Cspf calculates a traffic-engineered path, Figure – Brocade Multi-Service IronWare Multiprotocol Label Switch (MPLS) Configuration Guide (Supporting R05.6.00) User Manual
Page 34
10
Multi-Service IronWare Multiprotocol Label Switch (MPLS) Configuration Guide
53-1003031-02
Using MPLS in traffic engineering
1
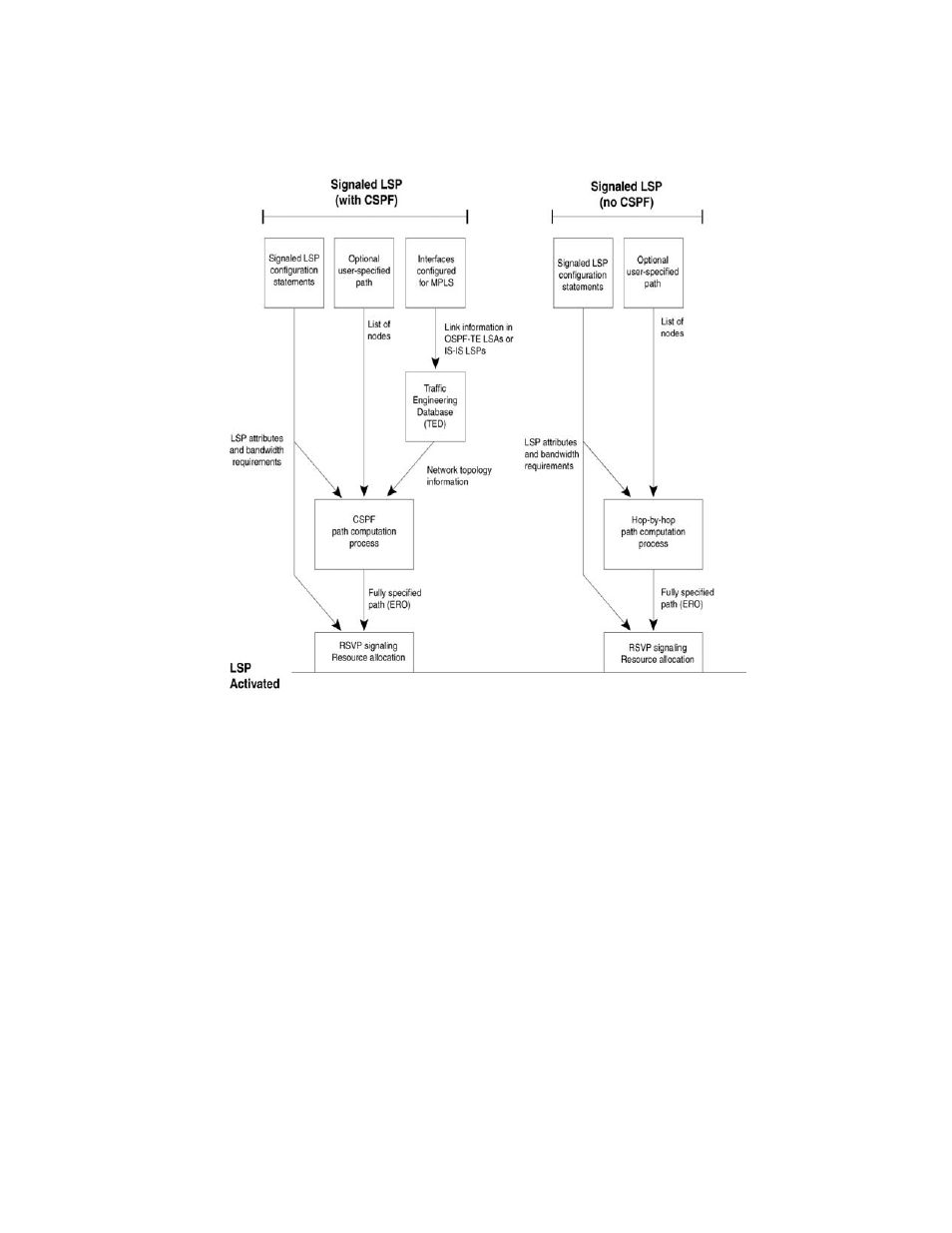
FIGURE 5
How traffic-engineered LSPs are configured, established, and activated
Traffic-engineered, signaled LSPs are configured, established, and activated by the following
processes (but with some differences between OSPF and IS-IS):
CSPF calculates a traffic-engineered path
When the user configures a signaled Label Switched Path, the user specifies the address of the
egress LER, as well as optional attributes, such as the LSPs priority and bandwidth requirements.
The user can optionally specify a path of LSRs that the LSP must pass through on the way to the
egress LER. When the user enables the signaled LSP, the Constrained Shortest Path First (CSPF)
process on the ingress LER uses this information to calculate a traffic-engineered path between
the ingress and egress LERs.
CSPF is an advanced form of the Shortest Path First (SPF) process used by IGP routing protocols.
The CSPF process on the ingress LER uses the configured attributes of the LSP, user-specified path
(when there is one), and the information in the Traffic Engineering Database (TED) to calculate the
traffic-engineered path. This process consists of a sequential list of the physical interfaces that
packets assigned to this LSP pass through to travel from the ingress LER to the egress LER. The
traffic-engineered path takes into account the network topology, available resources, and
user-specified constraints. The traffic-engineered path calculated by CSPF may or may not be the
same as the shortest path that would normally be calculated by standard IGP routing protocols.
