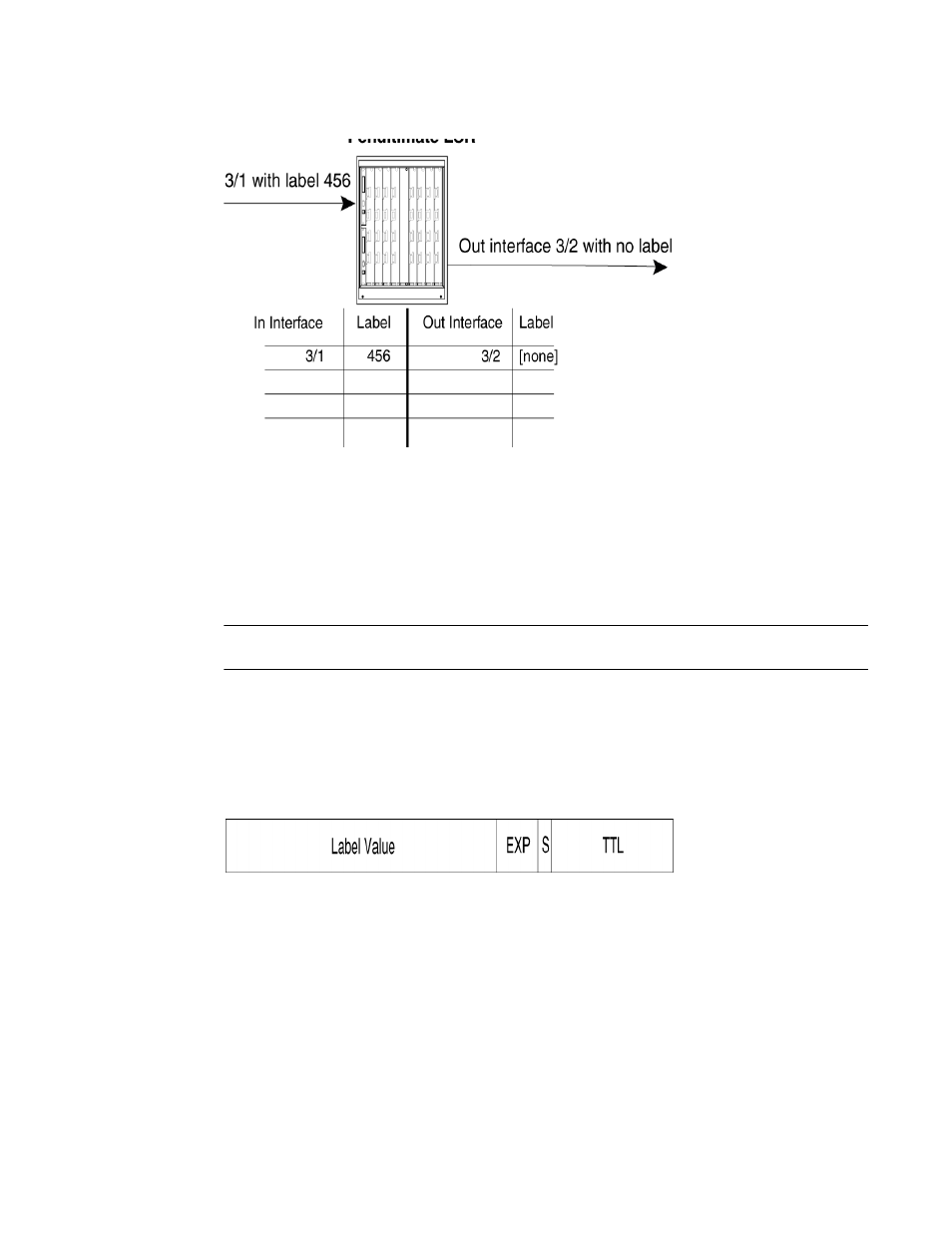
When an LSR receives an MPLS packet, it looks up the label in its MPLS forwarding table. Normally,
this table maps the label and inbound interface to a new label and outbound interface. However,
when this is the penultimate LSR in an LSP, the label and inbound interface map only to an
outbound interface. The penultimate LSR pops the label and forwards the packet – now a regular
IP packet – out the outbound interface. When the packet reaches the egress LER, there is no
indication that it had been forwarded over an LSP. The packet is forwarded using standard
hop-by-hop routing protocols.
NOTE
Penultimate hop popping is always performed on signaled LSPs.
MPLS label header encoding
The following diagram illustrates the structure of the 32-bit MPLS label header. When a packet
enters an LSP, the ingress LER pushes a label onto the packet.
FIGURE 4
Structure of an MPLS Label Header
An MPLS label header is composed of the following parts:
Label value (20 bits)
The label value is an integer in the range 16 – 1048575. (Labels 0 – 15 are reserved by the IETF
for special usage.) For signaled LSPs, the device dynamically assigns labels in the range 1024 –
499999.
EXP field (3 bits)
