Configuring mvr domain settings, Figure 390 confi, Configuring mvr – Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch Configuration Guide (Supporting R2.2.0.0) User Manual
Page 1172: Domain settings
1116
Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch Configuration Guide
53-1002651-02
47
Multicast VLAN Registration for IPv4
Interface
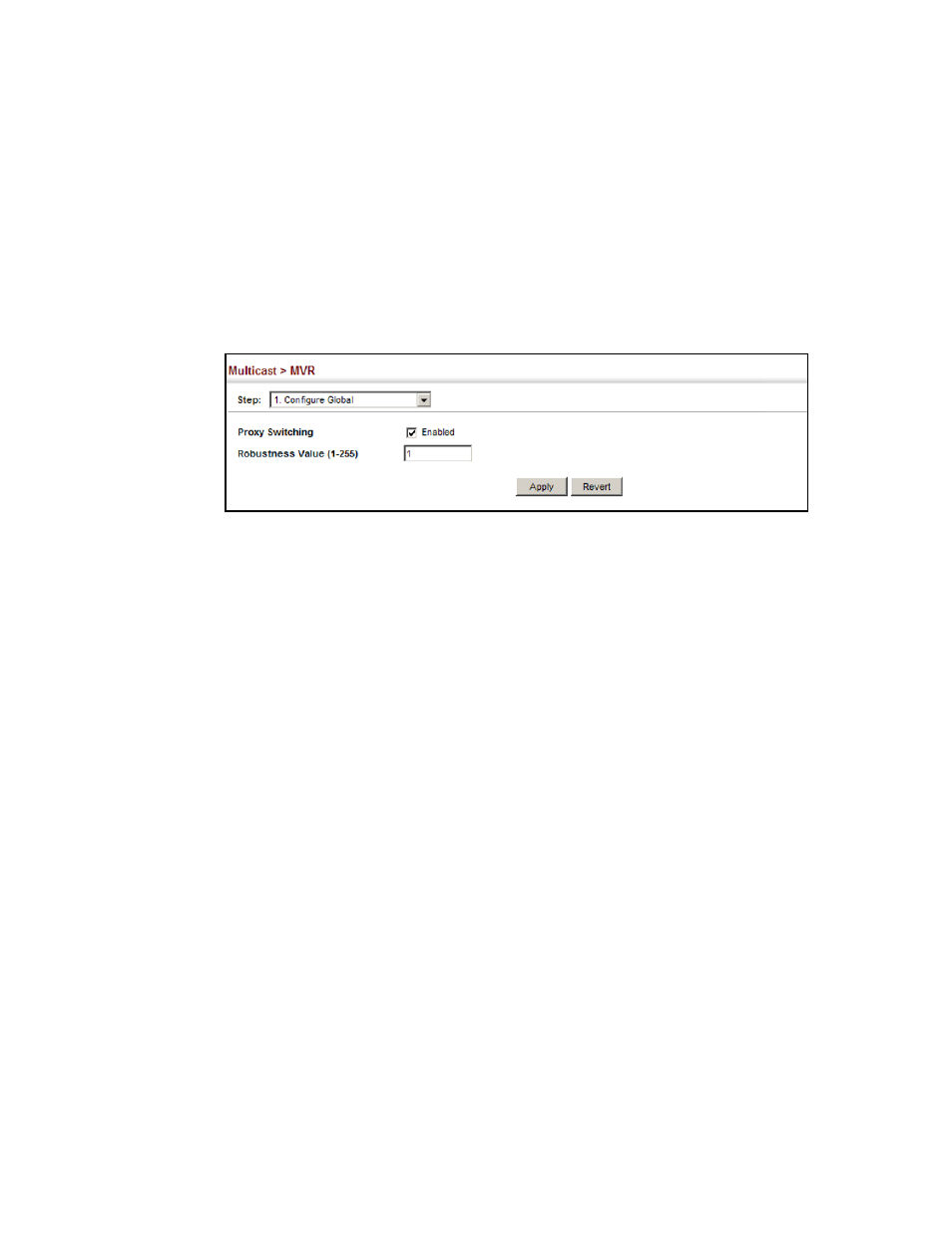
To configure global settings for MVR:
1. Click Multicast, MVR.
2. Select Configure Global from the Step list.
3. Set the status for MVR proxy switching and the robustness value used for report and query
messages.
4. Click Apply.
FIGURE 390
Configuring Global Settings for MVR
Configuring MVR Domain Settings
Use the Multicast > MVR (Configure Domain) page to enable MVR globally on the switch, and select
the VLAN that will serve as the sole channel for common multicast streams supported by the
service provider.
CLI References
•
Parameters
These parameters are displayed:
•
Domain ID– An independent multicast domain. (Range: 1-5)
•
MVR Status – When MVR is enabled on the switch, any multicast data associated with an MVR
group is sent from all designated source ports, to all receiver ports that have registered to
receive data from that multicast group. (Default: Disabled)
•
MVR VLAN – Identifier of the VLAN that serves as the channel for streaming multicast services
using MVR. MVR source ports should be configured as members of the MVR VLAN (see
on page 754), but MVR receiver ports should not be manually
configured as members of this VLAN. (Default: 1)
•
MVR Running Status – Indicates whether or not all necessary conditions in the MVR
environment are satisfied. Running status is Active as long as MVR is enabled, the specified
MVR VLAN exists, and a source port with a valid link has been configured (see
•
MVR Current Learned Groups – The number of MVR groups currently assigned to this domain.
•
Forwarding Priority – The CoS priority assigned to all multicast traffic forwarded into this
domain. (Range: 0-6, where 6 is the highest priority)
This parameter can be used to set a high priority for low-latency multicast traffic such as a
video-conference, or to set a low priority for normal multicast traffic not sensitive to latency.
