Ca policy, Architecture of pki, Entity – H3C Technologies H3C SecPath F1000-E User Manual
Page 776
2
CA policy
A CA policy is a set of criteria that a CA follows in processing certificate requests, issuing and revoking
certificates, and publishing CRLs. Usually, a CA advertises its policy in the form of certification practice
statement (CPS). A CA policy can be acquired through out-of-band means such as phone, disk, and
e-mail. As different CAs may use different methods to check the binding of a public key with an entity,
make sure that you understand the CA policy before selecting a trusted CA for certificate request.
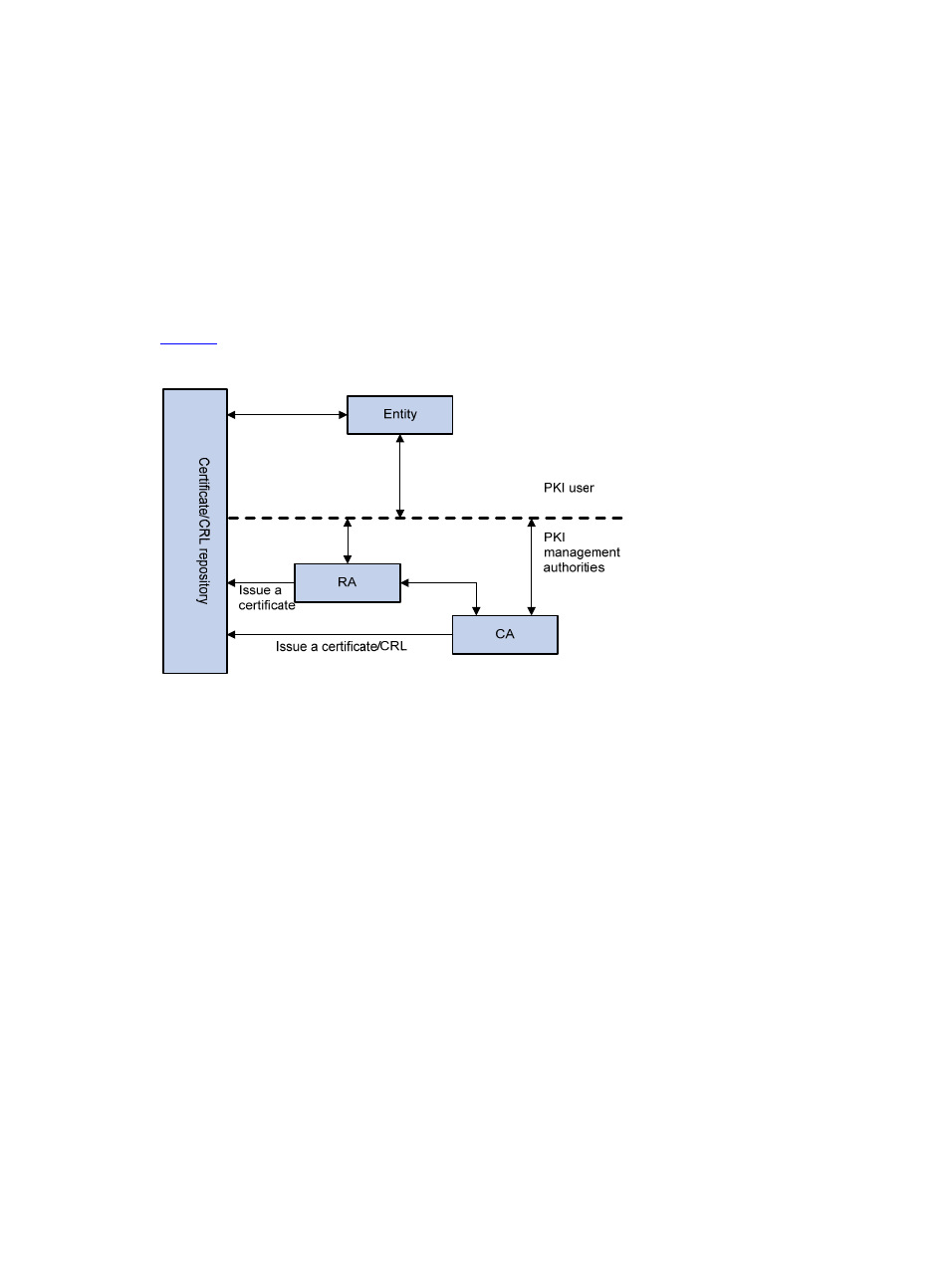
Architecture of PKI
A PKI system consists of entities, a CA, a registration authority (RA) and a PKI repository, as shown in
.
Figure 1 PKI architecture
Entity
An entity is an end user of PKI products or services, such as a person, an organization, a device, or a
process running on a computer.
CA
A certificate authority (CA) is a trusted authority responsible for issuing and managing digital certificates.
A CA issues certificates, specifies the validity periods of certificates, and revokes certificates as needed
by publishing CRLs.
RA
A registration authority (RA) is an extended part of a CA or an independent authority. An RA can
implement functions including identity authentication, CRL management, key pair generation and key
pair backup. It receives registration requests, examines the qualifications of users, and decides whether
the CA can assign digital certificates to the users. Sometimes, a CA assumes the registration
management responsibility and therefore there is no independent RA. The PKI standard recommends
that an independent RA be used for registration management to achieve higher security of application
systems.
