Napt, Easy ip, Internal server – H3C Technologies H3C SecPath F1000-E User Manual
Page 444
3
NAPT
Network Address Port Translation (NAPT) is a variation of NAT. It allows multiple internal addresses to
be mapped to the same public IP address, which is called multiple-to-one NAT or address multiplexing.
NAPT mapping is based on both the IP address and the port number. With NAPT, packets from multiple
internal hosts are mapped to the same external IP address with different port numbers.
depicts NAPT operation.
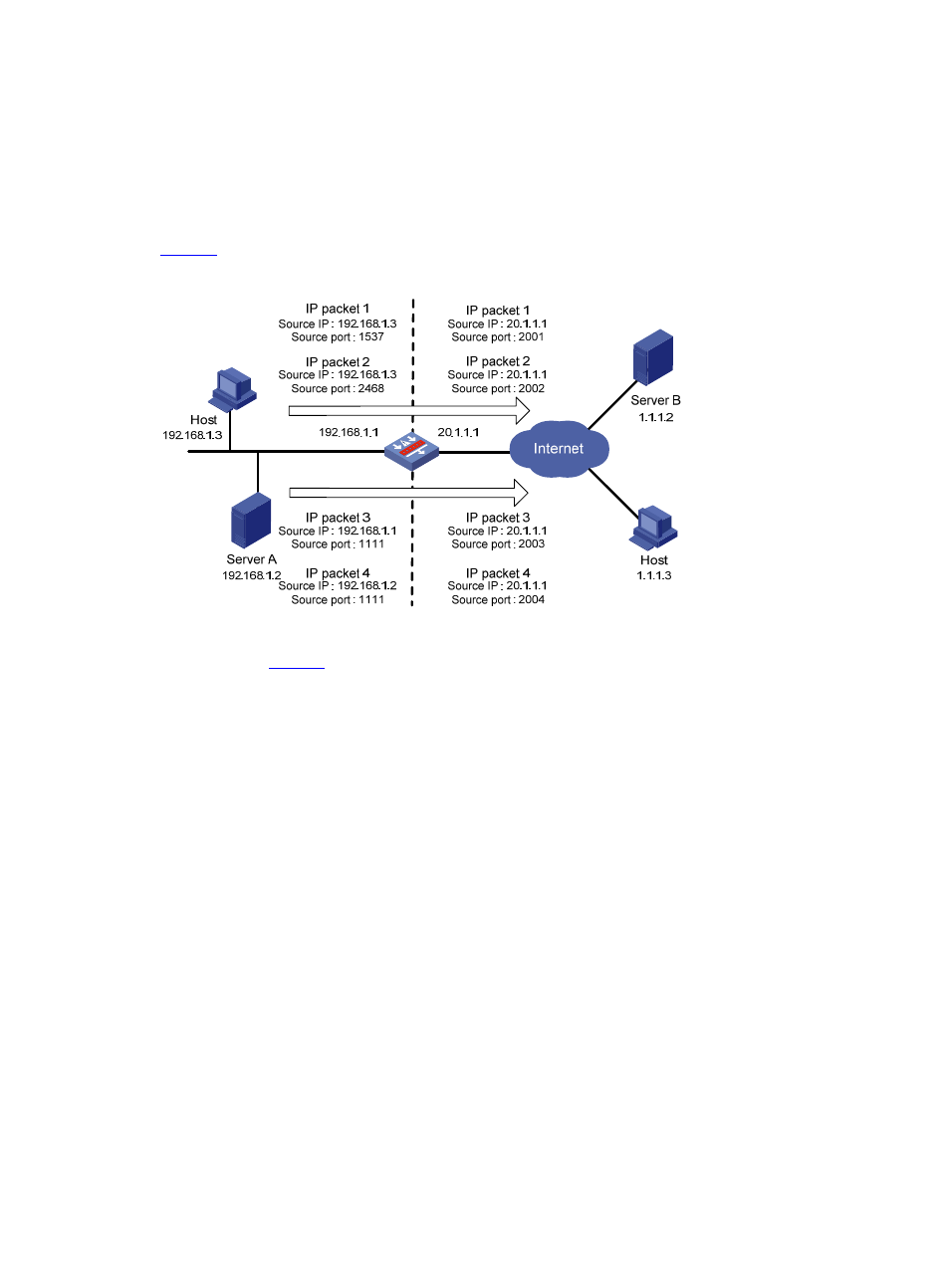
Figure 2 Diagram for NAPT operation
, four IP packets arrive at the NAT gateway. Packets 1 and 2 are from the same
internal address but have different source port numbers. Packets 3 and 4 are from different internal
addresses but have the same source port number. NAPT maps their source IP addresses to the same
external address but with different source port numbers. Therefore, the packets can still be discriminated.
When response packets arrive, the NAT gateway can forward them to corresponding hosts based on
the destination addresses and port numbers.
NAPT can better utilize IP address resources, enabling more internal hosts to access the external
network at the same time.
Easy IP
Easy IP uses the public IP address of an interface on the device as the translated source address to save
IP address resources, and uses ACLs to permit only certain internal IP addresses to be NATed.
Internal server
NAT hides the internal network structure as well as the identities of internal hosts. However, internal
hosts such as a Web server or an FTP server may need to be accessed by external hosts in practice.
NAT satisfies this requirement by supporting internal servers.
With NAT, you can deploy an internal server easily and flexibly. For instance, you can use 20.1.1.10 as
the Web server’s external address and 20.1.1.11 as the FTP server’s external address. You can even use
an address like 20.1.1.12:8080 as the Web server’s external address.
With an internal server configured, the NAT device, when receiving a packet to the server, translates the
destination address of the packet to the internal IP address of the internal server. When a response
packet from the internal server arrives, the NAT device translates the private source address of the
packet into the public IP address.
