Root port, Designated bridge and designated port, Path cost – H3C Technologies H3C SecPath F1000-E User Manual
Page 195
2
Root port
On a non-root bridge, the port nearest to the root bridge is called the root port. The root port is
responsible for communication with the root bridge. Each non-root bridge has one and only one root port.
The root bridge has no root port.
Designated bridge and designated port
The following table describes designated bridges and designated ports.
Table 1 Description of designated bridges and designated ports:
Classification
Designated bridge
Designated port
For a device
A device directly connected with the local
device and responsible for forwarding
BPDUs to the local device
The port through which the designated
bridge forwards BPDUs to the local
device
For a LAN
The device responsible for forwarding
BPDUs to this LAN segment
The port through which the designated
bridge forwards BPDUs to this LAN
segment
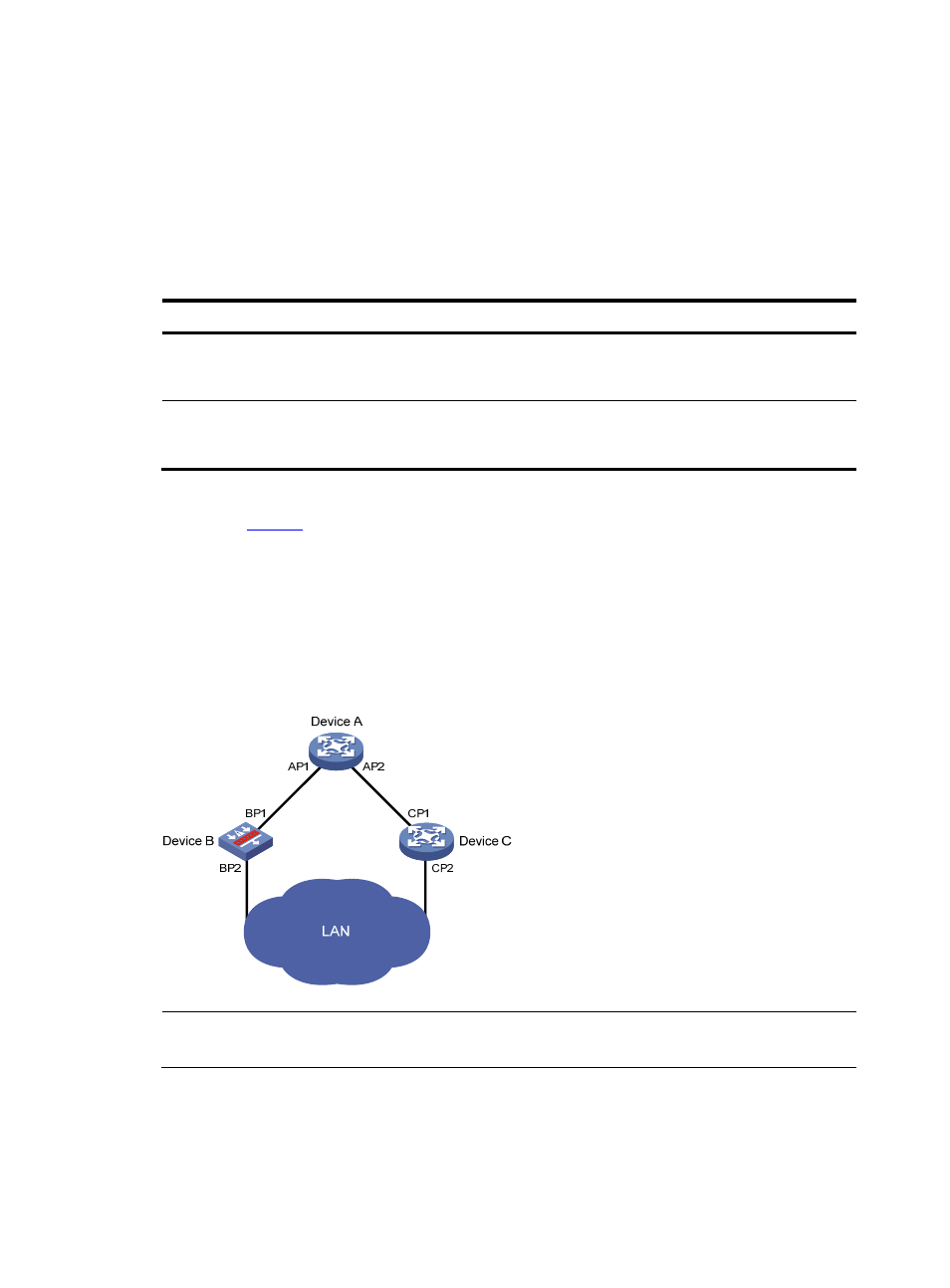
As shown in
, AP1 and AP2, BP1 and BP2, and CP1 and CP2 are ports on Device A, Device B,
and Device C respectively.
•
If Device A forwards BPDUs to Device B through AP1, the designated bridge for Device B is Device
A, and the designated port of Device B is port AP1 on Device A.
•
Two devices are connected to the LAN: Device B and Device C. If Device B forwards BPDUs to the
LAN, the designated bridge for the LAN is Device B, and the designated port for the LAN is the port
BP2 on Device B.
Figure 1 A schematic diagram of designated bridges and designated ports
NOTE:
All the ports on the root bridge are designated ports.
Path cost
Path cost is a reference value used for link selection in STP. By calculating path costs, STP selects relatively
robust links and blocks redundant links, and finally prunes the network into a loop-free tree.
