25 2-wire serial interface, 1 features, 2 2-wire serial interface bus definition – Rainbow Electronics ATmega128RFA1 User Manual
Page 377: 1 twi terminology, Atmega128rfa1
377
8266A-MCU Wireless-12/09
ATmega128RFA1
25 2-wire Serial Interface
25.1 Features
•
Simple yet powerful and flexible communication interface, only two bus lines
needed
•
Both master and slave operation supported
•
Device can operate as transmitter or receiver
•
7-bit address space allows up to 128 different slave addresses
•
Multi-master arbitration support
•
Up to 400 kHz data transfer speed
•
Slew-rate limited output drivers
•
Noise suppression circuitry rejects spikes on bus lines
•
Fully programmable slave address with general call support
•
Address recognition causes wake-up when microcontroller is in sleep mode
25.2 2-wire Serial Interface Bus Definition
The 2-wire Serial Interface (TWI) is ideally suited for typical microcontroller applications.
The TWI protocol allows the systems designer to interconnect up to 128 different
devices using only two bi-directional bus lines, one for clock (SCL) and one for data
(SDA). The only external hardware needed to implement the bus is a single pull-up
resistor for each of the TWI bus lines. All devices connected to the bus have individual
addresses, and mechanisms for resolving bus contention are inherent in the TWI
protocol.
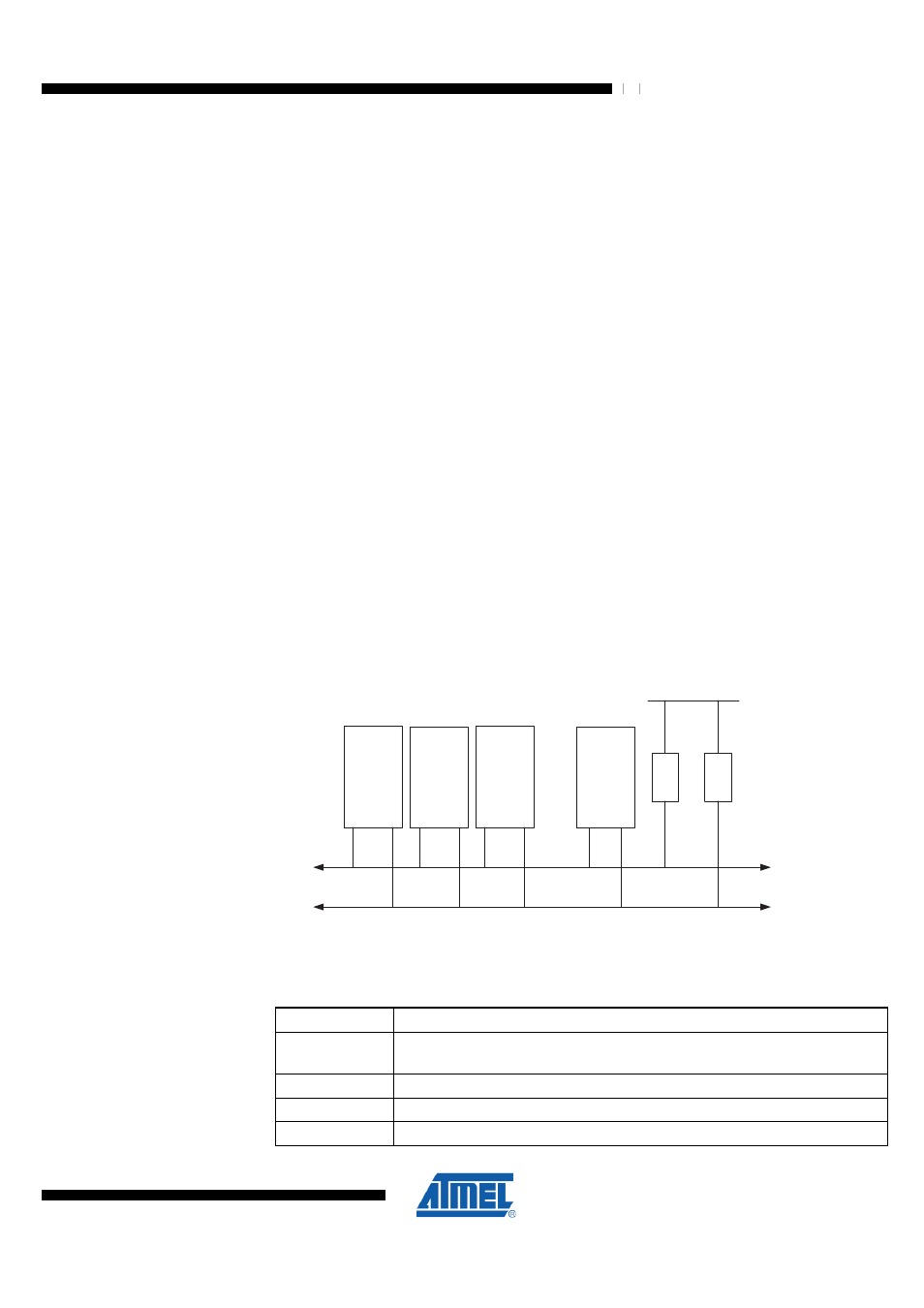
Figure 25-1. TWI Bus Interconnection
Device 1
Device 2
Device 3
Device n
SDA
SCL
........
R1
R2
DEVDD
25.2.1 TWI Terminology
The following definitions are frequently encountered in this section.
Table 25-1. TWI Terminology
Term
Description
Master
The device that initiates and terminates a transmission. The Master also
generates the SCL clock.
Slave
The device addressed by a Master.
Transmitter
The device placing data on the bus.
Receiver
The device reading data from the bus.
