Route types, Ospf network types – H3C Technologies H3C SecPath F1000-E User Manual
Page 302
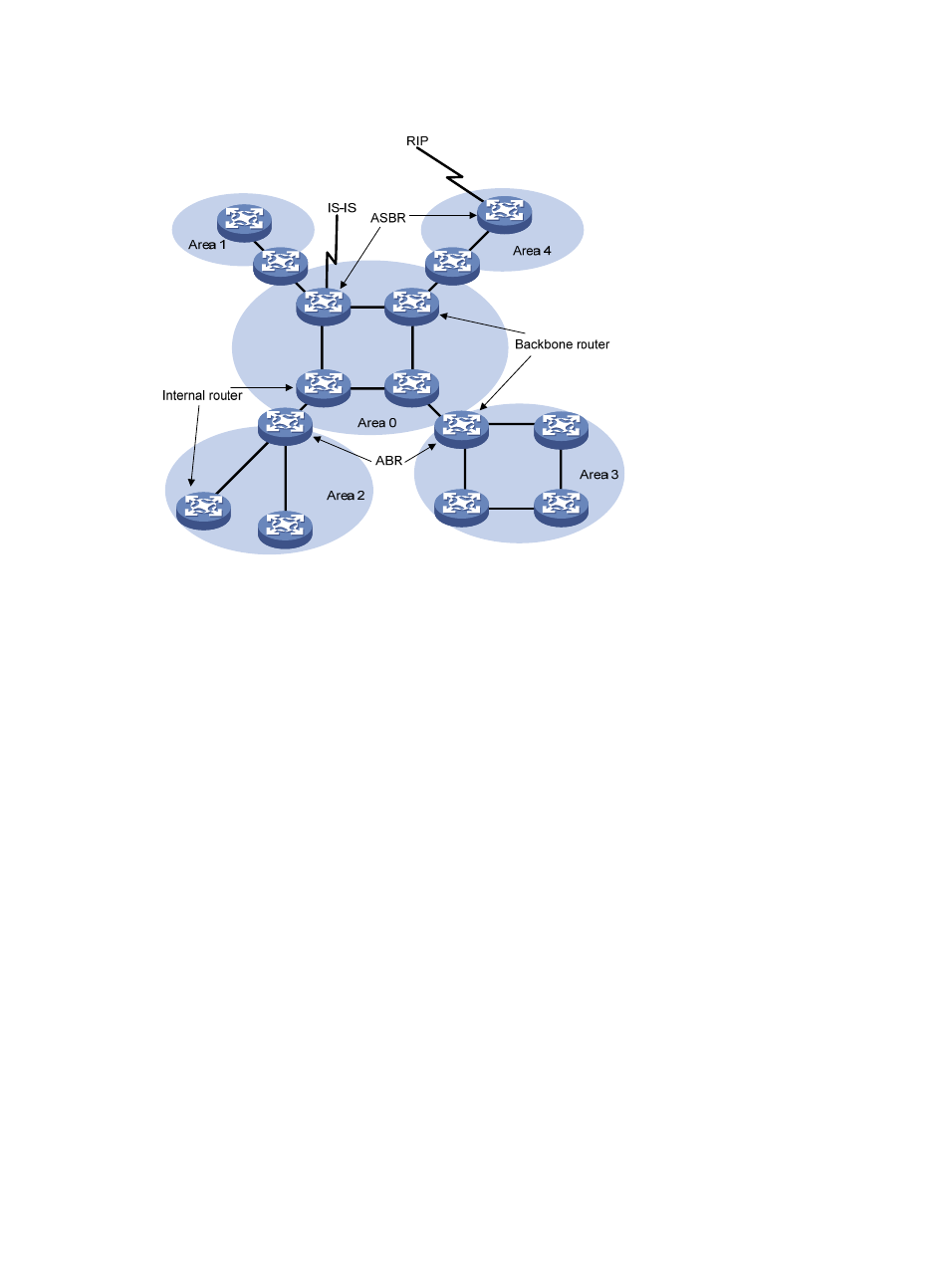
7
Figure 5 OSPF router types
Route types
OSPF prioritize routes into four levels:
•
Intra-area route
•
Inter-area route
•
Type-1 external route
•
Type-2 external route
The intra-area and inter-area routes describe the network topology of the AS, while external routes
describe routes to destinations outside the AS.
OSPF classifies external routes into two types: Type-1 and Type-2. A Type-1 external route is an IGP route,
such as a RIP or static route, which has high credibility and whose cost is comparable with the cost of an
OSPF internal route. The cost from a router to the destination of the Type-1 external route= the cost from
the router to the corresponding ASBR+ the cost from the ASBR to the destination of the external route.
A Type-2 external route is an EGP route, which has low credibility, so OSPF considers the cost from the
ASBR to the destination of the Type-2 external route is much greater than the cost from the ASBR to an
OSPF internal router. Therefore, the cost from the internal router to the destination of the Type-2 external
route= the cost from the ASBR to the destination of the Type-2 external route. If two routes to the same
destination have the same cost, then take the cost from the router to the ASBR into consideration.
OSPF Network Types
OSPF classifies networks into four types upon the link layer protocol:
•
Broadcast: When the link layer protocol is Ethernet or FDDI, OSPF considers the network type
broadcast by default. On Broadcast networks, hello packets, LSU packets, and LSAck packets are
