2 register description, Atmega128rfa1 – Rainbow Electronics ATmega128RFA1 User Manual
Page 408
408
8266A-MCU Wireless-12/09
ATmega128RFA1
ACME
ADEN
MUX5
MUX2:0
Analog Comparator Negative Input
1
0
0
101
ADC5
1
0
0
110
ADC6
1
0
0
111
ADC7
26.2 Register Description
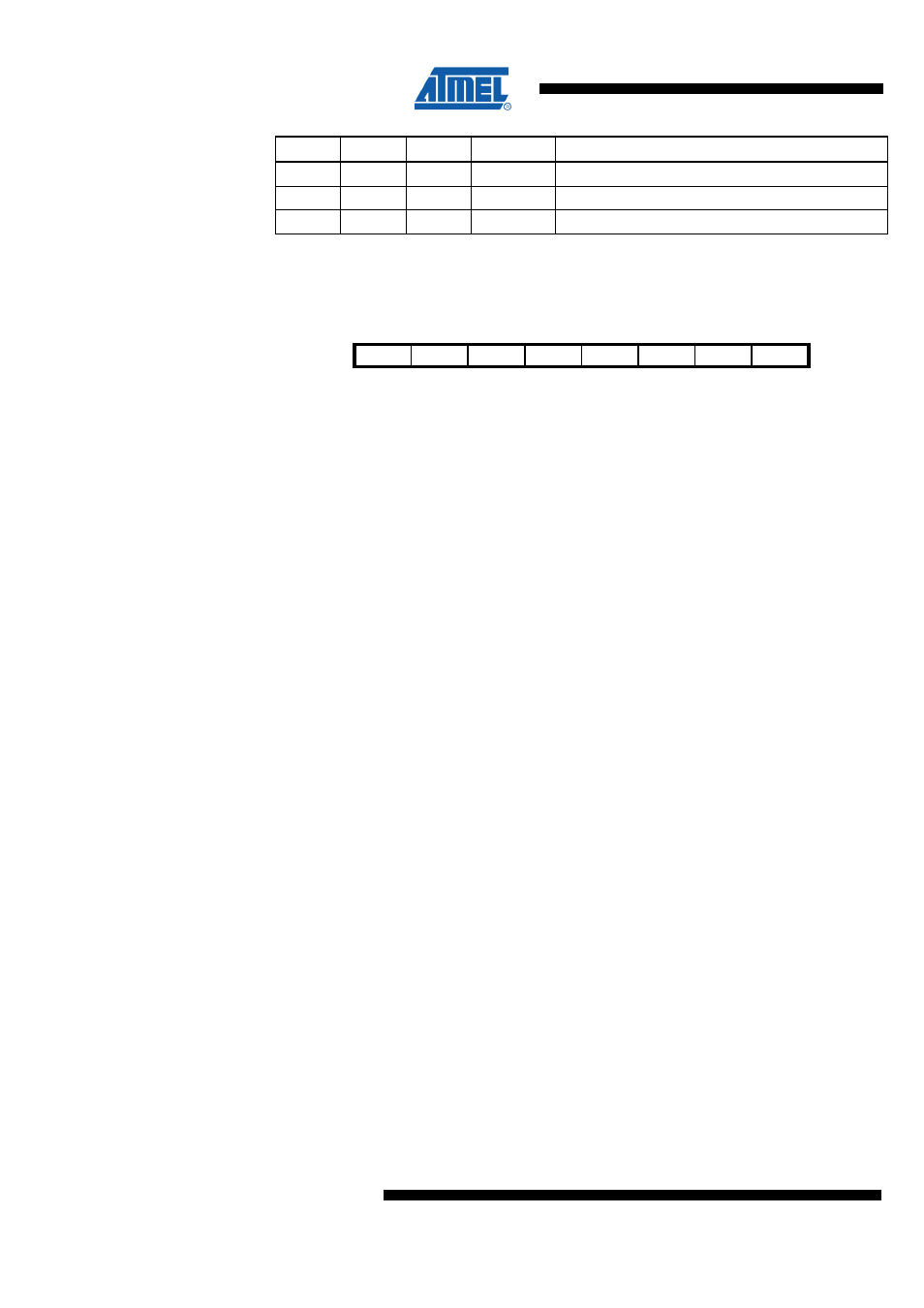
26.2.1 ACSR – Analog Comparator Control And Status Register
Bit
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
$30 ($50)
ACD
ACBG
ACO
ACI
ACIE
ACIC
ACIS1
ACIS0
ACSR
Read/Write
RW
RW
R
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
Initial Value
0
0
NA
0
0
0
0
0
•
Bit 7 – ACD - Analog Comparator Disable
When this bit is written logic one, the power to the Analog Comparator is switched off.
This bit can be set at any time to turn off the Analog Comparator. This will reduce power
consumption in Active and Idle mode. When changing the ACD bit, the Analog
Comparator Interrupt must be disabled by clearing the ACIE bit in ACSR. Otherwise an
interrupt can occur when the bit is changed.
•
Bit 6 – ACBG - Analog Comparator Bandgap Select
When this bit is set, a fixed bandgap reference voltage connects to the positive input of
the Analog Comparator. When this bit is cleared, AIN0 is applied to the positive input of
the Analog Comparator. When the bandgap reference is used as the input of the
Analog Comparator, it will take a certain time for the voltage to stabilize. If not
stabilized, the first comparison may give a wrong value. See section "Internal Voltage
Reference" for details.
•
Bit 5 – ACO - Analog Compare Output
The output of the analog comparator is synchronized and then directly connected to
ACO. The synchronization introduces a delay of 1-2 clock cycles.
•
Bit 4 – ACI - Analog Comparator Interrupt Flag
This bit is set by hardware when a comparator output event triggers the interrupt mode
defined by ACIS1 and ACIS0. The Analog Comparator Interrupt routine is executed if
the ACIE bit is set and the I-bit in SREG is set. ACI is cleared by hard-ware when
executing the corresponding interrupt handling vector. Alternatively, ACI is cleared by
writing a logic one to the flag.
•
Bit 3 – ACIE - Analog Comparator Interrupt Enable
When the ACIE bit is written logic one and the I-bit in the Status Register is set, the
analog comparator interrupt is activated. When written logic zero, the interrupt is
disabled.
•
Bit 2 – ACIC - Analog Comparator Input Capture Enable
When written logic one, this bit enables the input capture function in Timer/Counter1 to
be triggered by the Analog Comparator. The comparator output is in this case directly
connected to the input capture front-end logic, making the comparator utilize the noise
canceler and edge select features of the Timer/Counter1 Input Capture interrupt. When
written logic zero, no connection between the Analog Comparator and the input capture
function exists. To make the comparator trigger the Timer/Counter1 Input Capture
interrupt, the ICIE1 bit in the Timer Interrupt Mask Register (TIMSK1) must be set.
