Table, Specifying local vpls endpoints – Brocade Multi-Service IronWare Multiprotocol Label Switch (MPLS) Configuration Guide (Supporting R05.6.00) User Manual
Page 519
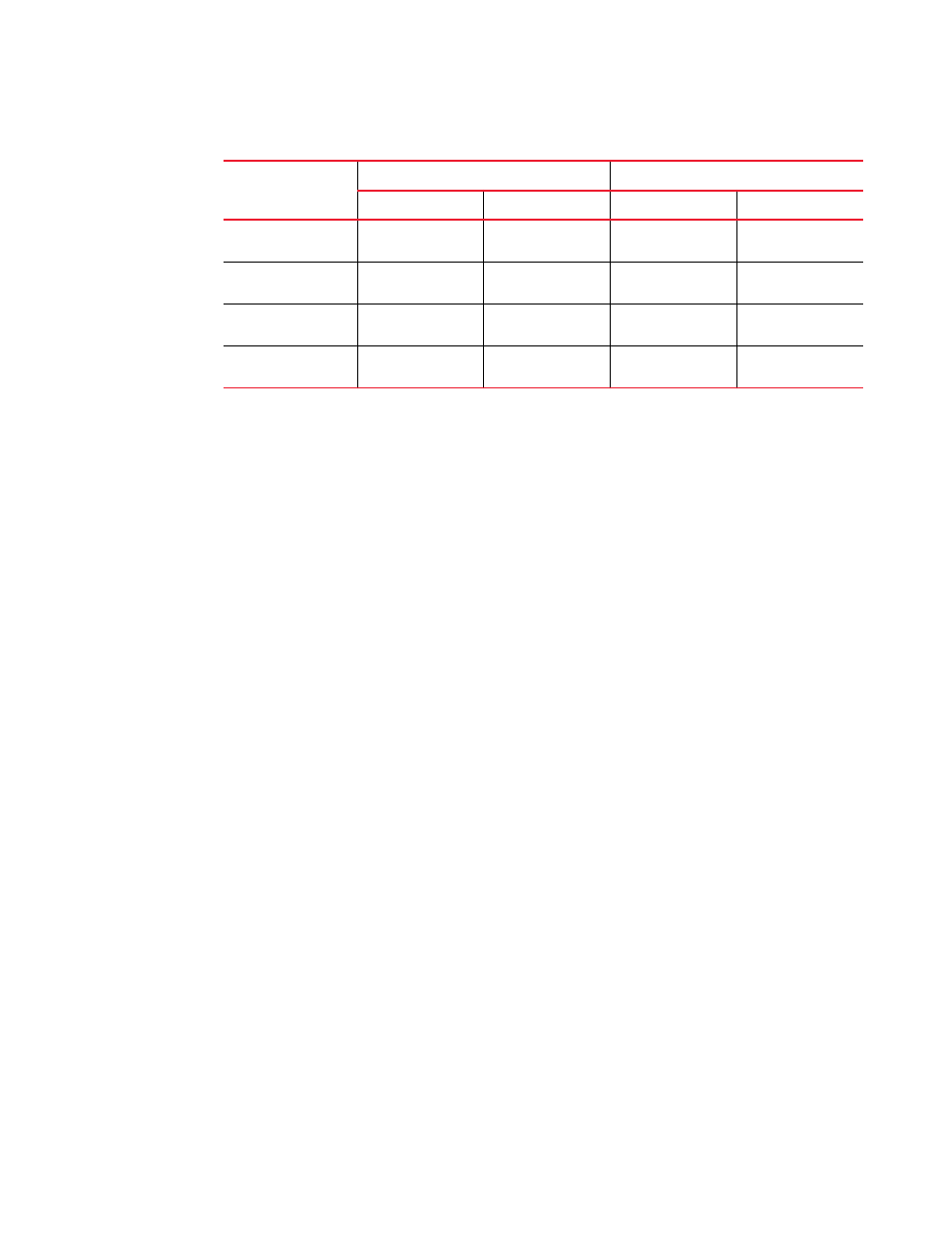
TABLE 75
Expected class of service behavior for Local VPLS
Local VPLS endpoints
Incoming packet
Outgoing packet
Outer VLAN
Inner VLAN
Outer VLAN
Inner VLAN
Dual-tagged to
dual-tagged
X
Y
X’ or X
Y
Single-tagged to
dual-tagged
X
N/A
X’ or X
X
Untagged to
dual-tagged
N/A
N/A
X’ or 0
0
Dual-tagged to
single-tagged
X
Y
X’ or Y
N/A
Multi-Service IronWare Multiprotocol Label Switch (MPLS) Configuration Guide
495
53-1003031-02
Local VPLS
3
Legend for Table 75
X = Original outer VLAN CoS.
Y = Original inner VLAN CoS.
X = Mapped CoS from internal priority (X contributes to internal priority) using CoS encode
table.
Specifying Local VPLS endpoints
Local VPLS can be configured between any combination of dual-tagged, single-tagged, and
untagged endpoints.
The following procedures describe how to configure VPLS endpoints:
•
“Configuring an untagged endpoint”
•
“Configuring a single-tagged endpoint”
•
“Configuring a dual-tagged endpoint”
Configuring an untagged endpoint
To configure untagged port 1/1 into Local VPLS instance “test1”, use the following commands.
Brocade(config)# router mpls
Brocade(config-mpls)# vpls test1 5000
Brocade(config-mpls)# vlan 100
Brocade(config-mpls-vpls-test1)# untagged ethernet 1/1
Syntax: [no] untagged ethernet slot /port / vpls-id
The vpls-id variable is the ID of a VPLS instance.
Configuring a single-tagged endpoint
Tagged ports are configured under a VLAN ID. This VLAN ID is only meaningful for the tagged port.
For tagged ports, a vlan-id, port variable pair constitutes a VPLS endpoint. When a port is currently
a member of a non-default VLAN as an untagged port, it must be returned to the default VLAN
before it can be assigned to a VPLS as a tagged port.
To configure a tagged port 1/2 with VLAN 200 into Local VPLS instance “test1”, use the following
commands.
