Address resolution protocol, Figure 346 t, Table 185 – Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch Configuration Guide (Supporting R2.2.0.0) User Manual
Page 1125: Ddress resolution protocol
Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch Configuration Guide
1069
53-1002651-02
44
Address Resolution Protocol
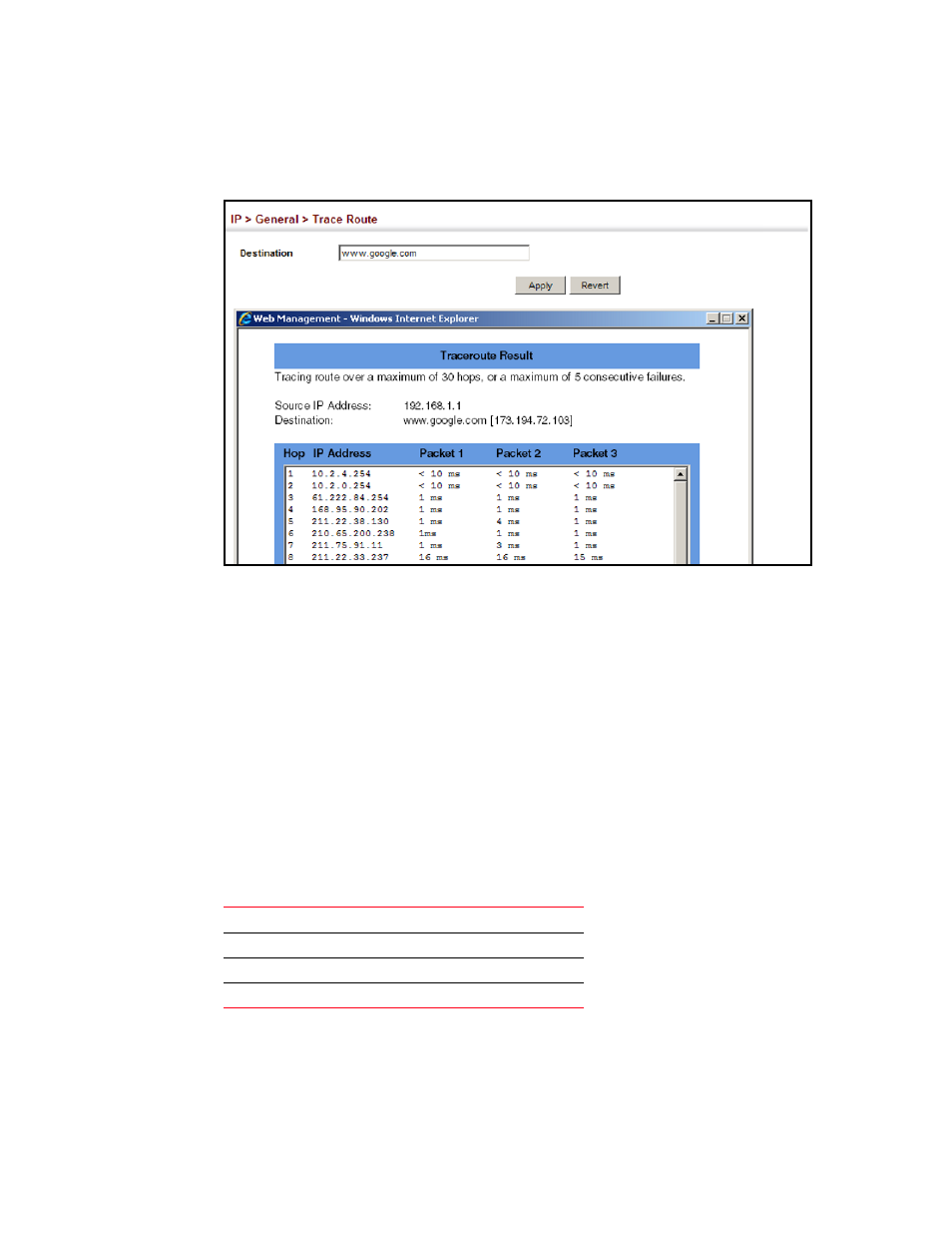
3. Click Apply.
FIGURE 346
Tracing the Route to a Network Device
Address Resolution Protocol
The switch uses its routing tables (for static routes and directly connected subnets) to make routing
decisions, and uses Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) to forward traffic from one hop to the next.
ARP is used to map an IP address to a physical layer (i.e., MAC) address. When an IP frame is
received by this switch (or any standards-based switch/router), it first looks up the MAC address
corresponding to the destination IP address in the ARP cache. If the address is found, the switch
writes the MAC address into the appropriate field in the frame header, and forwards the frame on
to the next hop. IP traffic passes along the path to its final destination in this way, with each routing
device mapping the destination IP address to the MAC address of the next hop toward the
recipient, until the packet is delivered to the final destination.
If there is no entry for an IP address in the ARP cache, the switch will broadcast an ARP request
packet to all devices on the network. The ARP request contains the following fields similar to that
shown in this example:
TABLE 185
Address Resolution Protocol
destination IP address
10.1.0.19
destination MAC address
?
source IP address
10.1.0.253
source MAC address
00-00-ab-cd-00-00
