Actions, Id numbers, How ingress packets are compared against acls – Allied Telesis AT-8100 Series User Manual
Page 1525: Access control list id number ranges 5
AT-8100 Switch Command Line User’s Guide
1525
Actions
The action defines the response to packets that match the filtering criterion
of the ACL. There are three possible actions:
Permit— A permit action instructs ports to forward ingress packets
that match the specified traffic flow of the ACL. By default, all
ingress packets are forwarded by the ports.
Deny— A deny action instructs ports to discard the specified
ingress packets.
Copy to mirror— This action causes a port to copy all ingress
packets that match the ACL to the destination port of the mirror
port. This action must be used in conjunction with the port mirror
feature, explained in Chapter 27, “Port Mirror” on page 465.
ID Numbers
For both Numbered IPv4 ACLs and Numbered MAC ACLs, you must
assign each ACL a unique ID number. There are two ID number ranges
that are displayed in Table 158.
How Ingress
Packets are
Compared
Against ACLs
As stated previously, ports that do not have an ACL forward all ingress
packets. Ports with one or more deny ACLs discard ingress packets that
match the ACLs and forward all other traffic. A port that has one ACL that
specifies a particular source IP address, for example, discards all ingress
packets with the specified source address and forwards all other traffic. In
situations where a port has more than one deny ACL, packets are
discarded at the first match.
Since ports forward all ingress packets unless they have deny ACLs,
permit ACLs are only necessary in situations where you want a port to
forward packets that are a subset of a larger traffic flow that is blocked, for
example, a port that forwards only packets having a specified destination
IP address. A permit ACL specifies the packets with the intended
destination IP address, and a deny ACL specifies all traffic.
When ports have both permit and deny ACLs, you must add the permit
ACLs first, because packets are compared against the ACLs in the order
they are added to the ports. If a permit ACL is added after a deny ACL,
ports are likely to discard packets specified by the permit ACL, thus
causing them to block packets you want them to forward. This concept is
illustrated in the examples in this chapter.
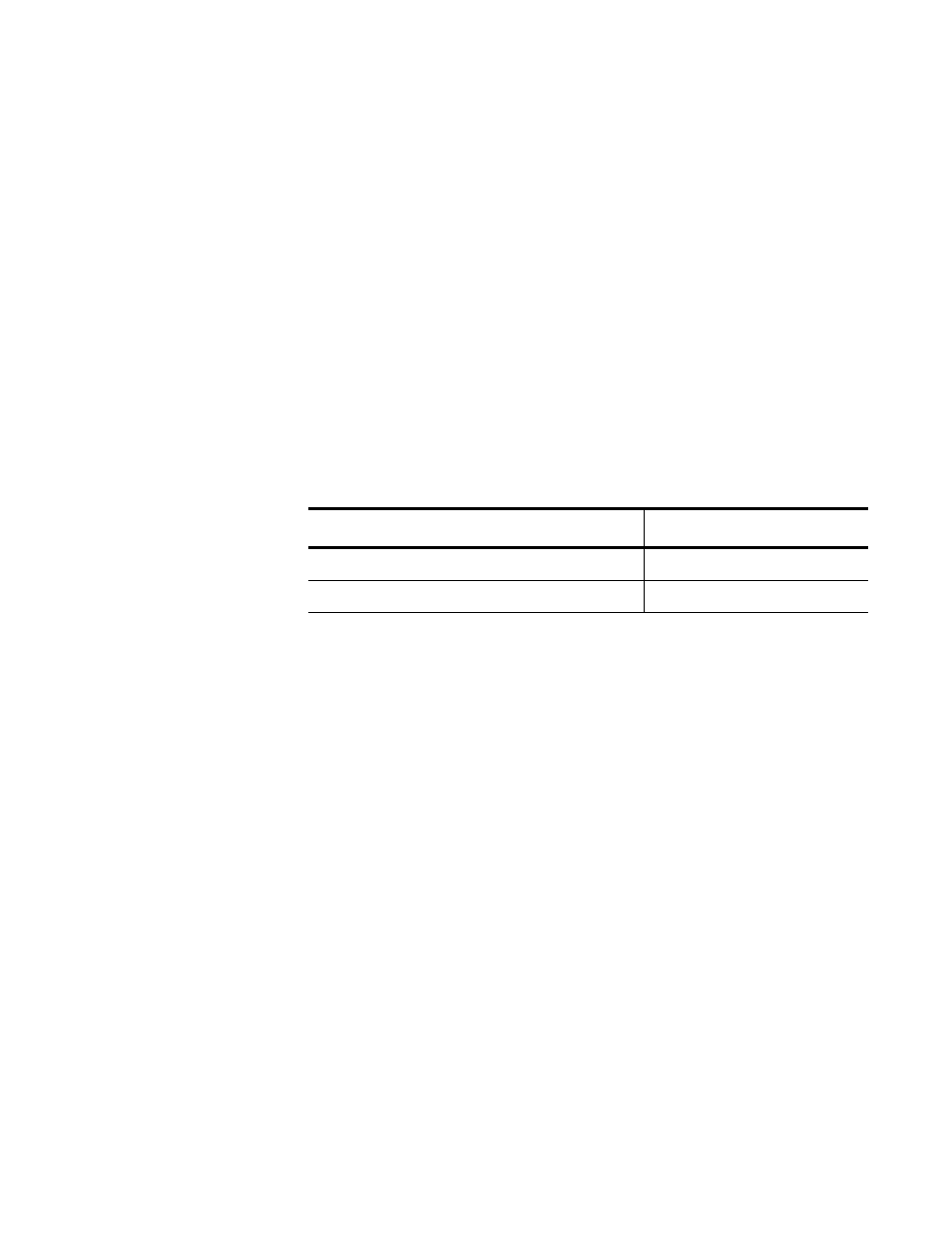
Table 158. Access Control List ID Number Ranges
Type of ACL
ID Number Range
Numbered IPv4 ACLs
3000 - 3699
Numbered MAC ACLs
4000 - 4699
