Vpls raw pass through mode – Brocade Multi-Service IronWare Multiprotocol Label Switch (MPLS) Configuration Guide (Supporting R05.6.00) User Manual
Page 483
Multi-Service IronWare Multiprotocol Label Switch (MPLS) Configuration Guide
459
53-1003031-02
Configuring VPLS instances
3
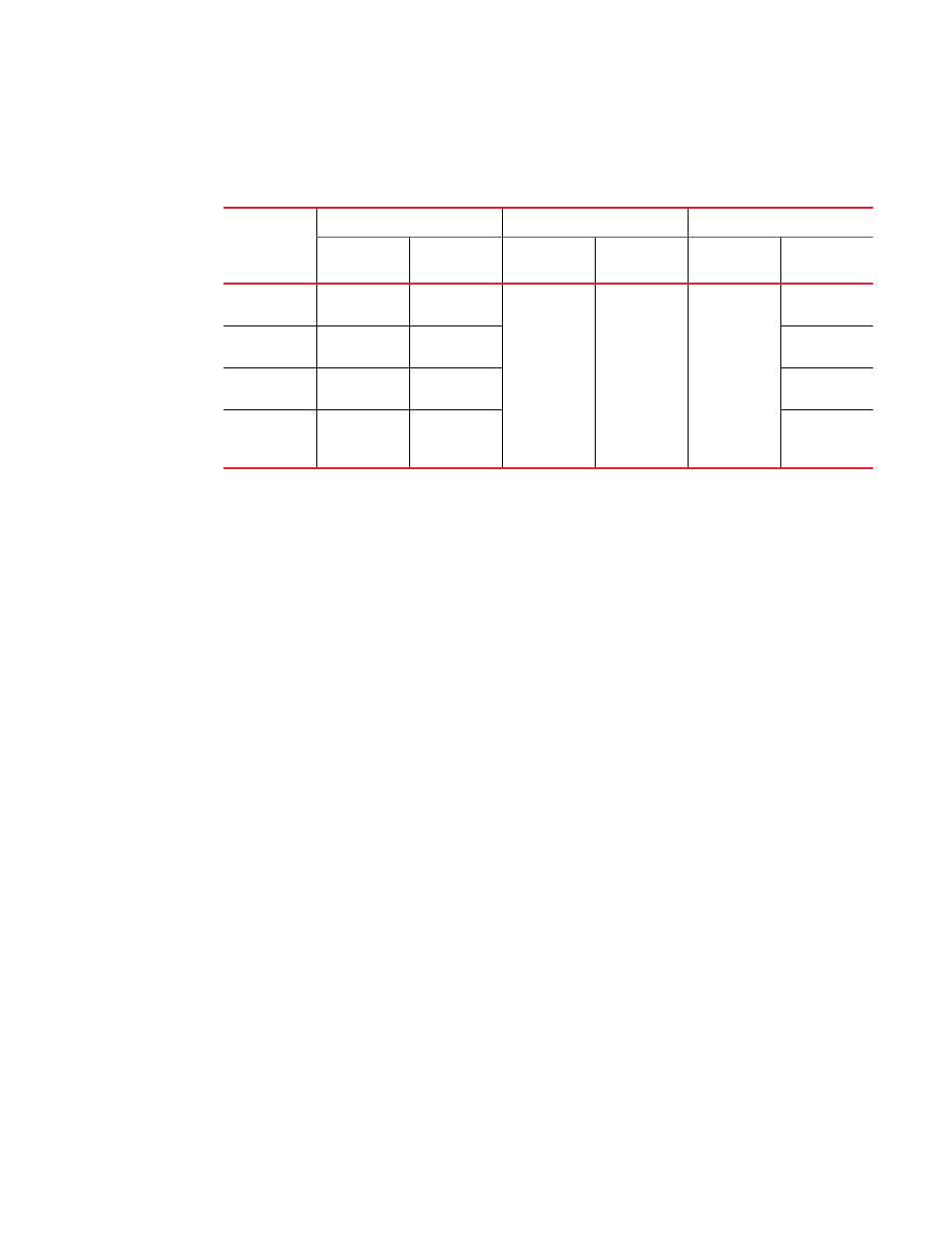
describes the expected Class of Service (CoS) behavior for VPLS packets when VPLS raw
mode is in effect.
TABLE 66
Expected class of service behavior for VPLS raw mode
VPLS endpoints Incoming packet
MPLS cloud
Outgoing packet
Outer VLAN
Inner VLAN
Tunnel/VC
label (Z)
Payload tag
Outer VLAN
Inner VLAN
Dual-tagged
to dual-tagged
X
Y
V or internal
priority
N/A
W or Z
Z
Single-tagged
to dual-tagged
X
N/A
Z
Untagged to
dual-tagged
N/A
N/A
Z
Dual-tagged
to
single-tagged
X
Y
N/A
Legend for Table 66
V = Mapped EXP bits from internal priority (X contributes to internal priority) using the EXP
encode table.
W = Mapped CoS from internal priority (Z contributes to internal priority) using the CoS encode
table.
X = Original outer VLAN CoS.
Y = Original inner VLAN CoS.
Z = Incoming EXP bits as described by the Tunnel / VC label column = V or internal priority.
•
The Tunnel/VC label column differentiates the behavior when qos exp encode policy is ON
(default) or OFF.
•
The Outgoing packet Outer VLAN column differentiates the behavior when qos pcp encode
policy is ON (default) or OFF.
VPLS raw pass through mode
By default, VPLS packets are sent to remote peers over the MPLS cloud in raw mode. This means
that no VLAN tag information in the payload is carried across the MPLS cloud. In raw mode, the
VLAN priority (Class of Service) of the original (incoming) packets is lost once the packets are sent
through the cloud.
Although Brocade implementation follows RFC 4448 in terms of how raw mode and tagged mode
operates, Brocade devices occasionally cannot interoperate with certain VPLS vc raw mode third
party equipment that has interpreted RFC 4448 differently.
When a third party device remote peer is connected to a Brocade device, and it was identified
under raw mode, the remote peer may expect the presence of the tag in the packet it received from
its MPLS uplink. It may also send the payload tag towards its remote peer when sending packets by
way of the MPLS uplink towards the Brocade device peer. This causes the two peers to not
communicate correctly.
