Backbone area and virtual links – H3C Technologies H3C SecPath F1000-E User Manual
Page 299
4
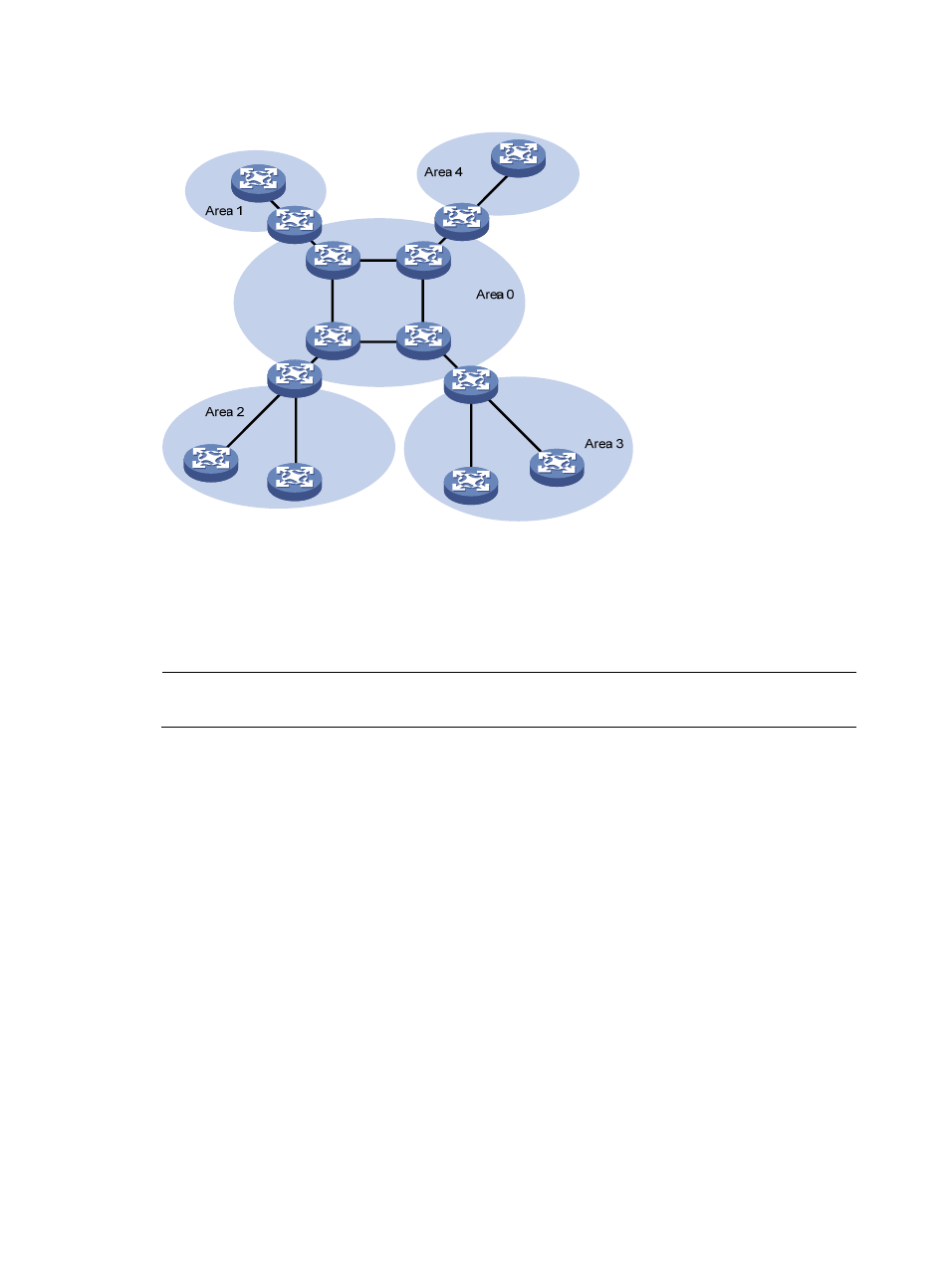
Figure 1 OSPF area partition
After area partition, area border routers perform route summarization to reduce the number of LSAs
advertised to other areas and minimize the effect of topology changes.
Backbone area and virtual links
NOTE:
Currently, vitual link configuration is not supported on the web interface.
Each AS has a backbone area, which is responsible for distributing routing information between
none-backbone areas. Routing information between non-backbone areas must be forwarded by the
backbone area. Therefore, OSPF requires that:
•
All non-backbone areas must maintain connectivity to the backbone area.
•
The backbone area itself must maintain connectivity.
In practice, due to physical limitations, the requirements may not be satisfied. In this case, configuring
OSPF virtual links is a solution.
A virtual link is established between two area border routers via a non-backbone area and is configured
on both ABRs to take effect. The area that provides the non-backbone area internal route for the virtual
link is a “transit area”.
In the following figure, Area 2 has no direct physical link to the backbone area 0. Configuring a virtual
link between ABRs can connect Area 2 to the backbone area.
