Configuring ip subnet vlans, Creating ip subnet vlans, Figure 99 – Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch Configuration Guide (Supporting R2.2.0.0) User Manual
Page 827: Ip subnet vlans
Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch Configuration Guide
771
53-1002651-02
35
Configuring IP Subnet VLANs
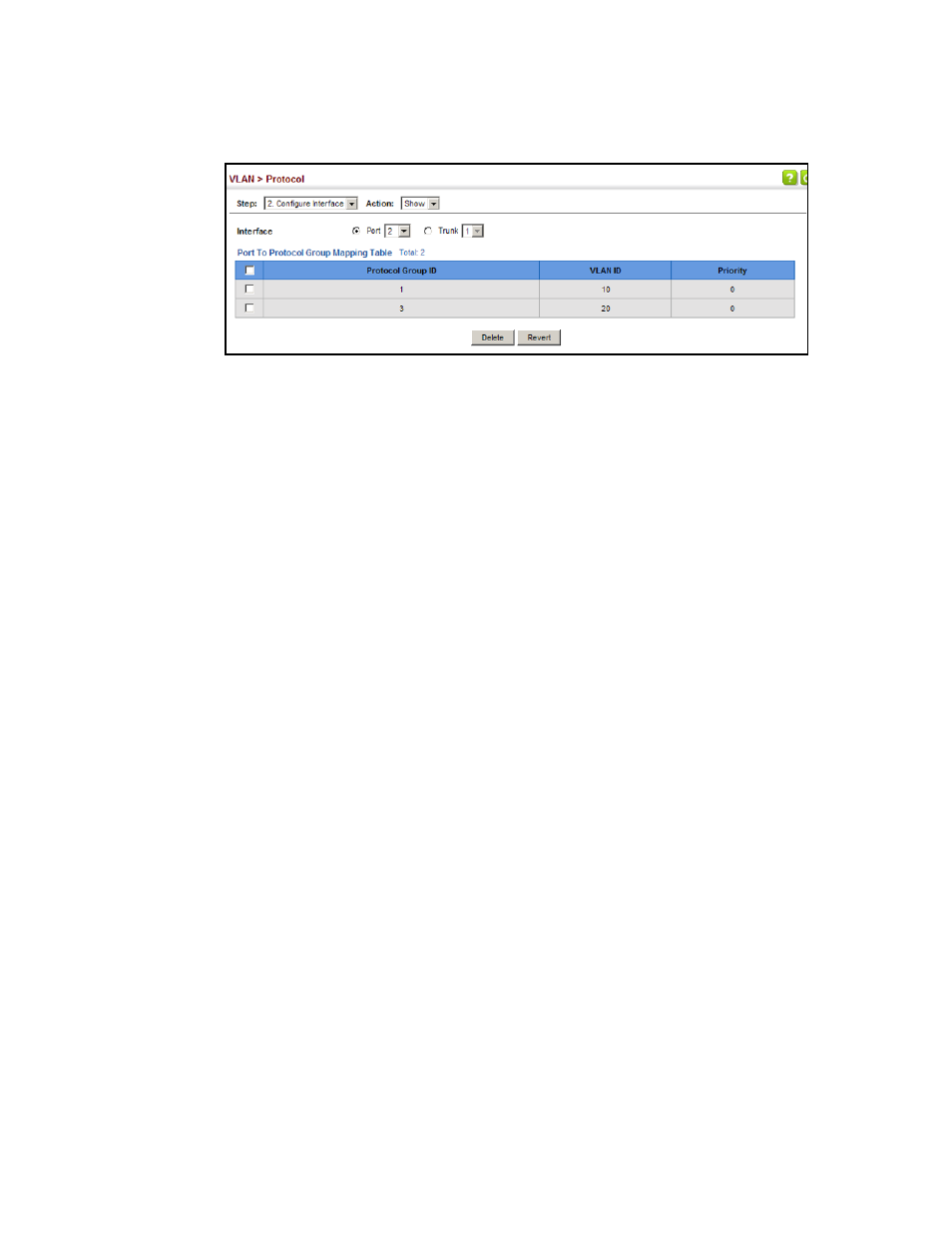
FIGURE 99
Showing the Interface to Protocol Group Mapping
Configuring IP Subnet VLANs
When using port-based classification, all untagged frames received by a port are classified as
belonging to the VLAN whose VID (PVID) is associated with that port.
When IP subnet-based VLAN classification is enabled, the source address of untagged ingress
frames are checked against the IP subnet-to-VLAN mapping table. If an entry is found for that
subnet, these frames are assigned to the VLAN indicated in the entry. If no IP subnet is matched,
the untagged frames are classified as belonging to the receiving port’s VLAN ID (PVID).
Creating IP Subnet VLANs
Use the VLAN > IP Subnet (Configure IP Subnet - Add) page to create IP subnet-based VLANs.
CLI References
•
“subnet-vlan (Global Configuration)”
Command Usage
•
Each IP subnet can be mapped to only one VLAN ID. An IP subnet consists of an IP address and
a mask. The specified VLAN need not be an existing VLAN.
•
When an untagged frame is received by a port, the source IP address is checked against the IP
subnet-to-VLAN mapping table, and if an entry is found, the corresponding VLAN ID is assigned
to the frame. If no mapping is found, the PVID of the receiving port is assigned to the frame.
•
The IP subnet cannot be a broadcast or multicast IP address.
•
When MAC-based, IP subnet-based, and protocol-based VLANs are supported concurrently,
priority is applied in this sequence, and then port-based VLANs last.
•
Use the Configure IP Subnet (Add) page to create a IP subnet VLAN. Then use the Configure
Interface (Add) page described in the next section to bind an interface to an IP subnet VLAN.
Parameters
These parameters are displayed:
•
IP Address – The IP address for a subnet. Valid IP addresses consist of four decimal numbers,
0 to 255, separated by periods.
•
Subnet Mask – This mask identifies the host address bits of the IP subnet.
•
VLAN – VLAN to which matching IP subnet traffic is forwarded. (Range: 1-4093)
