Traffic policing configuration, Overview, Introduction to traffic policing – H3C Technologies H3C SecPath F1000-E User Manual
Page 556
1
Traffic Policing Configuration
Overview
Introduction to Traffic Policing
Without limits on user traffic, a network can be overwhelmed very easily. To help assign network
resources such as bandwidth efficiently to improve network performance and hence user satisfaction,
QoS technologies such as traffic policing, traffic shaping, and rate limit were introduced. Traffic policing
limits traffic rate and resource usage according to traffic specifications.
Traffic policing regulates particular flows entering or leaving a device according to configured
specifications. When a flow exceeds the specification, some restriction or punishment measures can be
taken to prevent overconsumption of network resources and protect the network resources. For example,
you can limit the bandwidth for HTTP packets to less than 50% of the total and drop the HTTP packets
exceeding the threshold.
NOTE:
Traffic policing supports policing traffic in the inbound direction and the outbound direction. For the ease
of description, the outbound direction is taken for example to describe traffic policing.
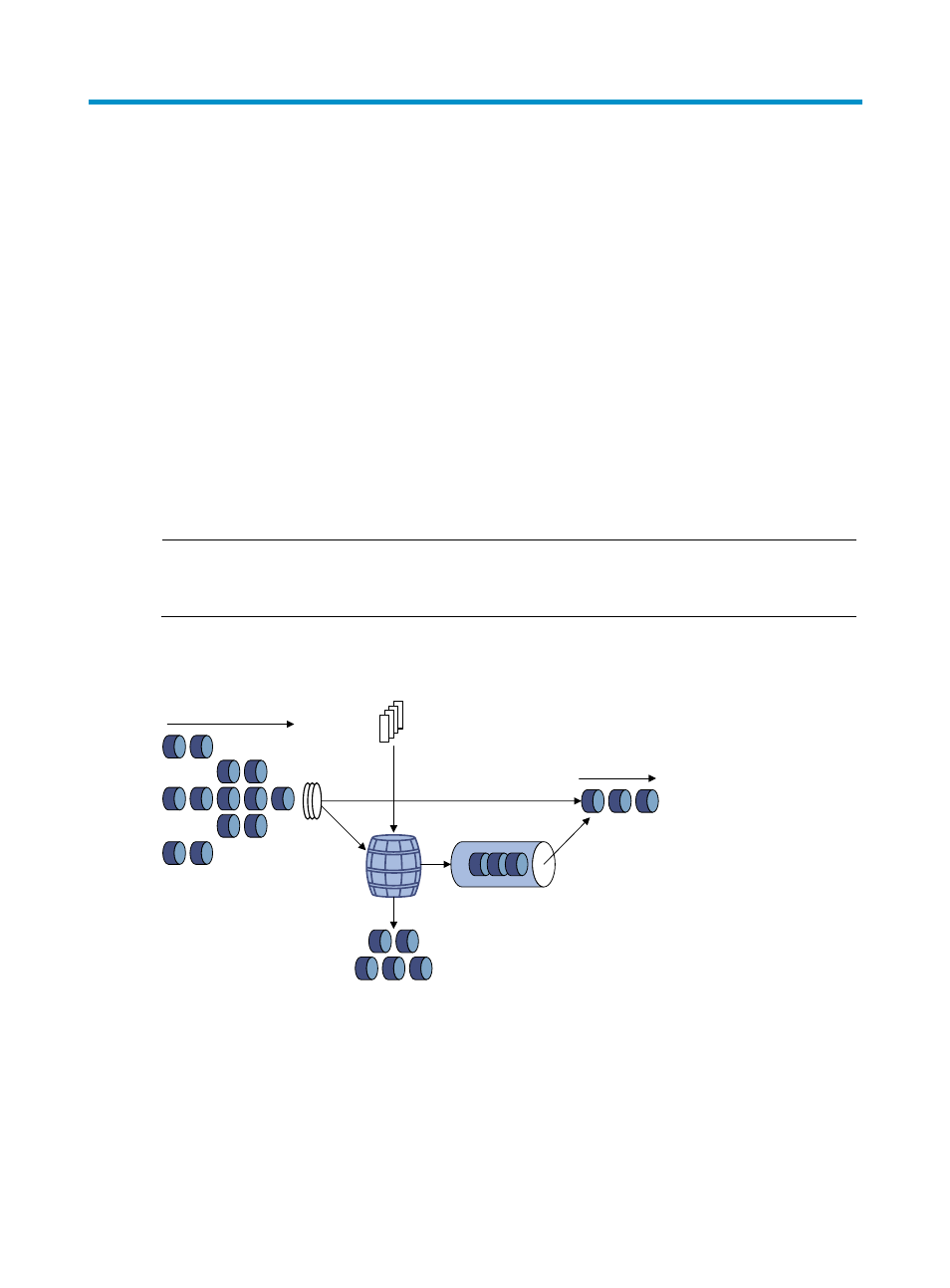
Figure 1 Schematic diagram for traffic policing
Token
bucket
Packets dropped
Packet
classification
Packets to be sent
through this interface
Packets sent
Tokens are put into the
bucket at the set rate
Queue
Traffic policing is widely used in policing traffic entering the networks of internet service providers (ISPs).
It can classify the policed traffic and perform pre-defined policing actions specific to evaluation results.
These actions include:
•
Forwarding the packets whose evaluation result is “conforming”.
•
Dropping the packets whose evaluation result is “excess”.
