Brocade Multi-Service IronWare Multiprotocol Label Switch (MPLS) Configuration Guide (Supporting R05.6.00) User Manual
Page 46
22
Multi-Service IronWare Multiprotocol Label Switch (MPLS) Configuration Guide
53-1003031-02
Traffic engineering database
1
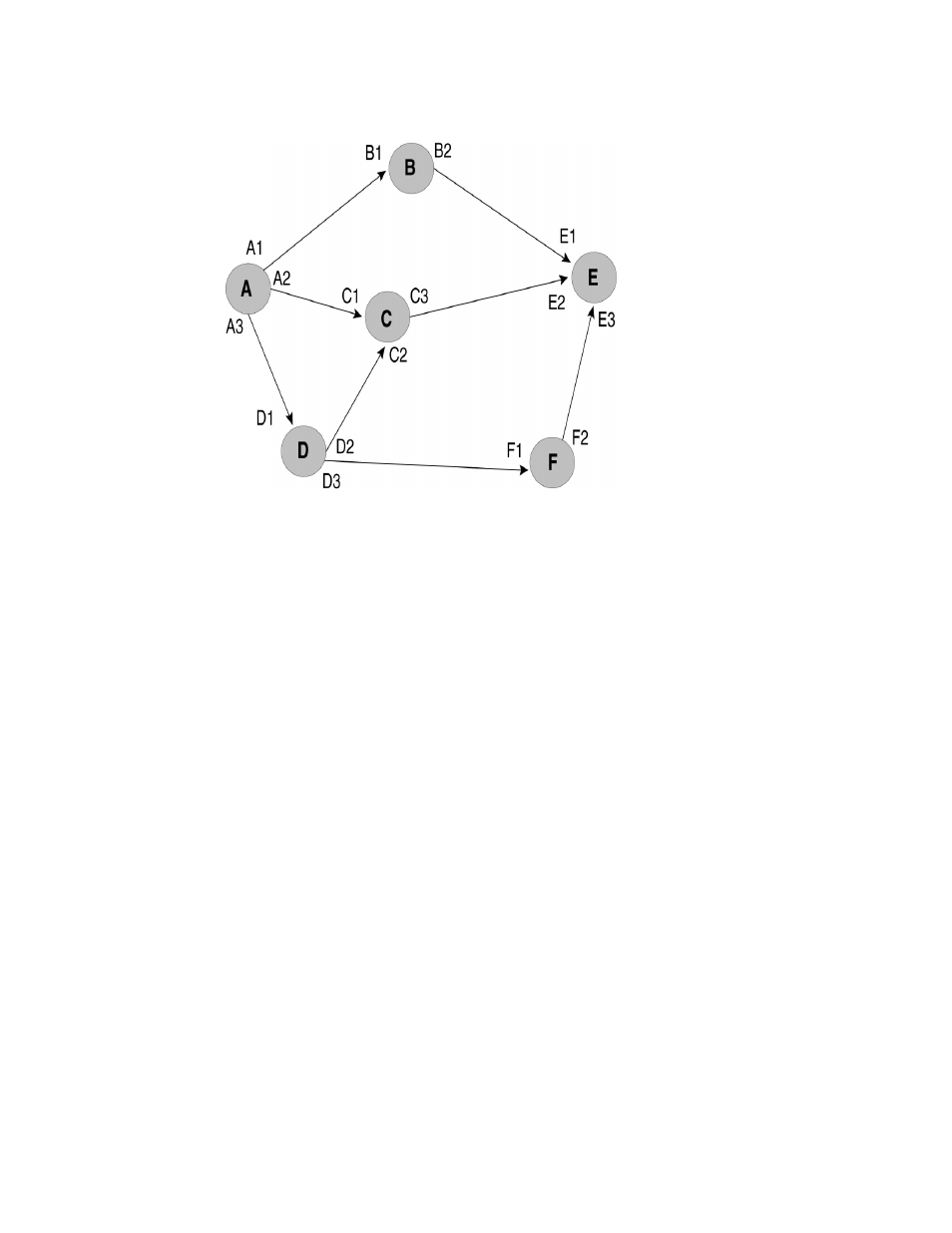
The global cspf-interface-constraint command directs the router to include the interface address as
a constraint when it determines the shortest path. When invoked, this command ensures that a
specified interface must be included in an LSP. This constraint can be turned on and off
dynamically and does not affect established primary or secondary LSPs. CSPF interface constraint
is significant for the ingress node only, where CSPF calculation takes place for an LSP.
When configuring CSPF interface constraint, the user must be aware that the imposition of this
additional constraint can increase the possibility of no path being found where otherwise there
could be a path. One case where this can occur is where the path required to conform to the
interface constraint fails the configured bandwidth constraint. Additionally, no path may be found
where a configured path contains an inherently contradictory condition. For example, when a path
is configured “B1 (strict) to E2 (loose) as shown in
, no path is found. This is because CSPF
always appends B1 into the final CSPF path. This has the effect of making “B” the source node of
the next hop and therefore excludes “E1 as a traversed interface in subsequent paths to the
destination node “E”. Consequently, in this example the LSP is down. However, when the
cspf-interface-constraint command is not active, a CSPF path is found and the LSP goes up.
FIGURE 9
Example of where no path is found
