4 eecr - eeprom control register, Atmega128rfa1 – Rainbow Electronics ATmega128RFA1 User Manual
Page 24
24
8266A-MCU Wireless-12/09
ATmega128RFA1
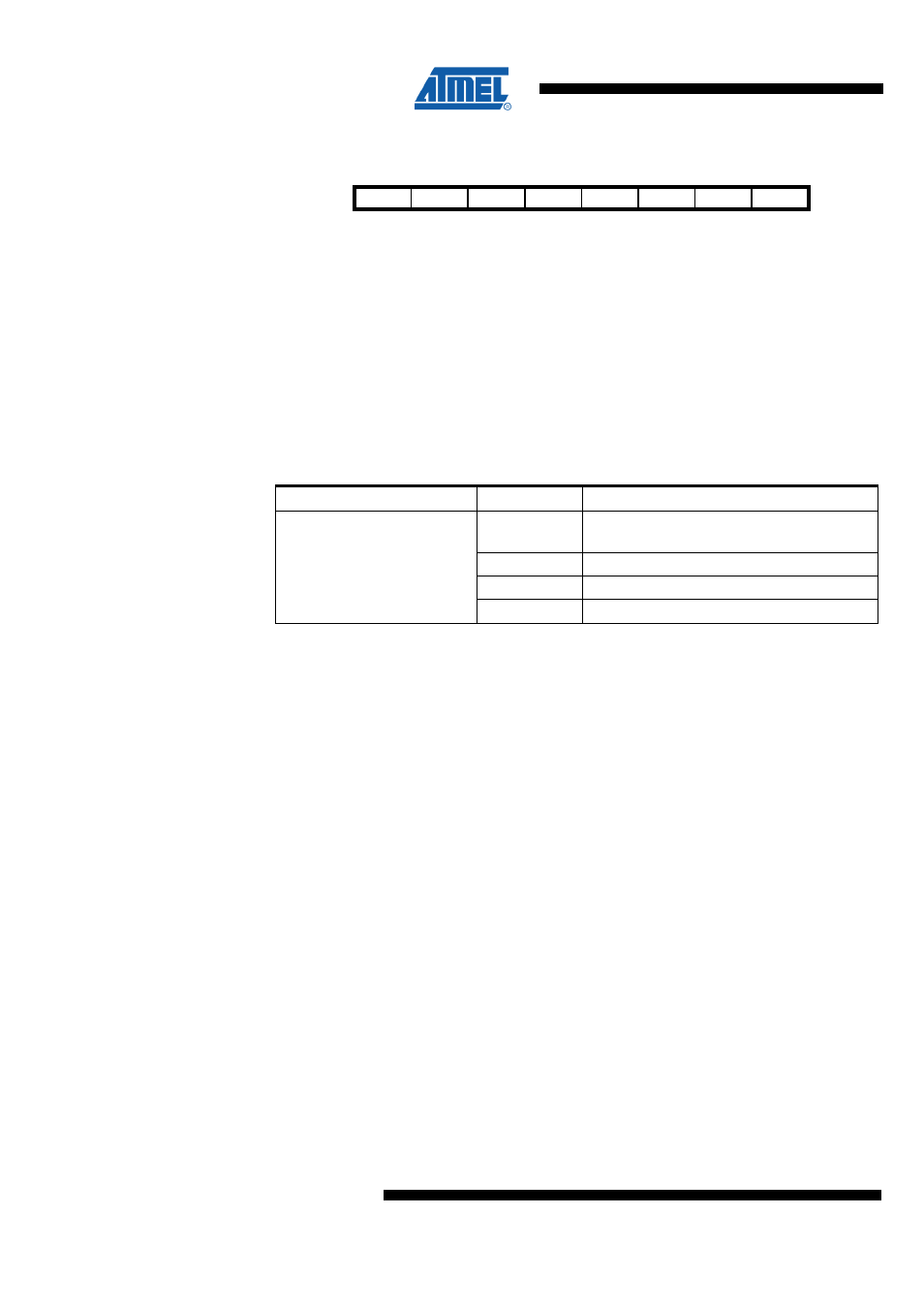
8.4.4 EECR – EEPROM Control Register
Bit
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
$1F ($3F)
Res1
Res0
EEPM1
EEPM0
EERIE
EEMPE
EEPE
EERE
EECR
Read/Write
R
R
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
Initial Value
0
0
X
X
0
0
X
0
•
Bit 7:6 – Res1:0 - Reserved
•
Bit 5:4 – EEPM1:0 - EEPROM Programming Mode
The EEPROM Programming mode bit setting defines which programming action will be
triggered when writing EEPE. It is possible to program data in one atomic operation
(erase the old value and program the new value) or to split the Erase and Write
operations in two different operations. The Programming times for the different modes
are shown in the following table. While EEPE is set, any write to EEPM1:0 will be
ignored. During reset, the EEPM1:0 bits will be reset to 0 unless the EEPROM is busy
programming.
Table 8-4 EEPM Register Bits
Register Bits
Value
Description
0x00
Erase and Write in one operation (Atomic
Operation)
0x01
Erase only
0x02
Write only
EEPM1:0
0x03
Reserved for future use
•
Bit 3 – EERIE - EEPROM Ready Interrupt Enable
Writing EERIE to one enables the EEPROM Ready Interrupt if the I bit in SREG is set.
Writing EERIE to zero disables the interrupt. The EEPROM Ready interrupt generates a
constant interrupt when EEPE is cleared.
•
Bit 2 – EEMPE - EEPROM Master Write Enable
The EEMPE bit determines whether setting EEPE to one causes the EEPROM to be
written. When EEMPE is set, setting EEPE within four clock cycles will write data to the
EEPROM at the selected address If EEMPE is zero, setting EEPE will have no effect.
When EEMPE has been written to one by software, hardware clears the bit to zero after
four clock cycles. See the description of the EEPE bit for an EEPROM write procedure.
•
Bit 1 – EEPE - EEPROM Programming Enable
The EEPROM Write Enable Signal EEPE is the write strobe to the EEPROM. When
address and data are correctly set up, the EEPE bit must be written to one to write the
value into the EEPROM. The EEMPE bit must be written to one before a logical one is
written to EEPE, otherwise no EEPROM write takes place. The following procedure
should be adopted when writing the EEPROM (the order of steps 3 and 4 is not
essential):
1. Wait until EEPE becomes zero.
2. Wait until SPMEN in SPMCSR becomes zero.
3. Write new EEPROM address to EEAR (optional).
4. Write new EEPROM data to EEDR (optional).
5. Write a logical one to the EEMPE bit while writing a zero to EEPE in EECR.
6. Within four clock cycles after setting EEMPE, write a logical one to EEPE.
