Congestion management, Causes, impacts, and countermeasures of congestion – H3C Technologies H3C SecPath F1000-E User Manual
Page 511
3
NOTE:
Traffic policing supports policing traffic in both inbound and outbound directions. Thereafter, the
outbound direction is taken for example.
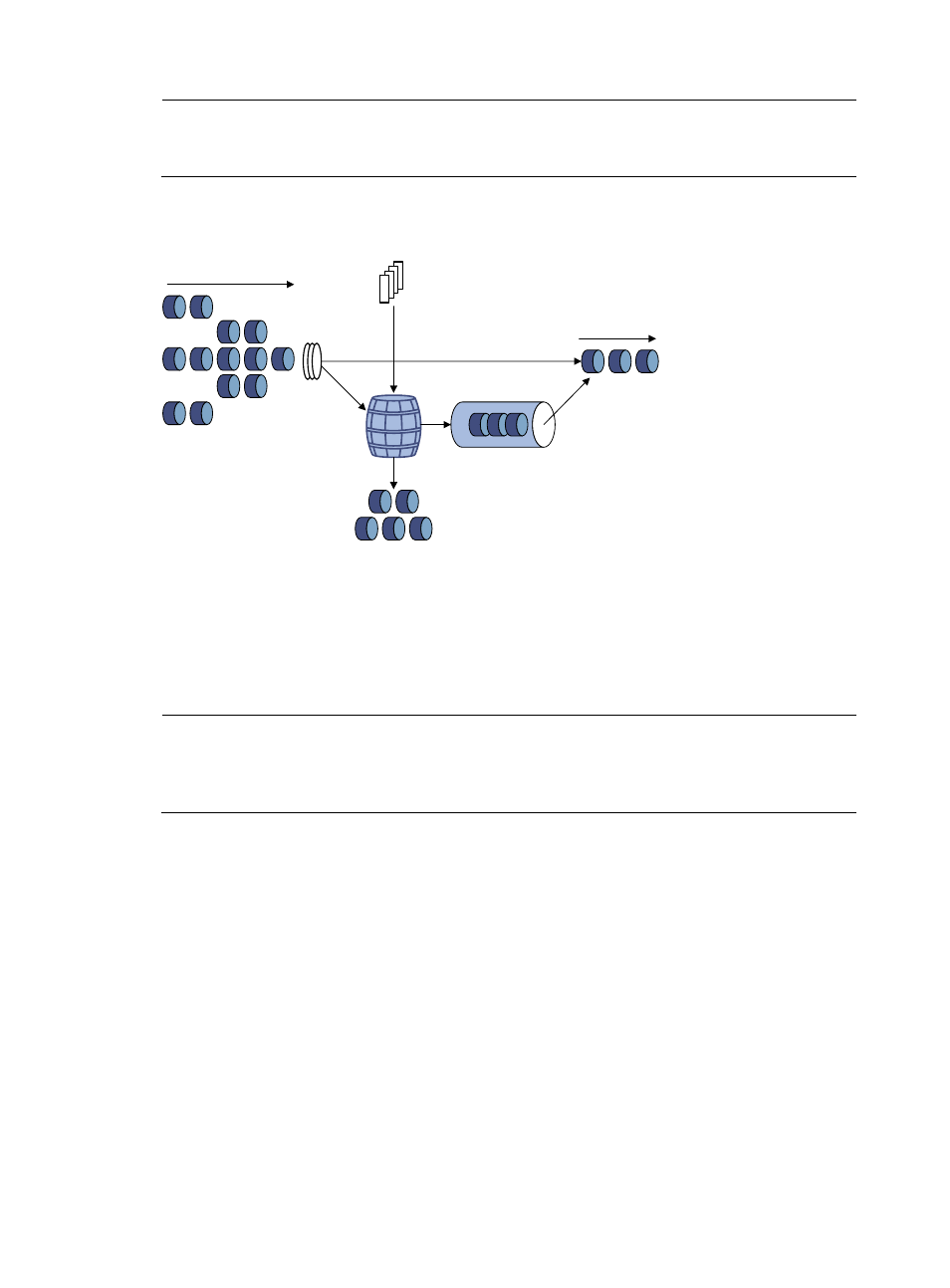
Figure 1 Schematic diagram for traffic policing
Token
bucket
Packets dropped
Packet
classification
Packets to be sent
through this interface
Packets sent
Tokens are put into the
bucket at the set rate
Queue
Traffic policing is widely used in policing traffic entering the networks of internet service providers (ISPs).
It can classify the policed traffic and perform pre-defined policing actions specific to evaluation results.
These actions include:
•
Forwarding the packets if the evaluation result is “conforming.”
•
Dropping the packets if the evaluation result is “excess.”
NOTE:
Traffic policing can be configured in the policy-based approach or CAR list-based approach. This chapter
introduces only how to configure traffic policing in the policy-based approach. For how to configure traffic
policing in the CAR list-based approach, see
Traffic Policing Configuration.
Congestion Management
Causes, impacts, and countermeasures of congestion
Congestion occurs on a link or node when traffic size is so large that the processing capability of the link
or node is exceeded. It is typical of a statistical multiplexing network and can be caused by link failure,
insufficient resources, and various other causes. The following figure shows two common congestion
scenarios:
