Aspf configuration, Aspf policy overview, Configuring aspf – H3C Technologies H3C SecPath F1000-E User Manual
Page 584
1
ASPF Configuration
ASPF Policy Overview
Application Specific Packet Filter (ASPF) applications are based on zone management and session
management. Zone management is an independent common module. It does not concern service
packet processing; it only maintains information relevant to zones and provides policy interfaces for
other modules. The session management module simplifies the design of function modules such as
Network Address Translation (NAT), ASPF, Application Level Gateway (ALG), attack defense, and
connection number limit modules. It is responsible for processing kinds of session information, aging
sessions based on session states, and providing the uniform interfaces for the function modules.
ASPF policies are configured between zones. When used for packet processing, they use information
provided by the session management module, such as whether the connection status is correct, whether
a packet is an initial one, and whether a packet is an ICMP error packet. Based on information
provided by the session management module and ASPF policies, ASPF applications determine which
packets are allowed to pass.
ASPF is often used to cooperate with the static packet filter function. In some cases, ASPF cannot
determine whether packets are allowed to pass, and it is the static packet filter function that makes the
decision. For example, whether broadcast packets are allowed to pass is determined by the static
packet filter function based on ACLs or default inter-zone priorities.
Configuring ASPF
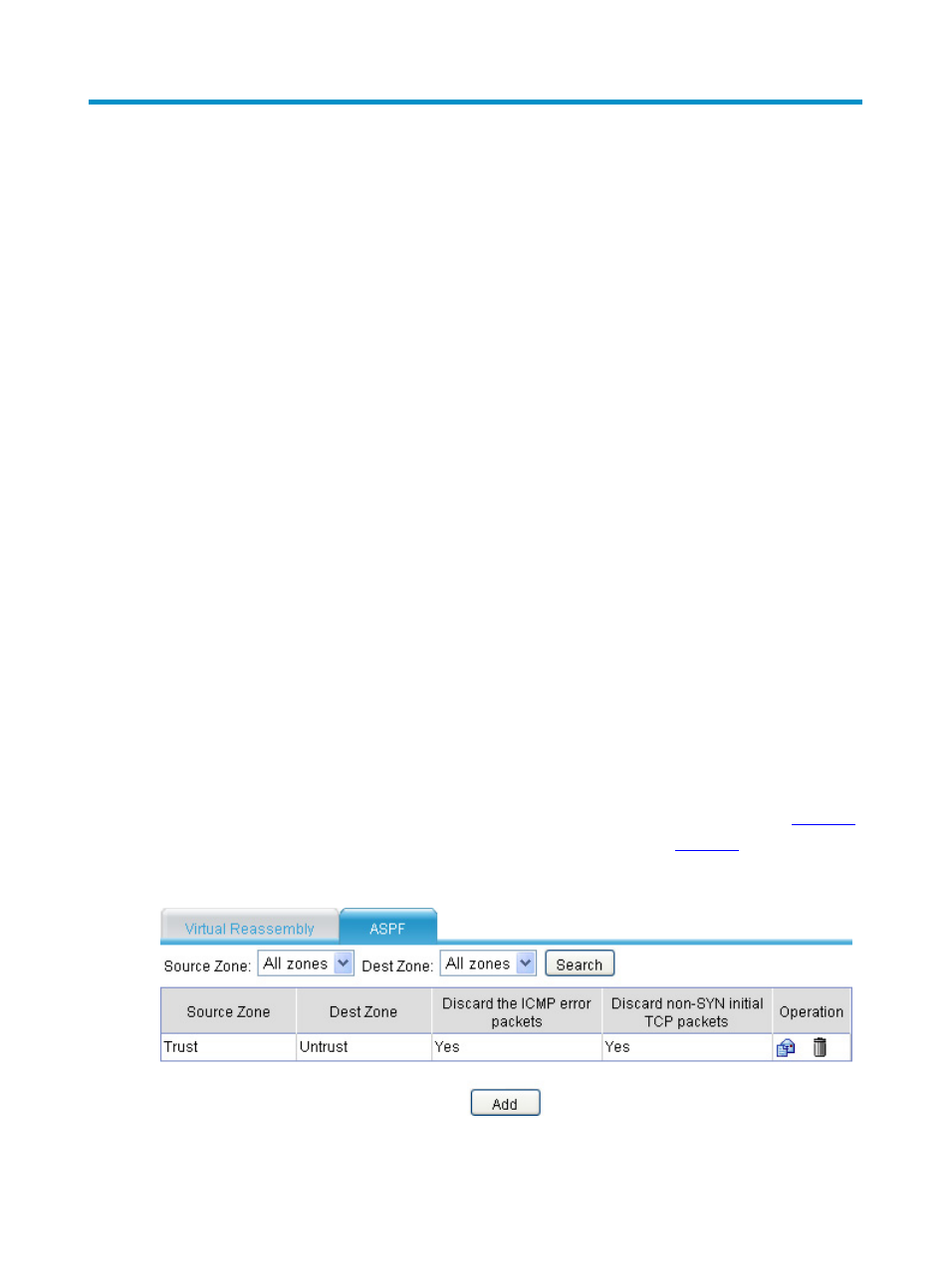
After logging in to the Web interface, select Firewall > Session Table > Advanced from the
navigation tree, and then click the ASPF tab to enter the ASPF policy list page, as shown in
.
Then, click Add to enter the page for adding an ASPF policy, as shown in
.
Figure 13 ASPF policy list
