Bgp or mpls vpn operation, Creating routes in a bgp or mpls vpn – Brocade Multi-Service IronWare Multiprotocol Label Switch (MPLS) Configuration Guide (Supporting R05.6.00) User Manual
Page 642
618
Multi-Service IronWare Multiprotocol Label Switch (MPLS) Configuration Guide
53-1003031-02
BGP or MPLS VPN operation
6
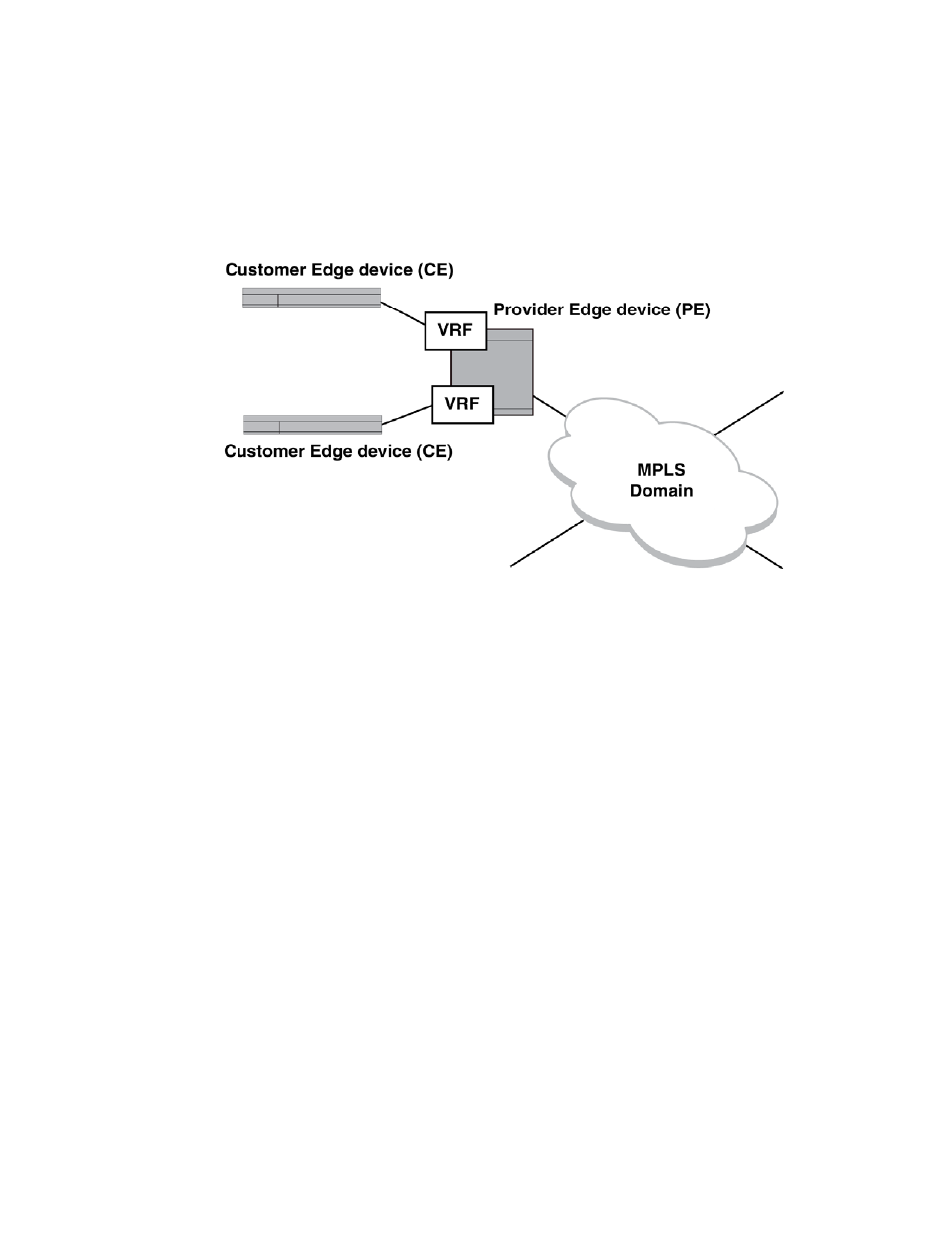
Provider MPLS domain – The Provider MPLS domain is composed of Provider (P) devices. An MPLS
domain can traverse more than one service provider’s MPLS network. The P devices do not store
any VPN information; they just switch traffic from the ingress PE device along the LSP to the egress
PE device.
FIGURE 70
BGP or MPLS VPN components
BGP or MPLS VPN operation
The purpose of a BGP or MPLS VPN is to forward packets between remote sites of a customer’s
network through a service provider’s MPLS infrastructure. The section titled
617 describes the network components required to
perform that task. The following sections describe how those components work together to create
this service:
•
“Creating routes in a BGP or MPLS VPN”
•
“Routing a packet through a BGP or MPLS VPN”
Creating routes in a BGP or MPLS VPN
A CE device maintains the connection to the customer’s network and is configured within that
network to share access to its available network prefixes and to receive packets from other
VPN-connected networks. That CE is connected to a PE through an interface that is configured for a
specified VRF for connection to the BGP or MPLS VPN. This connection places the CE in the BGP or
MPLS VPN. Routes that are available through the CE are then made available to the PE using RIP,
OSPF, EBGP or a static route. These routes are then stored in the VRF where they are associated
with the VPN. The route from the CE to the PE is kept in the CEs routing table.
