Ietf rfc and internet draft support, Bgp or mpls vpns – Brocade Multi-Service IronWare Multiprotocol Label Switch (MPLS) Configuration Guide (Supporting R05.6.00) User Manual
Page 640
616
Multi-Service IronWare Multiprotocol Label Switch (MPLS) Configuration Guide
53-1003031-02
What is a BGP or MPLS VPN
6
common MPLS-domain, multiple Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) can be configured across a
service-provider MPLS core network. Each VPN provides a secure data path that allows IP
packetized traffic to share the infrastructure while being effectively segregated from other VPNs
that are using the same MPLS domain.
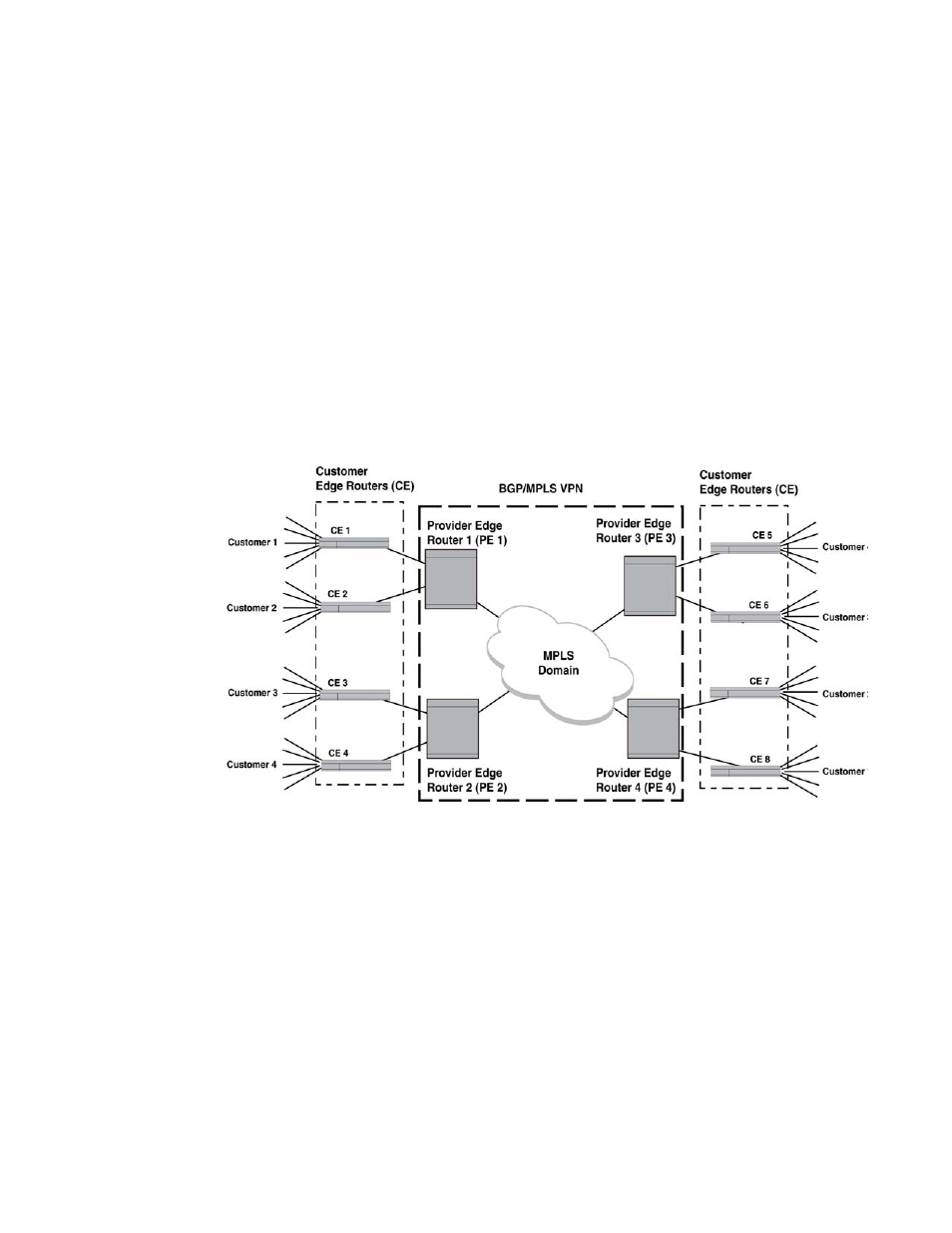
, four separate customers (1-4) each have remote sites. Each customer is connected to
a network at a remote site through the MPLS domain while being completely segregated and
secure from traffic between other sites. For instance, CE 1 and CE 8 belong to Customer 1. CE 1 is
connected to the BGP or MPLS VPN network through PE 1 and CE 8 through PE 4. Using the service
provider’s BGP or MPLS VPN service, traffic can be forwarded between CE1 and CE8 at the same
time that Customers 2 through 4 use VPNs that operate over the same network infrastructure.
Different customers can even use the same IP addresses without conflicting with other customers
networks or creating any routing problems.
FIGURE 69
BGP or MPLS VPN network
IETF RFC and Internet Draft support
The implementation of BGP or MPLS VPNs supports the following IETF RFCs and Internet Drafts:
BGP or MPLS VPNs
RFC 4364: BGP or MPLS IP VPNs
RFC 4577: OSPF as the PE or CE Protocol in BGP or MPLS IP VPNs
RFC 4576: Using LSA Options Bit to Prevent Looping in BGP or MPLS IP VPNs (DN Bit)
