Gre applications – H3C Technologies H3C SecPath F1000-E User Manual
Page 739
3
•
If the Key Present field of a GRE packet header is set to 1, the Key field will carry the key for the
receiver to authenticate the source of the packet. This key must be the same at both ends of a tunnel.
Otherwise, packets delivered over the tunnel will be discarded.
•
If the Checksum Present bit of a GRE packet header is set to 1, the Checksum field contains valid
information. The sender calculates the checksum for the GRE header and the payload and sends
the packet containing the checksum to the peer. The receiver calculates the checksum for the
received packet and compares it with that carried in the packet. If the checksums are the same, the
receiver considers the packet intact and continues to process the packet. Otherwise, the receiver
discards the packet.
GRE Applications
GRE supports these types of applications:
•
Communication Between local networks through a single-protocol backbone
•
Scope enlargement of a hop-limited protocol such as RIP
•
VPN establishment by connecting discontinuous subnets
•
Communication Between local networks through a single-protocol backbone
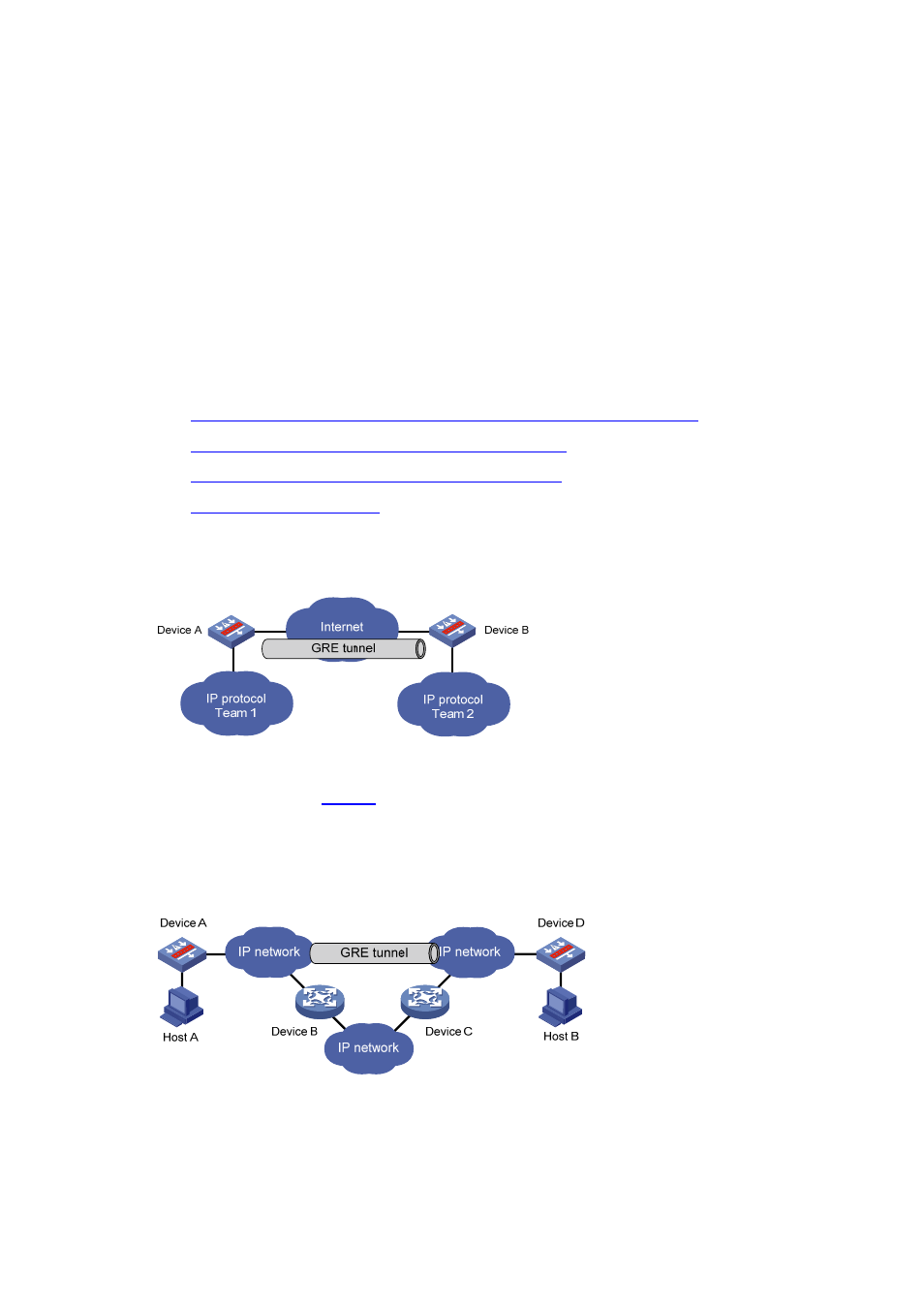
Figure 4 Communication between local networks through a single-protocol backbone
In the example shown in
, Team 1 and Team 2 are local networks running IP. Through the GRE
tunnel between Device A and Device, Team 1 can communicate with Team 2.
Scope enlargement of a hop-limited protocol such as RIP
Figure 5 Network scope enlargement
When the hop count between two terminals exceeds 15, the terminals cannot communicate with each
other. Using GRE, you can hide some hops so as to enlarge the scope of the network.
