Ieee 802.1q tunneling, Figure 89, Figure 90 – Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch Configuration Guide (Supporting R2.2.0.0) User Manual
Page 816: Conf
760
Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch Configuration Guide
53-1002651-02
35
IEEE 802.1Q Tunneling
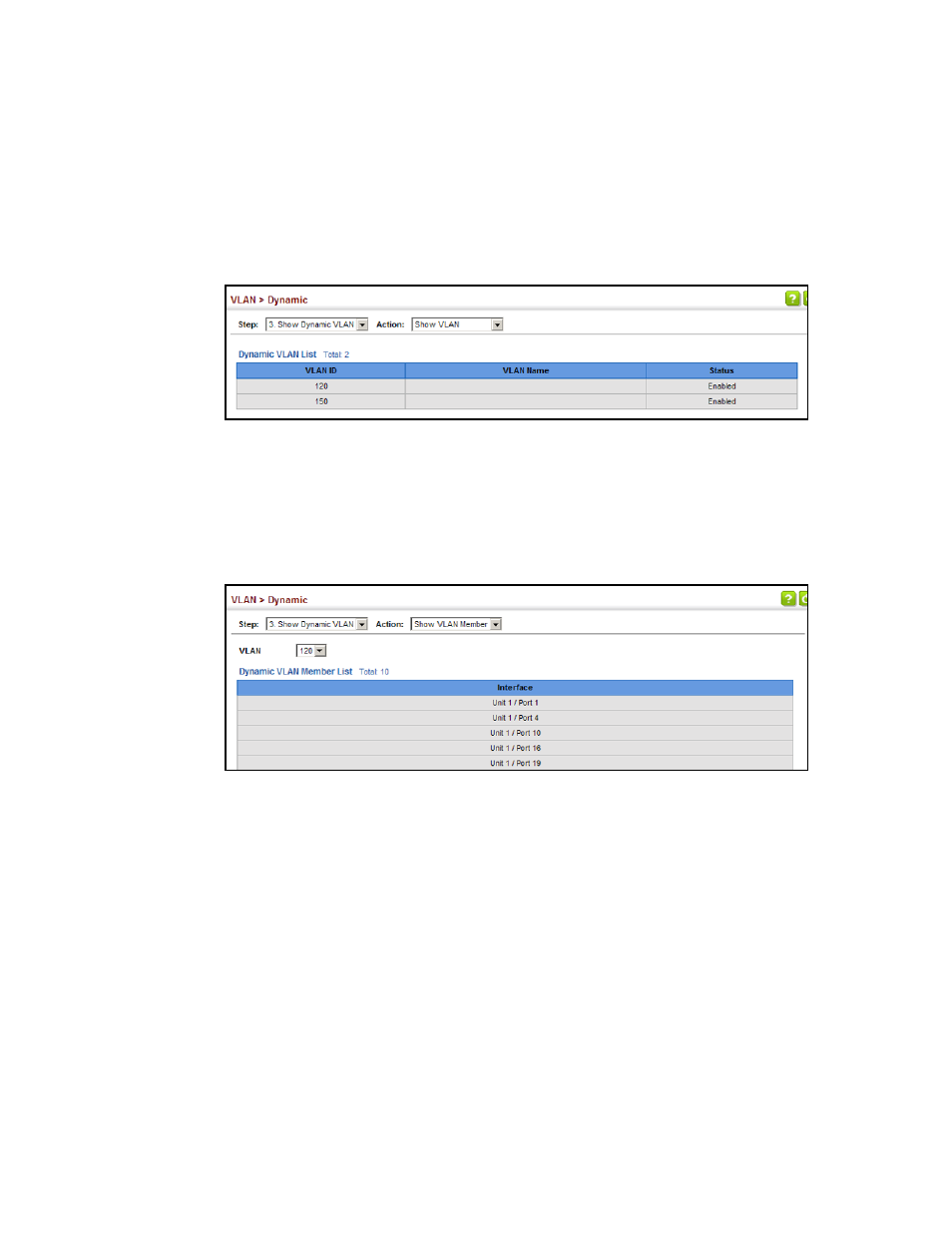
To show the dynamic VLAN joined by this switch:
1. Click VLAN, Dynamic.
2. Select Show Dynamic VLAN from the Step list.
3. Select Show VLAN from the Action list.
FIGURE 89
Showing Dynamic VLANs Registered on the Switch
To show the members of a dynamic VLAN:
1. Click VLAN, Dynamic.
2. Select Show Dynamic VLAN from the Step list.
3. Select Show VLAN Members from the Action list.
FIGURE 90
Showing the Members of a Dynamic VLAN
IEEE 802.1Q Tunneling
IEEE 802.1Q Tunneling (QinQ) is designed for service providers carrying traffic for multiple
customers across their networks. QinQ tunneling is used to maintain customer-specific VLAN and
Layer 2 protocol configurations even when different customers use the same internal VLAN IDs.
This is accomplished by inserting Service Provider VLAN (SPVLAN) tags into the customer’s frames
when they enter the service provider’s network, and then stripping the tags when the frames leave
the network.
A service provider’s customers may have specific requirements for their internal VLAN IDs and
number of VLANs supported. VLAN ranges required by different customers in the same
service-provider network might easily overlap, and traffic passing through the infrastructure might
be mixed. Assigning a unique range of VLAN IDs to each customer would restrict customer
configurations, require intensive processing of VLAN mapping tables, and could easily exceed the
maximum VLAN limit of 4096.
