How tcp proxy works, Unidirectional proxy, Bidirectional proxy – H3C Technologies H3C SecPath F1000-E User Manual
Page 644
2
As shown in
, all packets between the TCP client and TCP server go through the TCP proxy, and
thus you can configure unidirectional proxy or bidirectional proxy as desired.
Figure 2 Network diagram for unidirectional/bidirectional proxy
How TCP Proxy Works
Unidirectional proxy
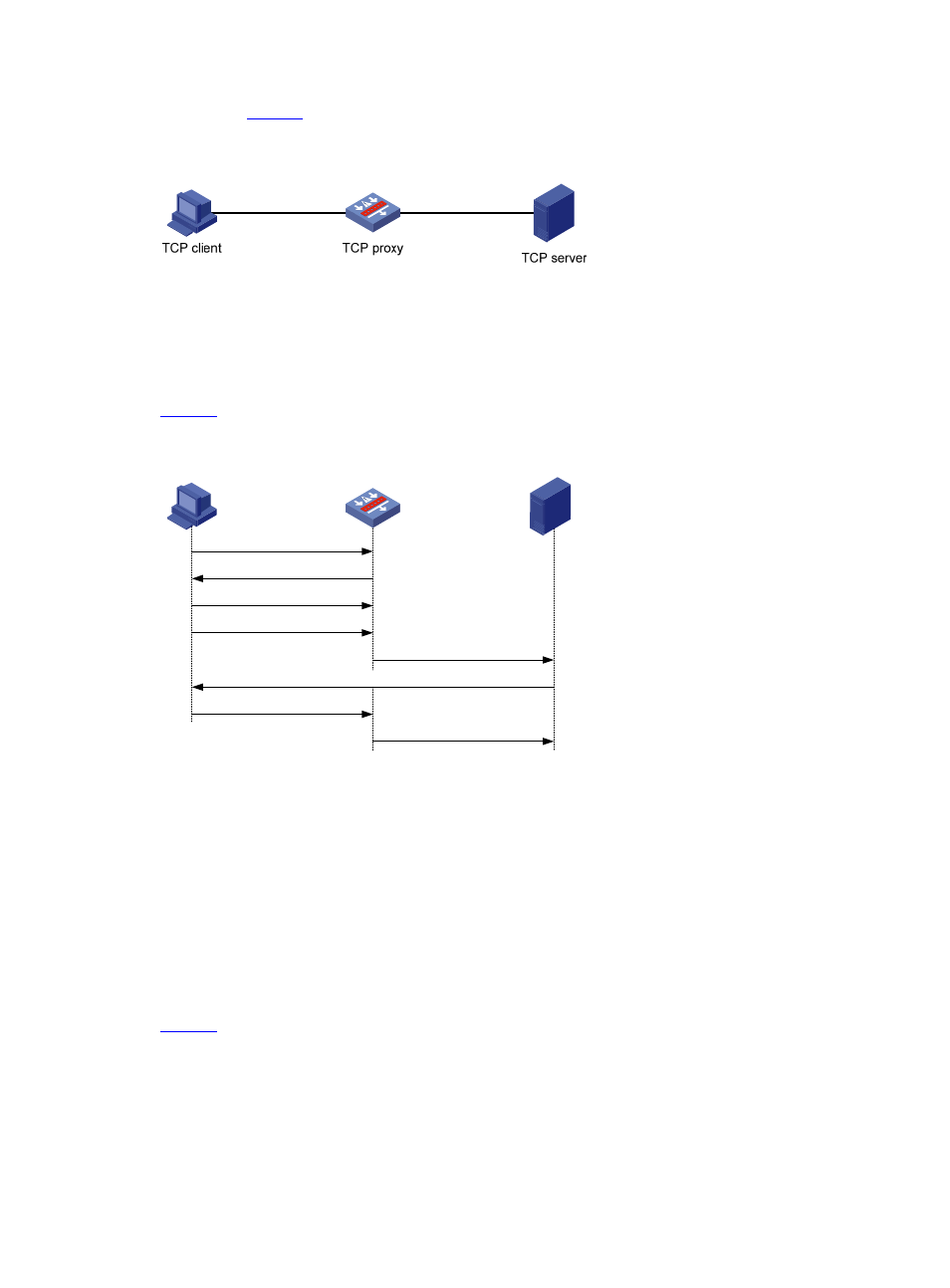
shows the data exchange process of unidirectional proxy.
Figure 3 Data exchange process of unidirectional proxy
TCP client
TCP proxy
TCP server
1) SYN
2) SYN ACK (invalid sequence
number)
3) RST
4) SYN (retransmitting)
5) SYN (forwarding)
6) SYN ACK
7) ACK
8) ACK (forwarding)
After receiving a SYN message from a client to the protected server (such a message matches a protected
IP address entry), the TCP proxy sends back a SYN ACK message with a wrong sequence number on
behalf of the server, that is, using the IP address and port number of the server. If the client is legitimate,
the TCP proxy will receive an RST message, and will receive a SYN message again from the client. The
TCP proxy then directly forwards the SYN, SYN ACK, and ACK messages to establish a TCP connection
between the client and the server.
After the TCP connection is established, the TCP proxy forwards the subsequent packets of the connection
without additional processing.
Bidirectional proxy
shows the data exchange process of bidirectional proxy.
