Showing ipv6 statistics, Figure 340 s – Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch Configuration Guide (Supporting R2.2.0.0) User Manual
Page 1116
1060
Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch Configuration Guide
53-1002651-02
44
Setting the Switch’s IP Address (IP Version 6)
Interface
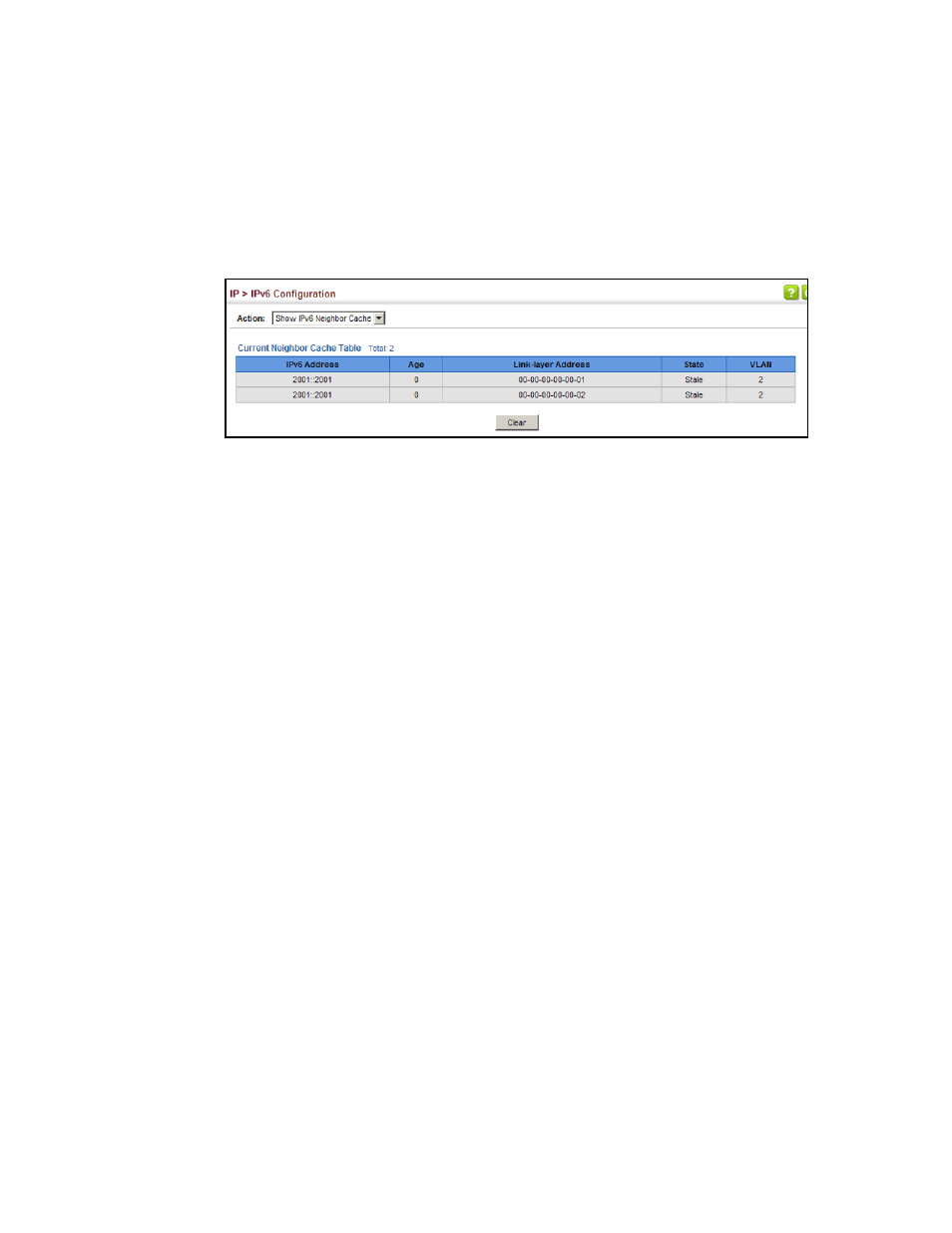
To show neighboring IPv6 devices:
1. Click IP, IPv6 Configuration.
2. Select Show IPv6 Neighbors from the Action list.
FIGURE 340
Showing IPv6 Neighbors
Showing IPv6 Statistics
Use the IP > IPv6 Configuration (Show Statistics) page to display statistics about IPv6 traffic
passing through this switch.
CLI References
•
Command Usage
This switch provides statistics for the following traffic types:
•
IPv6 – The Internet Protocol for Version 6 addresses provides a mechanism for transmitting
blocks of data (often called packets or frames) from a source to a destination, where these
network devices (that is, hosts) are identified by fixed length addresses. The Internet Protocol
also provides for fragmentation and reassembly of long packets, if necessary, for transmission
through “small packet” networks.
•
ICMPv6 – Internet Control Message Protocol for Version 6 addresses is a network layer
protocol that transmits message packets to report errors in processing IPv6 packets. ICMP is
therefore an integral part of the Internet Protocol. ICMP messages may be used to report
various situations, such as when a datagram cannot reach its destination, when the gateway
does not have the buffering capacity to forward a datagram, and when the gateway can direct
the host to send traffic on a shorter route. ICMP is also used by routers to feed back
information about more suitable routes (that is, the next hop router) to use for a specific
destination.
•
UDP – User Datagram Protocol provides a datagram mode of packet switched
communications. It uses IP as the underlying transport mechanism, providing access to IP-like
services. UDP packets are delivered just like IP packets – connection-less datagrams that may
be discarded before reaching their targets. UDP is useful when TCP would be too complex, too
slow, or just unnecessary.
