Rockwell Automation GMLC Reference Manual User Manual
Page 543
Publication GMLC-5.2 - November 1999
506
Fault Variables
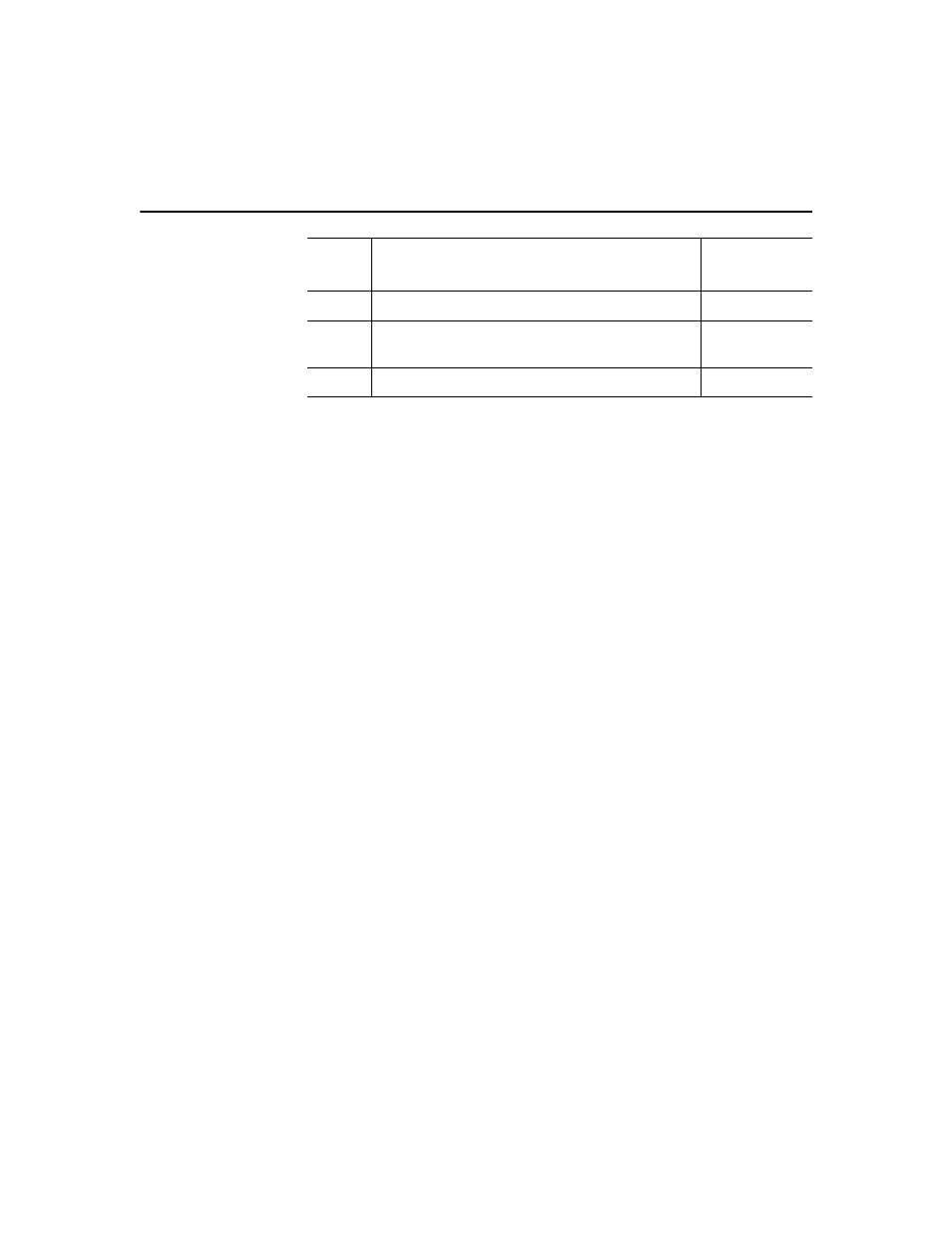
Global faults are prioritized from highest to lowest, in the order shown in
the table above. When multiple faults are active, the Global_fault value
represents the highest priority fault. For instance, if a hardware overtravel
fault is active for an axis, and a software travel limits exceeded condition
is also active on another axis, Global_fault has a value of 3. When the
highest priority fault is cleared, Global_fault has the value of the next
highest priority fault.
You use an End Program block, with both When End or Fault and Go to
When End if Global Fault Occurs selected, to intercept global faults that
occur when the application program is running. The When End or Fault
sequence should evaluate the Global_fault variable, correct the problem,
reset the specific fault variable to zero to clear the fault, and restart the
program or the tasks as required.
CNET Fault
CNET_fault is a logical (Boolean) variable, which has a value of:
•
1 (true) if a CNET error has occurred, and
•
0 (false) if not.
When CNET_fault = 1, Global_fault = 16.
Refer to the CNET_fault_code variable later in this chapter for a
description of the particular fault that occurred.
Refer to online help for the particular CNET_fault_code value for help in
diagnosing and clearing the fault.
This variable applies only to 1394 Turbo controllers.
2
Software_Overtravel_Fault on any axis
SFT LIM
1
Encoder_Loss_Fault or
Encoder_Noise_Fault on any axis
ENC FLT
0
No Faults
AXES OK
Fault
Value
Description
Runtime
Display
