2 twcr - twi control register, Atmega128rfa1 – Rainbow Electronics ATmega128RFA1 User Manual
Page 402
402
8266A-MCU Wireless-12/09
ATmega128RFA1
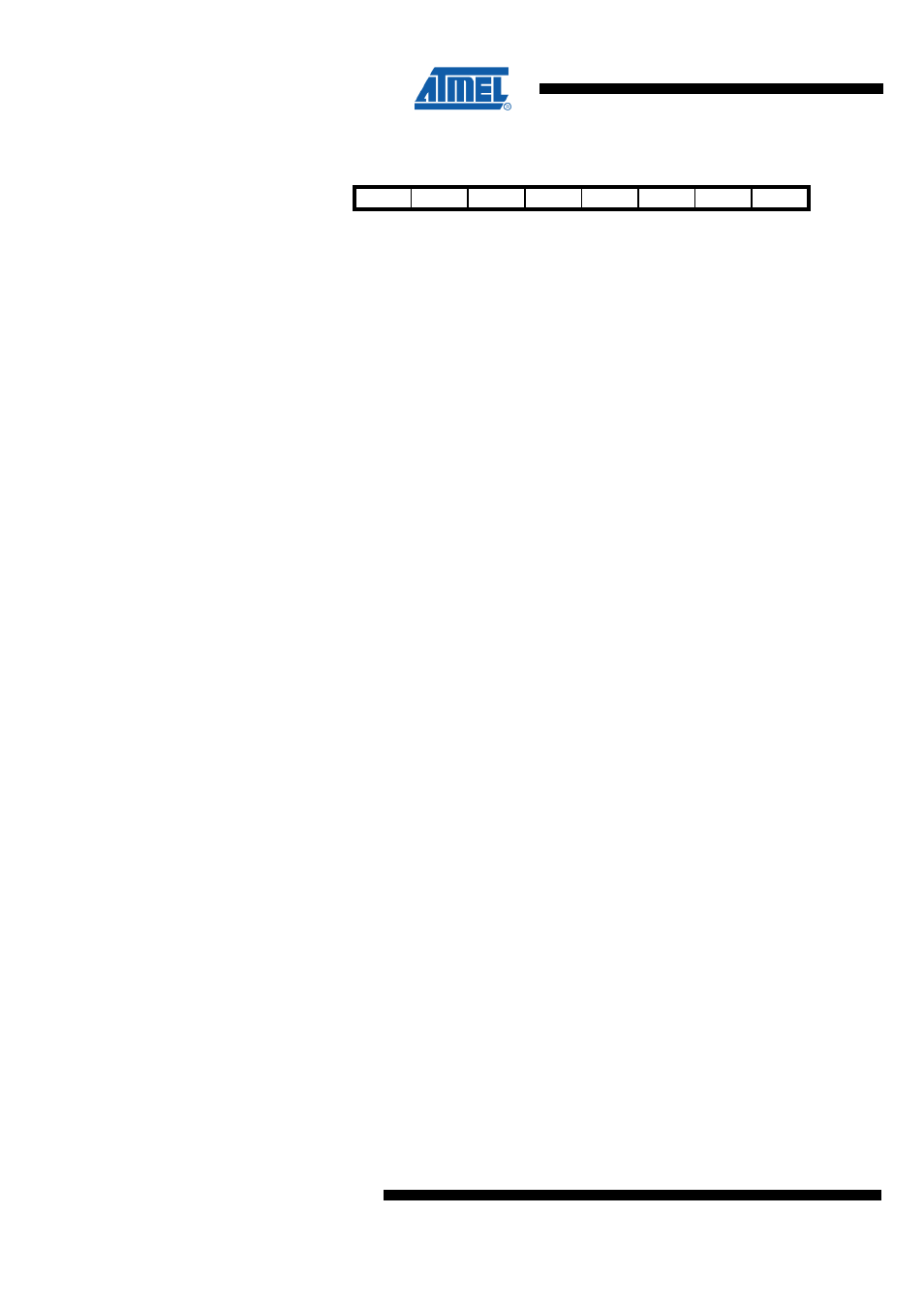
25.9.2 TWCR – TWI Control Register
Bit
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
NA ($BC)
TWINT
TWEA
TWSTA
TWSTO
TWWC
TWEN
Res
TWIE
TWCR
Read/Write
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
R
RW
Initial Value
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
The TWCR is used to control the operation of the TWI. It is used to enable the TWI, to
initiate a Master access by applying a START condition to the bus, to generate a
Receiver acknowledge, to generate a stop condition, and to control halting of the bus
while the data to be written to the bus are put into the TWDR. It also indicates a write
collision if data writing to TWDR is attempted while the register is inaccessible.
•
Bit 7 – TWINT - TWI Interrupt Flag
This bit is set by hardware when the TWI has finished its current job and expects
application software response. If the I-bit in SREG and TWIE in TWCR are set, the
MCU will jump to the TWI Interrupt Vector. While the TWINT Flag is set, the SCL low
period is stretched. The TWINT Flag must be cleared by software by writing a logic one
to it. Note that this flag is not automatically cleared by hardware when executing the
interrupt routine. Also note that clearing this flag starts the operation of the TWI. So all
accesses to the TWI Address Register (TWAR), TWI Status Register (TWSR) and TWI
Data Register (TWDR) must be complete before clearing this flag.
•
Bit 6 – TWEA - TWI Enable Acknowledge Bit
The TWEA bit controls the generation of the acknowledge pulse. If the TWEA bit is
written to one, the ACK pulse is generated on the TWI bus if the following conditions
are met: 1. The devices own slave address has been received; 2. A general call has
been received, while the TWGCE bit in the TWAR is set. 3. A data byte has been
received in Master Receiver or Slave Receiver mode. By writing the TWEA bit to zero,
the device can be virtually disconnected from the 2-wire Serial Bus temporarily.
Address recognition can then be resumed by writing the TWEA bit to one again.
•
Bit 5 – TWSTA - TWI START Condition Bit
The application writes the TWSTA bit to one when it desires to become a Master on the
2-wire Serial Bus. The TWI hardware checks if the bus is available and generates a
START condition on the bus if it is free. However, if the bus is not free, the TWI waits
until a STOP condition is detected and then generates a new START condition to claim
the bus Master status. TWSTA must be cleared by software when the START condition
has been transmitted.
•
Bit 4 – TWSTO - TWI STOP Condition Bit
Writing the TWSTO bit to one in Master mode will generate a STOP condition on the 2-
wire Serial Bus. When the STOP condition is executed on the bus, the TWSTO bit is
cleared automatically. In Slave mode, setting the TWSTO bit can be used to recover
from an error condition. This will not generate a STOP condition, but the TWI returns to
a well-defined not-addressed Slave mode and releases the SCL and SDA lines to a
high impedance state.
•
Bit 3 – TWWC - TWI Write Collision Flag
The TWWC bit is set when attempting to write to the TWI Data Register TWDR when
TWINT is low. This flag is cleared by writing the TWDR Register when TWINT is high.
•
Bit 2 – TWEN - TWI Enable Bit
The TWEN bit enables TWI operation and activates the TWI interface. When TWEN is
written to one, the TWI takes control over the I/O ports connected to the SCL and SDA
