2 electrical interconnection, 3 data transfer and frame format, 1 transferring bits – Rainbow Electronics ATmega128RFA1 User Manual
Page 378: 2 start and stop conditions
378
8266A-MCU Wireless-12/09
ATmega128RFA1
The Power Reduction TWI bit, PRTWI bit in
"PRR0 – Power Reduction Register0" on
must be written to zero to enable the 2-wire Serial Interface.
25.2.2 Electrical Interconnection
, both bus lines are connected to the positive
supply voltage through pull-up resistors. The bus drivers of all TWI-compliant devices
are open-drain or open-collector. This implements a wired-AND function which is
essential to the operation of the interface. A low level on a TWI bus line is generated
when one or more TWI devices output a zero. A high level is output when all TWI
devices trim-state their outputs, allowing the pull-up resistors to pull the line high. Note
that all AVR devices connected to the TWI bus must be powered in order to allow any
bus operation.
The number of devices that can be connected to the bus is only limited by the bus
capacitance limit of 400 pF and the 7-bit slave address space. A detailed specification
of the electrical characteristics of the TWI is given in
. Two different sets of specifications are presented there,
one relevant for bus speeds below 100 kHz, and one valid for bus speeds up to 400
kHz.
25.3 Data Transfer and Frame Format
25.3.1 Transferring Bits
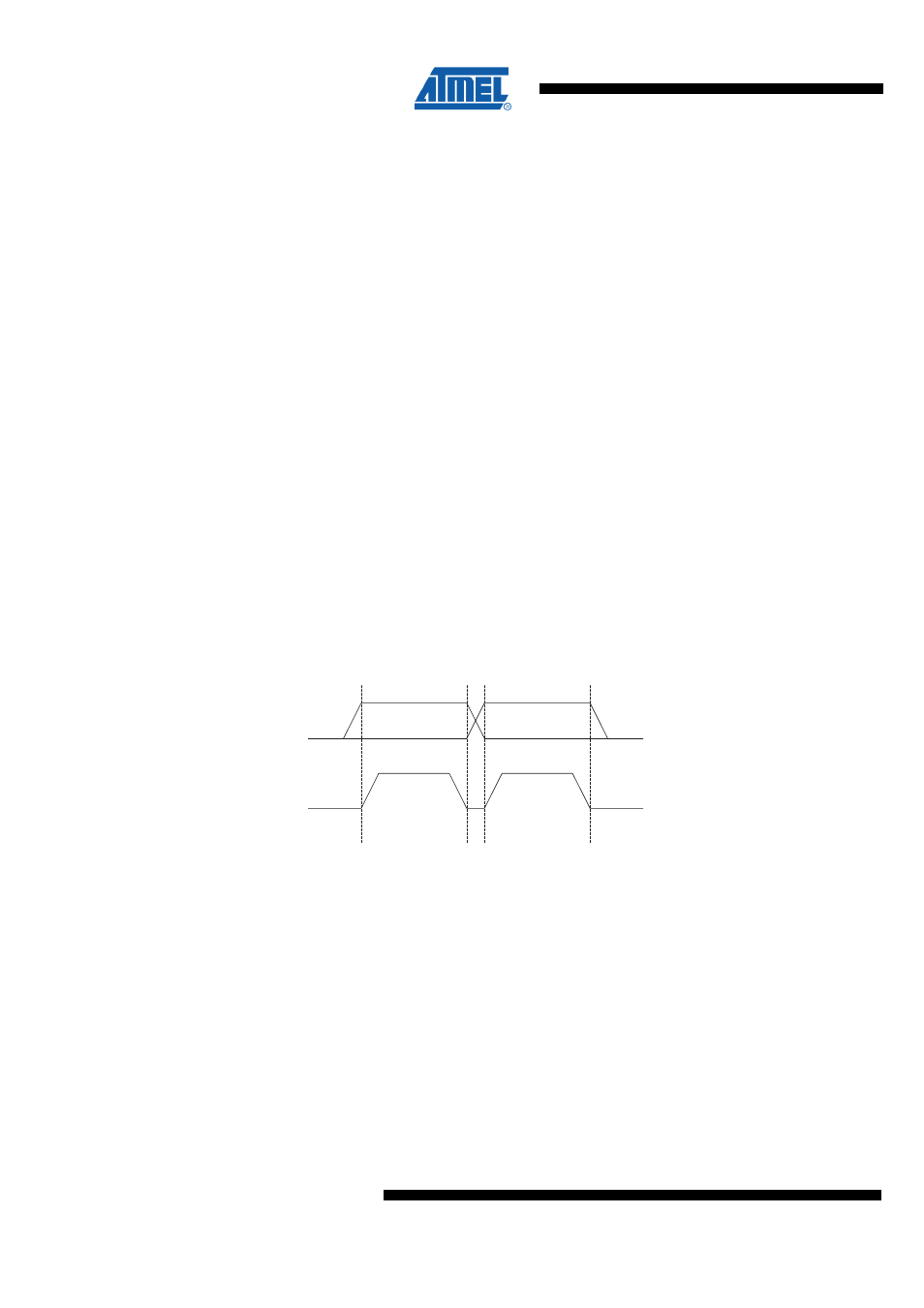
Each data bit transferred on the TWI bus is accompanied by a pulse on the clock line.
The level of the data line must be stable when the clock line is high. The only exception
to this rule is for generating start and stop conditions.
Figure 25-2. Data Validity
SDA
SCL
Data Stable
Data Stable
Data Change
25.3.2 START and STOP Conditions
The Master initiates and terminates a data transmission. The transmission is initiated
when the Master issues a START condition on the bus, and it is terminated when the
Master issues a STOP condition. Between a START and a STOP condition, the bus is
considered busy, and no other master should try to seize control of the bus. A special
case occurs when a new START condition is issued between a START and STOP
condition. This is referred to as a REPEATED START condition, and is used when the
Master wishes to initiate a new transfer without relinquishing control of the bus. After a
REPEATED START, the bus is considered busy until the next STOP. This is identical to
the START behavior, and therefore START is used to describe both START and
REPEATED START for the remainder of this datasheet, unless otherwise noted. As
depicted below, START and STOP conditions are signaled by changing the level of the
SDA line when the SCL line is high.
