Neighbor discovery, Dr election, Construction of spt – H3C Technologies H3C SecPath F1000-E User Manual
Page 379
11
Compared with the ASM model, the SSM model only needs the support of IGMPv3 and some subsets of
PIM-SM. The operation mechanism of PIM-SSM can be summarized as follows:
•
Neighbor discovery
•
DR election
•
SPT building
Neighbor discovery
PIM-SSM uses the same neighbor discovery mechanism as in PIM-DM and PIM-SM. For more information,
see
DR election
PIM-SSM uses the same DR election mechanism as in PIM-SM. For more information, see
.
Construction of SPT
Whether to build an RPT for PIM-SM or an SPT for PIM-SSM depends on whether the multicast group the
receiver is to join falls in the SSM group range (SSM group range reserved by IANA is 232.0.0.0/8).
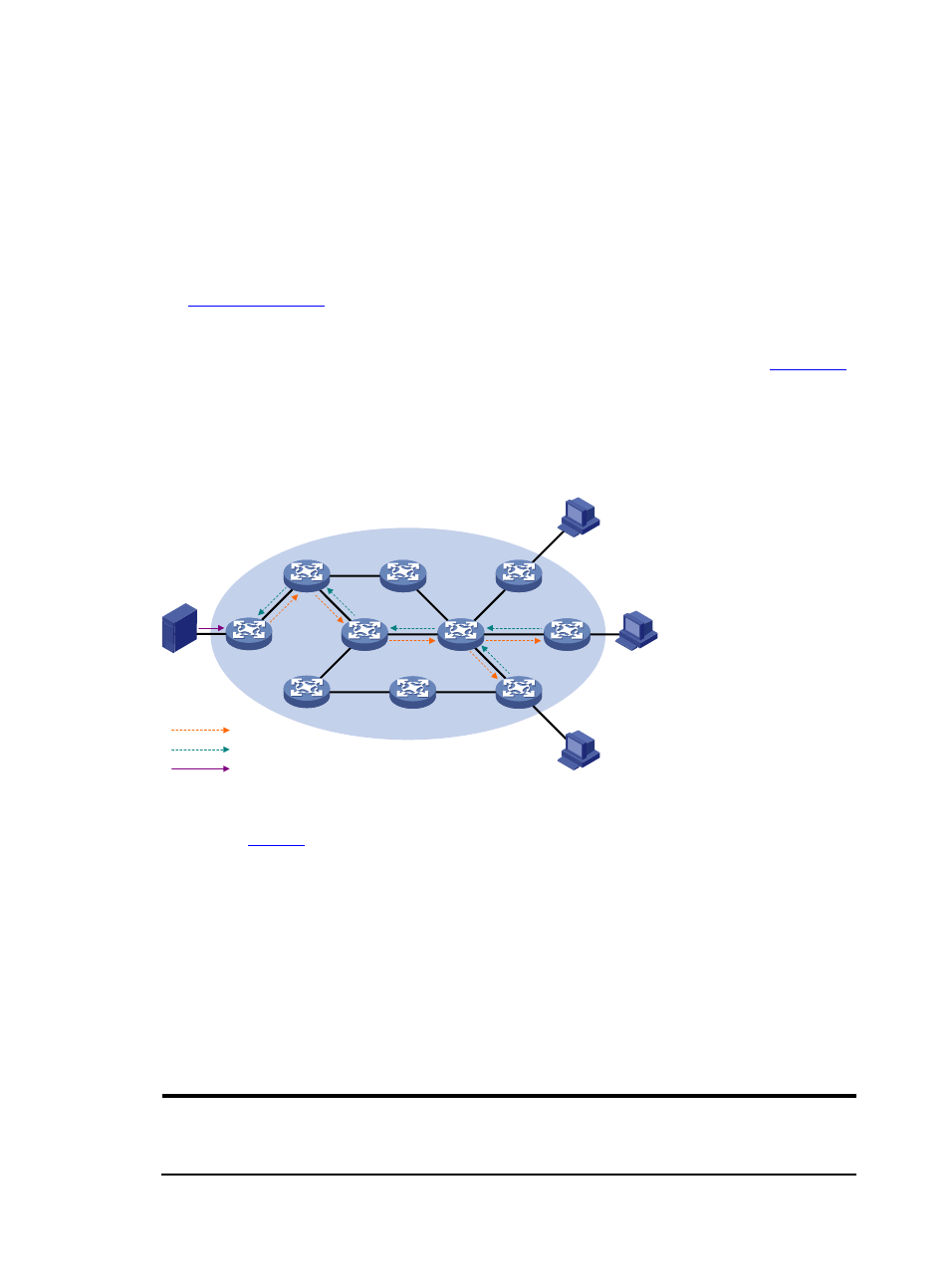
Figure 7 SPT establishment in PIM-SSM
Source
Server
Host A
Host B
Host C
Receiver
Receiver
Multicast packets
SPT
Subscribe message
RP
DR
DR
As shown in
, Host B and Host C are multicast information receivers. They send IGMPv3 report
messages to the respective DRs to express their interest in the information of the specific multicast source
S.
Upon receiving a report message, the DR first checks whether the group address in this message falls in
the SSM group range:
•
If so, the DR sends a subscribe message for channel subscription hop by hop toward the multicast
source S. An (S, G) entry is created on all routers on the path from the DR to the source. Thus, an SPT
is built in the network, with the source S as its root and receivers as its leaves. This SPT is the
transmission channel in PIM-SSM.
•
If not, the PIM-SM process is followed: the DR needs to send a (*, G) join message to the RP, and
a multicast source registration process is needed.
NOTE:
In PIM-SSM, the “channel” concept is used to refer to a multicast group, and the “channel
subscription” concept is used to refer to a join message.
