Types of vlan – H3C Technologies H3C SecPath F1000-E User Manual
Page 392
2
The format of VLAN-tagged frames is defined in IEEE 802.1Q issued by Institute of Electrical and
Electronics Engineers (IEEE) in 1999.
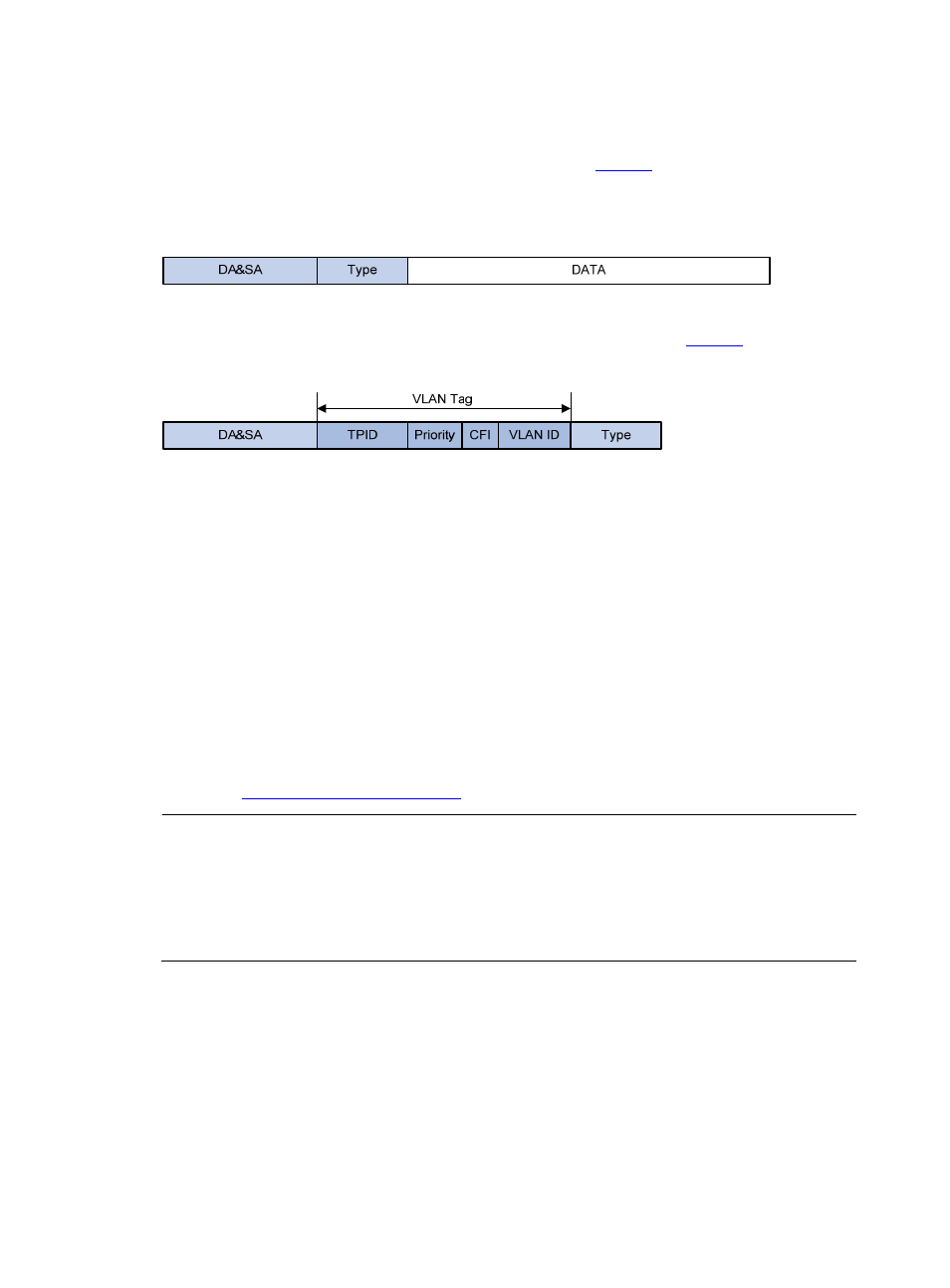
In the header of a traditional Ethernet data frame as shown in
, the field after the destination
MAC address and the source MAC address fields (DA&SA in the figure) is the Type field indicating the
upper layer protocol type.
Figure 2 The format of a traditional Ethernet frame
IEEE 802.1Q inserts a four-byte VLAN tag before the Type field, as shown in
.
Figure 3 The position and format of VLAN tag
A VLAN tag comprises four fields: tag protocol identifier (TPID), priority, canonical format indicator (CFI),
and VLAN ID.
•
The 16-bit TPID field with a value of 0x8100 indicates that the frame is VLAN tagged.
•
The 3-bit priority field indicates the 802.1p priority of the frame.
•
The 1-bit CFI field specifies whether the MAC addresses are encapsulated in the canonical format
for the receiving device to correctly interpret the MAC addresses. Value 0 indicates that the MAC
addresses are encapsulated in canonical format; value 1 indicates that the MAC addresses are
encapsulated in non-canonical format. The field is set to 0 by default.
•
The 12-bit VLAN ID field identifies the VLAN the frame belongs to. The VLAN ID range is 0 to 4095.
As 0 and 4095 are reserved by the protocol, the VLAN ID range available for assignment is 1 to
4094.
When receiving a frame, a network device looks at its VLAN tag to decide how to handle the frame. For
details, see
Introduction to Port-Based VLAN
.
NOTE:
•
The Ethernet II encapsulation format is used in this section. Besides this format, other encapsulation
formats, including 802.2 LLC, 802.2 SNAP, and 802.3 raw, are also supported by Ethernet. The VLAN
tag fields are also used in these encapsulations for VLAN identification.
•
For a frame with multiple VLAN tags, the device handles it according to its outer-most VLAN tag and
transmits its inner VLAN tags as payload.
Types of VLAN
You can create VLANs based on:
•
Port
•
MAC address
•
Protocol
•
IP subnet
