Working mechanism of link load balancing, Outbound link load balancing – H3C Technologies H3C SecPath F1000-E User Manual
Page 872
7
Figure 7 Network diagram for combination of firewall and server load balancing
Host
IP network
LB device B
Server A
IP A
Server B
IP B
Server C
IP C
Cluster A
VSIP
LB device A
Firewall A
Firewall B
Cluster B
Cluster A adopts firewall load balancing, and Cluster B adopts NAT-mode server load balancing. The
combination of these two modes is to combine the work flows of them. This networking mode not only
prevents firewalls from being the bottleneck in the network, but also enhances the performance and
availability of multiple network services such as HTTP and FTP.
Working Mechanism of Link Load Balancing
Link load balancing falls into outbound link load balancing and inbound link load balancing:
•
Outbound link load balancing is used to help intranet users select the best path to access the
external resources through an LB device according to the destination IP address of packets and
outbound link load balancing configurations.
•
Inbound link load balancing is used to help extranet users select the best path for accessing an LB
device according to the domain name of DNS requests and inbound link load balancing
configurations. Inbound link load balancing can be used in combination of server load balancing.
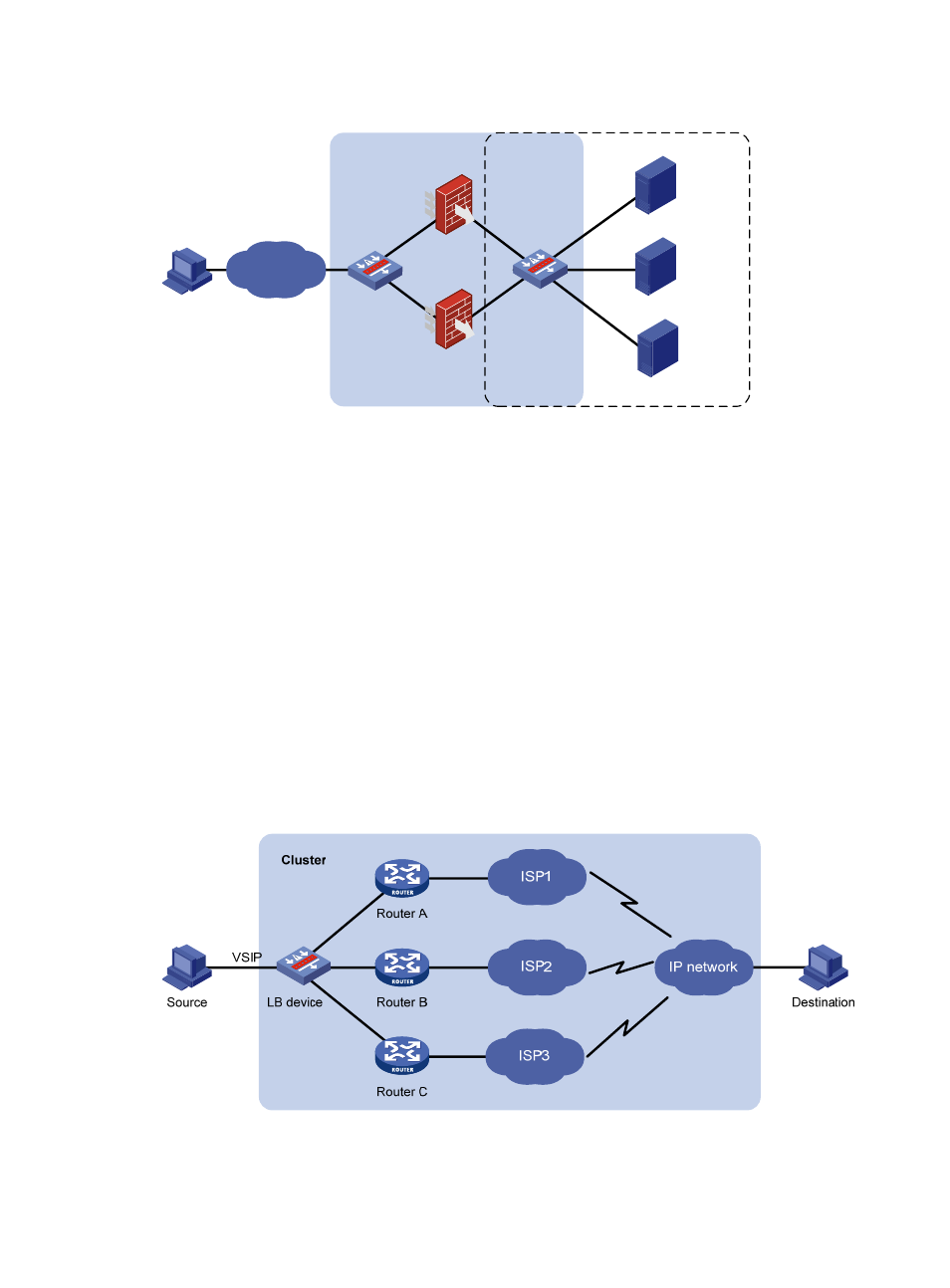
Outbound link load balancing
Figure 8 Network diagram for outbound link load balancing
Outbound link load balancing includes the following basic elements:
