Auto-qos-med macro examples, Auto-qos-med macro examples 3 – Allied Telesis AT-8100 Series User Manual
Page 1683
AT-8100 Switch Command Line User’s Guide
1683
Auto-QoS-MED
Macro Examples
Note
LLDP must be enabled globally before Auto-QoS-MED
configuration.
Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) and Link Layer Discovery Protocol
for Media Endpoint Devices (LLDP-MED) allow Ethernet network devices,
such as switches and routers, to receive and transmit device-related
information to directly-connected devices. LLDP-MED is used between a
LAN network connectivity device, such the AT-8100 switch, and media
endpoint device, such as an IP phone. For more information about LLDP-
MED, see Chapter 78, “LLDP and LLDP-MED” on page 1229.
You can use the AUTO-QOS-MED command to support a voice VLAN and
optionally specify to trust DSCP (instead of CoS) ingress traffic on a port.
This command also enables LLDP-MED support. In addition, you can set
the AUTO-QOS-MED command to specify the type of trusted traffic
without assigning a voice VLAN to the switch.
With the AUTO-QOS-MED command, you can create the following
scenarios:
“Auto-QoS-MED Functionality and Voice VLAN Support” on page 1684
“Auto-QoS-MED with Trust DSCP Functionality and Voice VLAN
Support” on page 1685
“Auto-QoS Functionality” on page 1681
“Auto-QoS with Trust DSCP Functionality” on page 1682
For more information about this command, see “AUTO-QOS-MED” on
page 1597.
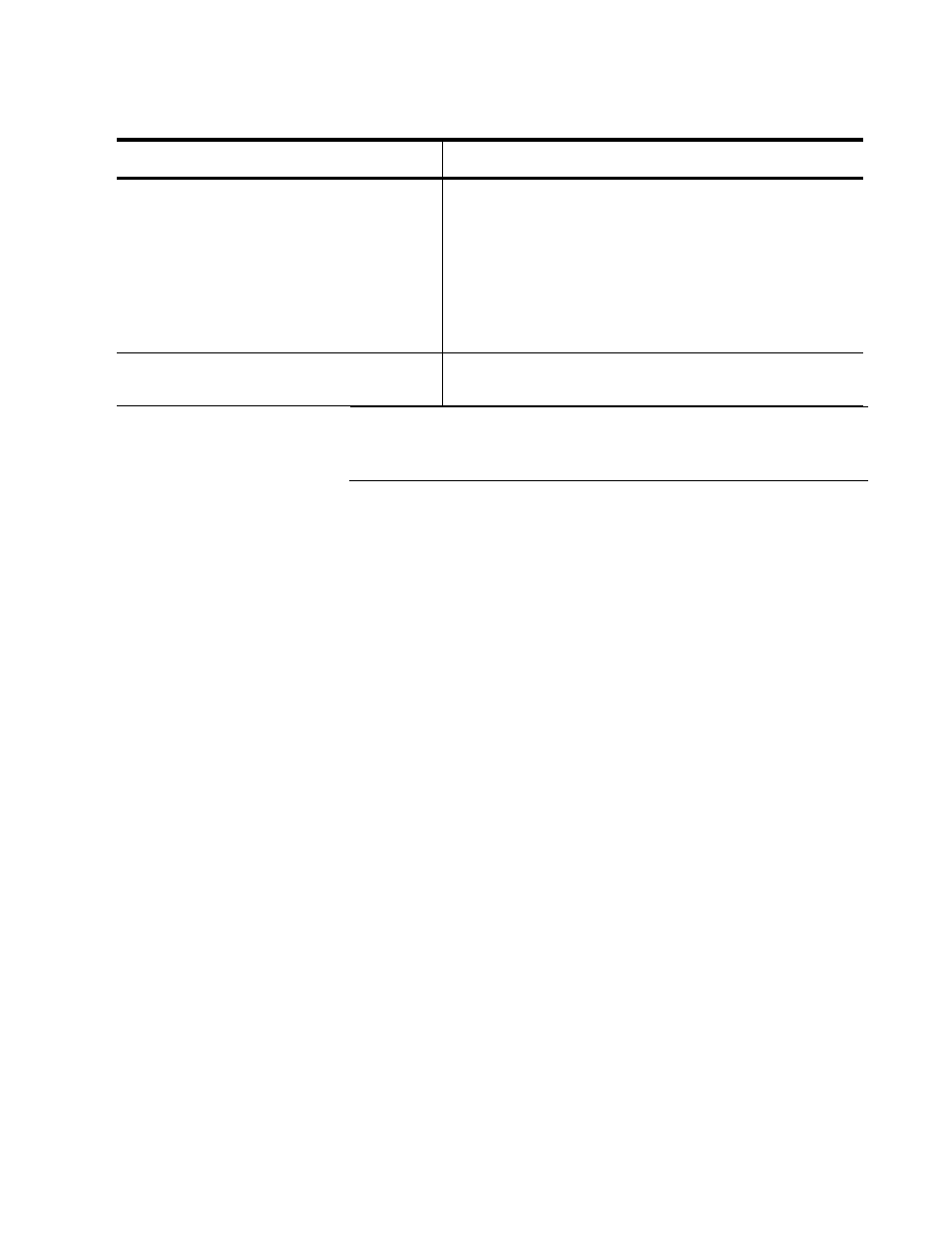
awplus (config-if)# wrr-queue
weight 3,3,1,1,2,0,0,0
Assigns a weight to the eight default DSCP queues
where weight specifies the number of packets a port
transmits from a queue before going to the next
queue. By default, the DSCP queues start with queue
0. DSCP queues 0 and 1 are assigned a weight of 3.
DSCP queues 2 and 3 are assigned a weight of 1.
DSCP queue 4 is assigned a weight of 2. DSCP
queues 5 through 7 are assigned a weight of 0.
awplus (config-if)# service-
policy input autoqos
Associates policy map “AutoQoS” with the given port
which, in this case, is port 1.
Table 227. Auto-QoS Trust DSCP Functionality Example (Continued)
Command
Description
